Abstract
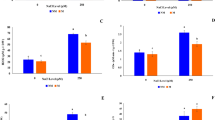
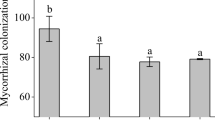
This study investigated how inoculation of salt-stressed Pistacia vera seedlings with Rhizophagus irregularis, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (AMF), affects their biomass, oxidative damage, antioxidant enzyme activity, and gene expression. Pistachio seedlings (N:36) were randomly assigned to AMF inoculation and non-inoculation groups in a pot experiment with 9 replications. Each group was further divided and randomly assigned to two salinity treatments (0 and 300 mM NaCl). At the end of week 4, three pistachio plantlets were randomly selected from each group for Rhizophagus irregularis colonization inspection, physiological and biochemical assays, and biomass measurements. Salinity activated enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant systems in the pistachio plants were studied. The negative effects of salinity included reduced biomass and relative water content (RWC), increased O2·−, H2O2, MDA, and electrolytic leakage. Generally, Rhizophagus irregularis was found to mitigate the adverse effects of salinity in pistachio seedlings. AMF inoculation resulted in even further increases in the activities of SODs, POD, CAT, and GR enzymes, upregulating Cu/Zn-SOD, Fe-SOD, Mn-SOD, and GR genes expression in plants under salinity stress. Moreover, AMF significantly increased AsA, α-tocopherol, and carotenoids under both control and salinity conditions. The study concludes with a call for future research into the mechanisms of mycorrhiza-induced tolerance in plants under salinity stress.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour H, Saeidi-Sar S, Afshari H, Abdel-Wahhab MA (2012) Tolerance of Mycorrhiza infected pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) seedling to drought stress under glasshouse conditions. J Plant Physiol 169:704–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.01.014
Abbaspour H, Pour FSN, Abdel-Wahhab MA (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis regulates the physiological responses, ion distribution and relevant gene expression to trigger salt stress tolerance in pistachio. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27:1765–1778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01043-w
Abd Allah EF, Hashem A, Alqarawi AA, Bahkali AH, Alwhibi MS (2015) Enhancing growth performance and systemic acquired resistance of medicinal plant Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under salt stress. Saudi J Biol Sci 22:274–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.03.004
Abdelaal KA, EL-Maghraby LM, Elansary H, Hafez YM, Ibrahim EI, El-Banna M, El-Esawi M, Elkelish A (2019) Treatment of sweet pepper with stress tolerance-inducing compounds alleviates salinity stress oxidative damage by mediating the physio-biochemical activities and antioxidant systems. Agronomy 10:26. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010026
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Naz S, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Tiwari RK, Lal MK, Shahid MA, Kumar R, Nawaz MA, Jahan MS, Jan BL, Ahmad P (2022) Melatonin improves drought stress tolerance of tomato by modulating plant growth, root architecture, photosynthesis, and antioxidant defense system. Antioxidants (basel) 11:309. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020309
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Balestrini R, Brunetti C, Chitarra W, Nerva L (2020) Photosynthetic traits and nitrogen uptake in crops: which is the role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi? Plants (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091105
Begum N, Qin C, Ahanger MA, Raza S, Khan MI, Ashraf M, Ahmed N, Zhang L (2019) Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plant growth regulation: implications in abiotic stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci 10:1068. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01068
Bennett AE, Groten K (2022) The costs and benefits of plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal interactions. Annu Rev Plant Biol 73:649–672. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-102820-124504
Bibi N, Shah MH, Khan N, Al-Hashimi A, Elshikh MS, Iqbal A, Ahmad S, Abbasi AM (2022) Variations in total phenolic, total flavonoid contents, and free radicals’ scavenging potential of onion varieties planted under diverse environmental conditions. Plants (basel) 11:950. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070950
Biermann B, Linderman R (1981) Quantifying vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae: a proposed method towards standardization. New Phytol 87:63–67
Bijalwan P, Jeddi K, Saini I, Sharma M, Kaushik P, Hessini K (2021) Mitigation of saline conditions in watermelon with mycorrhiza and silicon application. Saudi J Biol Sci 28:3678–3684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.05.019
Bistgani ZE, Hashemi M, DaCosta M, Craker L, Maggi F, Morshedloo MR (2019) Effect of salinity stress on the physiological characteristics, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Thymus vulgaris L. and Thymus daenensis Celak. Ind Crops Prod 135:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.04.055
Cao J, Wang C, Dou Z, Liu M, Ji D (2018) Hyphospheric impacts of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on soil bacterial community to promote oxytetracycline degradation. J Hazard Mater 341:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.038
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1985) [59] Glutathione reductase. In: Methods in enzymology. Elsevier.
