Abstract
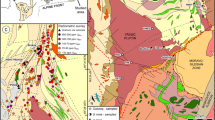
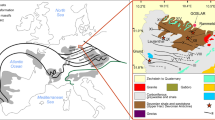
Metallic ore deposits of various genetic types are distributed in the Taebaeksan mineralized district in South Korea. The different basements or host rocks for these deposits vary across the northern and southern regions of the district with the Baegunsan Syncline as its center. Previous and newly analyzed sulfur isotope data of 374 sulfide minerals collected from 45 ore deposits were reviewed to compare the genetic characteristics of the two regions. Metallic deposits in the study area were classified into skarn, hydrothermal replacement, and hydrothermal vein based on genetic types and W-Mo, Fe-Cu(-Mo-Pb-Zn), Pb-Zn(-Cu-Au- Ag), and Au-Ag(-Cu-Pb-Zn) deposits with regard to ore species. For each genetic type, average sulfur isotope values were found to be 6.8‰, 7.7‰, and 6.3‰ in the northern region, and 2.3‰, 3.6‰, and 3.5‰ in the southern region, respectively. Average sulfur isotope values for each of the ore species were 11.3‰, 2.6‰, 6.6‰, and 6.9‰ in the northern region, and 1.3‰,–0.2‰, 4.2‰, and 3.3‰ in the southern region, respectively. The results indicate that sulfur isotope compositions for both genetic types and ore species are distinctly higher in the northern region than in the southern region. These differences could be ascribed to different sulfur isotope compositions of basement and host rocks that provided sulfur to ore minerals during the evolution of hydrothermal fluids, though the mineralizing fluids were originated from magmatic source. In the northern region, higher δ34S values of ore sulfurs could be attributed to high δ34S values of sulfate and sulfide in carbonate rocks formed in seawater. On the contrary, lower δ34S values of sulfide minerals in the southern region seem to be attributed to metasedimentary rocks that have lower δ34S values as a result of bacterial sulfate reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cates, N.L. and Mojzsis, S.J., 2006, Chemical and isotopic evidence for widespread Eoarchean metasedimentary enclaves in southern West Greenland. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70, 4229–4257.
Chang, H.W., Cheong, C.S., Park, H.I., and Chang, B.U., 1995, Lead isotopic study on the Dongnam Fe-Mo skarn deposit. Economic and Environmental Geology, 28, 25–31. (in Korean with English abstract)
Chang, H.W., Lee, M.S., Park, H.I., Kim, J.H., and Chi, J.M., 1990, Study of the Taebaeksan Mineralized Area. Korea Science and Engineering Foundation, KOSEF 87-0609, 649 p. (in Korean with English abstract)
Choi, S.G., Choi, B.K., Ahn, Y.H., and Kim, T.H., 2009, Re-evaluation of genetic environments of zinc-lead deposits to predict hidden skarn orebody. Economic and Environmental Geology, 42, 301–314. (in Korean with English abstract)
Choi, S.G., Choi, S.H., and Lee, H.K., 1997, Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Ogkye gold deposits, Gangwondo province. Economic and Environmental Geology, 30, 15–23. (in Korean with English abstract)
Choi, S.G., Ryu, I.C., Pak, S.J., Wee, S.M., Kim, C.S., and Park, M.E., 2005, Cretaceous epithermal gold-silver mineralization and geodynamic environment, Korea. Ore Geology Reviews, 26, 115–135. (in Korean with English abstract)
Chough, S.K., 2013, Geology and Sedimentology of the Korean Peninsula. Elsevie,r Amsterdam, 363 p.
Chough, S.K., Kwon, S.T., Ree, J.H., and Choi, D.K., 2000, Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of the Korean peninsula: a review and new view. Earth-Science Review, 52, 175–235.
Duan, J., Tang, J., and Lin, B., 2016, Zinc and lead isotope signatures of the Zhaxikang Pb-Zn deposit, South Tibet: implications for the source of the ore-forming metals. Ore Geology Reviews, 78, 58–68.