Chandrasekaran M, Chanratana M, Kim K, Seshadri S, Sa T (2019) Impact of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on photosynthesis, water status, and gas exchange of plants under salt stress-a meta-analysis. Front Plant Sci 10:457. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00457
Chang W, Sui X, Fan XX, Jia TT, Song FQ (2018) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis modulates antioxidant response and ion distribution in salt-stressed Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings. Front Microbiol 9:652. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00652
Chele KH, Tinte MM, Piater LA, Dubery IA, Tugizimana F (2021) Soil salinity, a serious environmental issue and plant responses: a metabolomics perspective. Metabolites. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110724
Chen J, Zhang H, Zhang X, Tang M (2017) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis alleviates salt stress in black locust through improved photosynthesis, water status, and K(+)/Na(+) homeostasis. Front Plant Sci 8:1739. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01739
Chen Q, Deng X, Elzenga JTM, van Elsas JD (2022) Effect of soil bacteriomes on mycorrhizal colonization by Rhizophagus irregularis—interactive effects on maize (Zea mays L.) growth under salt stress. Biol Fertil Soils 58:515–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-022-01636-x
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90:856–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13299
Comas LH, Becker SR, Cruz VM, Byrne PF, Dierig DA (2013) Root traits contributing to plant productivity under drought. Front Plant Sci 4:442. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00442
Das K, Roychoudhury A (2014) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2014.00053
Dastogeer KMG, Zahan MI, Tahjib-Ul-Arif M, Akter MA, Okazaki S (2020) Plant salinity tolerance conferred by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated mechanisms: a meta-analysis. Front Plant Sci 11:588550. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.588550
Ding YE, Zou YN, Wu QS, Kuca K (2022) Mycorrhizal fungi regulate daily rhythm of circadian clock in trifoliate orange under drought stress. Tree Physiol 42:616–628. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpab132
Elhindi KM, El-Din AS, Elgorban AM (2017) The impact of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mitigating salt-induced adverse effects in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Saudi J Biol Sci 24:170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.02.010
Elkelish A, Qari SH, Mazrou YSA, Abdelaal KAA, Hafez YM, Abu-Elsaoud AM, Batiha GE-S, El-Esawi MA, El Nahhas N (2020) Exogenous ascorbic acid induced chilling tolerance in tomato plants through modulating metabolism, osmolytes, antioxidants, and transcriptional regulation of catalase and heat shock proteins. Plants 9:431. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040431
Engel R, Szabo K, Abranko L, Rendes K, Fuzy A, Takacs T (2016) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and polyphenol profile of marjoram, lemon balm, and marigold. J Agric Food Chem 64:3733–3742. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00408
Evelin H, Giri B, Kapoor R (2012) Contribution of Glomus intraradices inoculation to nutrient acquisition and mitigation of ionic imbalance in NaCl-stressed Trigonella foenum-graecum. Mycorrhiza 22:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-011-0392-0
Evelin H, Giri B, Kapoor R (2013) Ultrastructural evidence for AMF mediated salt stress mitigation in Trigonella foenum-graecum. Mycorrhiza 23:71–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-012-0449-8
Evelin H, Devi TS, Gupta S, Kapoor R (2019) Mitigation of salinity stress in plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: current understanding and new challenges. Front Plant Sci 10:470. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00470
Fujita M, Hasanuzzaman M (2022) Approaches to enhancing antioxidant defense in plants. Antioxidants (basel) 11:925. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050925
Gao J (2006) Experimental guidance for plant physiology. China Higher Education Press, Beijing
García-Caparrós P, De Filippis L, Gul A, Hasanuzzaman M, Ozturk M, Altay V, Lao MT (2021) Oxidative stress and antioxidant metabolism under adverse environmental conditions: a review. Bot Rev 87:421–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-020-09231-1
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol 489–500.