Hoefs, J., 2004, Stable Isotope Geochemistry (5th edition). Springer, Heidelberg, 244 p.
Hur, S.D., 1997, Petrochemistry of the Jeongseon granitoids and genesis of associated Pb, Zn, Cu deposits. Ph.D. Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, 197 p. (in Korean with English abstract)
Hwang, J. and Park, H.I., 1996, Stable isotope of the Nackcheon, Enchi, Jungbong gold-silver deposits in the northern Taebaegsan mining district. Economic and Environmental Geology, 29, 159–170. (in Korean with English abstract)
Ishihara, S., Jin, M.S., and Kajiwara, Y., 2002a, Sulfur content and isotopic ratio of Cambro-Ordovician carbonate rocks from South Korea: a possible source for Mesozoic magmatic-hydrothermal ore sulfur. Resource Geology, 52, 41–48.
Ishihara, S., Jin, M.S., and Sasaki, A., 2000, Source diversity of ore sulfur from Mesozoic-Cenozoic mineral deposits in the Korean Peninsula region. Resource Geology, 50, 203–212.
Ishihara, S., Kajiwara, Y., and Jin, M.S., 2002b, Possible carbonate origin of ore sulfur from Geumseong Mo deposit, South Korea. Resource Geology, 52, 279–282.
Jemmali, N., Souissi, F., Carranza, E.J.M., and Bouabdellah, M., 2013, Lead and sulfur isotope constraints on the genesis of the polymetallic mineralization at Oued Maden, Jebel Hallouf and Fedj Hassene carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn (As-Cu-Hg-Sb) deposits, Northern Tunisia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 132, 6–14.
Jeong, Y.J., Cheong, C.S., Shin, D.B., Lee, K.S., Jo, H.J., Gautam, M.K., and Lee, I.S., 2012, Regional variations in the lead isotopic composition of galena from southern Korea with implications for the discrimination of lead provenance. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 61, 116–127.
Jo, J.G. and Shin, D.B., 2015, Sulfur isotope variations of metallic ore deposits in the Gyeongsang Basin, South Korea. Resource Geology, 65, 296–310.
Jwa, Y.J., 1998, Temporal, spatial and geochemical discriminations of granitoids in South Korea. Resource Geology, 48, 273–284.
Kim, J.H., Kee, W.S., and Seo, S.K., 1996, Geological structures of the Yeoryang-Imgye area, northern part of Mt. Taebaeg Region, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 32, 1–15. (in Korean with English abstract)
Kim, J.H. and Lee, J.D., 1991, Geologic structures of the Yemi area, Kangwon-do, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 27, 500–514. (in Korean with English abstract)
Kim, J.H, Lee, J.Y., and Lee, H.B., 1988, Geological structures of Baeksan- Sangcheolam area, Samcheog coalfield, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 24, 417–430. (in Korean with English abstract)
Kim, J.M. and Cho, M.S., 2003, Low-pressure metamorphism and leucogranite magmatism, northeastern Yeongnam Massif, Korea: implication for Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution. Precambrian Research, 122, 235–251.
Kim, K.H. and Nakai, N., 1980, Sulfur isotope composition and isotopic temperatures of some base metal ore deposits, South Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 16, 124–134.
Kim, K.H. and Nakaki, N., 1982, Sulfur isotope composition and isotopic temperatures of the Shinyemi lead and zinc ore deposits, western Taebaegsan metallogenic belt, Korea. Mining Geology, 15, 155–166.
Laouar, R., Boyce, A.J., Ahmed-Said, Y., Ouabadi, A., Fallick, A.E., and Toubal, A., 2002, Stable isotope study of the igneous, metamorphic and mineralized rocks of the Edough complex, Annaba, Northeast Algeria. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 35, 271–283.
Lee, C.H., Choi, S.W., Her, S.D., and Hwang, J., 1998, Epithermal mineralization of the Wangje antimony deposit, Korea; geochemistry and mineralogy. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 34, 228–242. (in Korean with English abstract)
Lee, C.H. and Park, H.I., 1996, Epithermal gold-silver mineralization and depositional environment of carbonate-hosted replacement type Baegjeon deposits, Korea. Economic and Environmental Geology, 29, 105–117. (in Korean with English abstract)
Lee, C.H. and Shin, D.B, 2009, Stable isotope characteristics and evolution of mineralizing fluids in the Au-Ag-Sb mineralized district in northern Taebaeksan region, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 45, 261–274. (in Korean with English abstract)
Lee, J.Y., Lee, I.H., and Hwang, D.H., 1996, Chemical composition of the Cretaceous granitoids and related ore deposits in the Taebaegsan Basin, Korea. Economic and Environmental Geology, 29, 247–256. (in Korean with English abstract)
Lee, M.S., 1985, Sulfur and carbon isotope studies of principal metallic deposits in the metallogenic province of the Taebaeg Mt. region. Korea. Journal of the Korean Institute of Mining Geology, 18, 247–251. (in Korean with English abstract)
Moon, K.J., 1987, Significance of the occurrences of the Sangdong granite and scheelite-bearing quartz veins in the Precambrian schist. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 23, 306–316. (in Korean with English abstract)
Moon, K.J., 1991, Review of skarn ore deposits at the southern limb of the Baegunsan syncline in the Taebaeg basin of South Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 27, 271–292.
Nie, F.J., Jiang, S.H., Su, X.X., and Wang, X.L., 2002, Geological features and origin of gold deposits occurring in the Baotou-Bayan Obo district, south-central Inner Mongolia, People’s Republic of China. Ore Geology Reviews, 20, 139–169.
Ohmoto, H. and Goldhaber, M.B., 1997, Sulfur and carbon isotopes. In: Barnes, H.L. (ed.), Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 517–612.
Pak, S.J., Choi, S.G., and Choi, S.H., 2004, Systematic mineralogy and chemistry of gold-silver vein deposits in the Taebaeksan district, Korea: distal relatives of a porphyry system. Mineralogical Magazine, 68, 467–487.
Park, H.I., Chang, H.W., and Jin, M.S., 1988, K-Ar ages of mineral deposits in the Taebaeg Mountain district. Journal of the Korean Institute of Mining Geology, 21, 57–67. (in Korean with English abstract)
Park, H.I. and Lee, C.H., 1992, Mineral chemistry and “Invisible Gold” of oscillatory zoned pyrite from the Baegjeon gold deposits. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 28, 627–636. (in Korean with English abstract)
Park, K.H. and Chang, H.W., 2005, Pb isotopic composition of Yeonhwa and Janggun Pb-Zn ore deposits and origin of Pb: role of Precambrian crustal basement and Mesozoic igneous rocks. Journal of Petrological Society of Korea, 14, 141–148.
Park, K.H., Park, H.I., Eastoe, C.J., and Choi, S.W., 1991, Ore minerals, fluid inclusions, and isotopic (S, C, O) compositions in the diatreme- hosted Nokdong As-Zn deposit, southeastern Korea: the character and evolution of the hydrothermal fluids. Journal of the Korean Institute of Mining Geology, 24, 131–150.
Ripley, E.M., Park, Y.R., Li, C., and Naldrett, A.J., 1999, Sulfur and oxygen isotopic evidence of country rock contamination in the Voisey’s Bay Ni-Cu-Co deposit, Labrador, Canada. Lithos, 47, 53–68.
Rubinstein, N.A., Ostera, H.A., Mallimacci, H., and Carpio, F., 2004, Lead isotopes from Gondwana polymetallic ore vein deposits, San Rafael Massif, Argentina. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 16, 579–586.
Sasaki, A. and Ishihara, S., 1979, Sulfur isotopic composition of the magnetite-series and ilmenite-series granitoids in Japan. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 68, 107–115.