Guidi L, Tattini M (2021) Antioxidant defenses in plants: a dated topic of current interest. Antioxidants (basel) 10:855. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060855
Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2022) Plant oxidative stress: biology. Physiol Mitigat Plants 11:1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11091185
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan M, Zulfiqar F, Raza A, Mohsin SM, Mahmud JA, Fujita M, Fotopoulos V (2020) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants (basel) 9:681. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080681
Hasanuzzaman M, Raihan MRH, Masud AAC, Rahman K, Nowroz F, Rahman M, Nahar K, Fujita M (2021) Regulation of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under salinity. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179326
Hashem A, Alqarawi AA, Radhakrishnan R, Al-Arjani AF, Aldehaish HA, Egamberdieva D, Abd Allah EF (2018) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi regulate the oxidative system, hormones and ionic equilibrium to trigger salt stress tolerance in Cucumis sativus L. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:1102–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.03.009
He J-D, Tao D, Hui-Hui W, Ying-Ning Z, Qiang-Sheng W, Kamil K (2019) Mycorrhizas induce diverse responses of root TIP aquaporin gene expression to drought stress in trifoliate orange. Sci Hortic 243:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.08.010
He J-D, Zou Y-N, Wu Q-S, Kuča K (2020) Mycorrhizas enhance drought tolerance of trifoliate orange by enhancing activities and gene expression of antioxidant enzymes. Sci Hortic 262:108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108745
Hnilickova H, Kraus K, Vachova P, Hnilicka F (2021) Salinity stress affects photosynthesis, malondialdehyde formation, and proline content in Portulaca oleracea L. Plants (basel) 10:845. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050845
Hosseini MS, Ebrahimi M, Abadía J, Kadkhodaei S, Amirian R (2022) Growth, phytochemical parameters and glycyrrhizin production in licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) grown in the field with saline water irrigation. Ind Crops Prod 177:114444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114444
Huang C-J, Wei G, Jie Y-C, Xu J-J, Zhao S-Y, Wang L-C, Anjum dS, (2015) Responses of gas exchange, chlorophyll synthesis and ROS-scavenging systems to salinity stress in two ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) cultivars. Photosynthetica 53:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-015-0127-0
Huang M, Guo Z (2005) Responses of antioxidative system to chilling stress in two rice cultivars differing in sensitivity. Biol Plant 49:81–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00000-005-1084-3
Jahromi F, Aroca R, Porcel R, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2008) Influence of salinity on the in vitro development of Glomus intraradices and on the in vivo physiological and molecular responses of mycorrhizal lettuce plants. Microb Ecol 55:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9249-7
Jajoo A, Mathur S (2021) Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as an underground saviuor for protecting plants from abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27:2589–2603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01091-2
Jiang F, Zhang L, Zhou J, George TS, Feng G (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance mineralisation of organic phosphorus by carrying bacteria along their extraradical hyphae. New Phytol 230:304–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17081
Kumar Yadav V, Krishna Jha R, Kaushik P, Altalayan FH, Al Balawi T, Alam P (2021) Traversing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Pseudomonas fluorescens for carrot production under salinity. Saudi J Biol Sci 28:4217–4223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.025
Lamuela-Raventós RM (2017) Folin-Ciocalteu method for the measurement of total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity. Meas Antioxid Act Capacit Recent Trends Appl. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119135388.ch6
Liu S, Guo X, Feng G, Maimaitiaili B, Fan J, He X (2016) Indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can alleviate salt stress and promote growth of cotton and maize in saline fields. Plant Soil 398:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2656-5
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lopez-Raez JA (2016) How drought and salinity affect arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis and strigolactone biosynthesis? Planta 243:1375–1385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2435-9
Ma S, Zhu L, Wang J, Liu X, Jia Z, Li C, Liu J, Zeng J, Zhang J (2022) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi promote Gleditsia sinensis root growth under salt stress by regulating nutrient uptake and physiology. Forests 13:688. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050688
Mansour MMF, Ali EF (2017) Evaluation of proline functions in saline conditions. Phytochemistry 140:52–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.04.016
Mishra P, Bhoomika K, Dubey RS (2013) Differential responses of antioxidative defense system to prolonged salinity stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive Indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma 250:3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-011-0365-3
Mohammadi F, Kavousi HR, Mansouri M (2019) Effects of salt stress on physio-biochemical characters and gene expressions in halophyte grass Leptochloa fusca (L.) Kunth. Acta Physiol Plant 41:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2935-5