Sasaki, A. and Ishihara, S., 1980, Sulfur isotope characteristics of granitoids and related mineral deposits in Japan. Proceedings of Fifth Quadrennial IAGOD Symposium, p. 325–335.
Sato, K., Shimazaki, H., and Chon, H.T., 1981, Sulfur isotopes of the ore deposits related to felsic magmatism in the southern Korean peninsula. Mining Geology, 31, 321–326.
Shields, G.A., Strauss, H., Howe, S.S., and Siegmund, H., 1999, Sulphur isotope composition of sedimentary phosphorites from the basal Cambrian of China: implications for Neoproterozoic–Cambrian biogeochemical cycling. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 156, 943–956.
Shimazaki, H., Sakai, H., Kaneda, H., and Lee, M.S., 1985, Sulfur isotopic ratios of ore deposits associated with mesozoic felsic magmatism in South Korea, with special reference to gold-silver deposits. Geochemical Journal, 19, 163–169.
Shin, D.B., Park, H.I., Lee, I.S, Lee, K.S., and Hwang, J., 2004, Hydrothermal As-Bi mineralization in the Nakdong deposits, South Korea: insight from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. The Canadian Mineralogist, 42, 1465–1481.
Shin, I.K, Kim, S.H., and Shin, D.B., 2016, Mineralogy and sulfur isotope compositions of the uraniferous black slates in the Ogcheon Metamorphic Belt, South Korea. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 169, 1–12.
Shin, S.C. and Jin, M.S., 1995, Radiometric age maps of volcanic, plutonic and metamorphic rocks and ore deposits in the Korean Peninsula. KIGAM Report, KR-95(B)-7, 43 p. (in Korean with English abstract)
So, C.S. and Yun, S.T., 1992, Geochemistry and genesis of hydrothermal Au-Ag-Pb-Zn deposits in the Hwanggangri mineralized district, Republic of Korea. Economic Geology, 87, 2056–2084.
So, C.S., Yun, S.T., and Koh, Y.K., 1993, Mineralogic, fluid inclusion, and stable isotope evidence for the genesis of carbonate-hosted Pb- Zn(-Ag) orebodies of the Taebaek Deposit, Republic of Korea. Economic Geology, 88, 855–872.
Strauss, H., Banerjee, D.M., and Kumar, V., 2001, The sulfur isotopic composition of Neoproterozoic to early Cambrian seawater-evidence from the cyclic Hanseran evaporites, NW India. Chemical Geology, 175, 17–28.
Takahashi, R., Matsueda, H., Okrugin, V.M., Shikazono, N., Ono, S., Imai, A., Andreeva, E.D., and Watanabe, K., 2013, Ore-forming ages and sulfur isotope study of hydrothermal deposits in Kamchatka, Russia. Resource Geology, 63, 210–223.
Wang, P. and Ishihara, S., 2000, Sulfur isotopic variation of Yanshanian magmatic-hydrothermal deposits in southern China. Resource Geology, 50, 257–268.
Yoo, C.M., Lee, Y.I., and Paik, I.S., 1994, Evidence for hypersaline conditions in the middle Ordovician Yeongheung Formation, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 30, 355–368.
Yoon, C.H., Kim, C.B., Lee, H.J., and Shimazaki, H., 2003, Sulfur isotope study of Precambrian basement and Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the southwestern part of Ryeongnam Massif, Korea. Resource Geology, 53, 11–20.
Yoon, C.H. and Shimazaki, H., 1993, Sulfur isotope study of gold-silver deposits in the Republic of Korea. Resource Geology, 43, 1–10.
Yun, S.T., Choi, S.H., Heo, C.H., So, C.S., Chae, G.T., and Kim, J.W., 1999, Hydrothermal antimony deposits of the Hyundong mine: geochemical study. Economic and Environmental Geology, 32, 435–444.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Shin, D. & Im, H. Regional variations of sulfur isotope compositions for metallic deposits in the Taebaeksan Mineralized District, South Korea. Geosci J 22, 79–89 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-017-0057-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-017-0057-x