Moustakas M (2022) Plant photochemistry, reactive oxygen species, and photoprotection. Photochem 2:5–8. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem2010002
Moustakas M, Moustaka J, Sperdouli I (2022) Hormesis in photosystem II: a mechanistic understanding. Curr Opin Toxicol 29:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2022.02.003
Mustafa G, Khong NG, Tisserant B, Randoux B, Fontaine J, Magnin-Robert M, Reignault P, Sahraoui AL (2017) Defence mechanisms associated with mycorrhiza-induced resistance in wheat against powdery mildew. Funct Plant Biol 44:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP16206
Ndiate NI, Zaman QU, Francis IN, Dada OA, Rehman A, Asif M, Goffner D, Kane A, Liqun C, Haider FU (2022) Soil amendment with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and biochar improves salinity tolerance, growth, and lipid metabolism of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063210
Okla MK, Rubnawaz S, Dawoud TM, Al-Amri S, El-Tayeb MA, Abdel-Maksoud MA, Akhtar N, Zrig A, AbdElgayed G, AbdElgawad H (2022) Laser light treatment improves the mineral composition, essential oil production and antimicrobial activity of mycorrhizal treated Pelargonium graveolens. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061752
Phillips JM, Hayman D (1970) Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans Br Mycol Soc 55:158–161
Puyang X, An M, Han L, Zhang X (2015) Protective effect of spermidine on salt stress induced oxidative damage in two Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.) cultivars. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 117:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.03.023
Qian R, Ma X, Zhang X, Hu Q, Liu H, Zheng J (2021) Effect of exogenous spermidine on osmotic adjustment, antioxidant enzymes activity, and gene expression of Gladiolus gandavensis seedlings under salt stress. J Plant Growth Regul 40:1353–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10198-x
Rahimi M, Kordrostami M, Mohamadhasani F, Chaeikar SS (2021) Antioxidant gene expression analysis and evaluation of total phenol content and oxygen-scavenging system in tea accessions under normal and drought stress conditions. BMC Plant Biol 21:494. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03275-0
Rajput VD, Harish, Singh RK, Verma KK, Sharma L, Quiroz-Figueroa FR, Meena M, Gour VS, Minkina T, Sushkova S, Mandzhieva S (2021) Recent developments in enzymatic antioxidant defence mechanism in plants with special reference to abiotic stress. Biology (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040267
Rohani N, Daneshmand F, Vaziri A, Mahmoudi M, Saber-Mahani F (2019) Growth and some physiological characteristics of Pistacia vera L. cv Ahmad Aghaei in response to cadmium stress and Glomus mosseae symbiosis. S Afr J Bot 124:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.06.001
Rossatto T, do Amaral MN, Benitez LC, Vighi IL, Braga EJB, de Magalhaes Junior AM, Maia MAC, da Silva Pinto L (2017) Gene expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes in rice plants, cv. BRS AG, under saline stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23: 865–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0467-2
Ruiz-Lozano JM, del Mar AM, Bárzana G, Vernieri P, Aroca R (2009) Exogenous ABA accentuates the differences in root hydraulic properties between mycorrhizal and non mycorrhizal maize plants through regulation of PIP aquaporins. Plant Mol Biol 70:565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9492-z
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Porcel R, Bárzana G, Azcón R, Aroca R (2012) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis to plant drought tolerance: state of the art. In: Aroca R (ed) Plant responses to drought stress. Springer, Berlin
Santander C, Ruiz A, Garcia S, Aroca R, Cumming J, Cornejo P (2020) Efficiency of two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inocula to improve saline stress tolerance in lettuce plants by changes of antioxidant defense mechanisms. J Sci Food Agric 100:1577–1587. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10166
Sharma K, Gupta S, Thokchom SD, Jangir P, Kapoor R (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhiza-mediated regulation of polyamines and aquaporins during abiotic stress: deep insights on the recondite players. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.642101
Thangaraj K, Li J, Mei H, Hu S, Han R, Zhao Z, Chen X, Li X, Kamatchi Reddiar D (2022) Mycorrhizal colonization Enhanced Sorghum bicolor tolerance under soil water deficit conditions by coordination of proline and reduced glutathione (GSH). J Agric Food Chem 70:4243–4255. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07184
Turan V (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and pistachio husk biochar combination reduces Ni distribution in mungbean plant and improves plant antioxidants and soil enzymes. Physiol Plant 173:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13490
Wang F, Sun Y, Shi Z (2019) Arbuscular mycorrhiza enhances biomass production and salt tolerance of sweet sorghum. Microorganisms 7:289. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090289
Wang J, Zhai L, Ma J, Zhang J, Wang GG, Liu X, Zhang S, Song J, Wu Y (2020) Comparative physiological mechanisms of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mitigating salt-induced adverse effects on leaves and roots of Zelkova serrata. Mycorrhiza 30:341–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-020-00954-y
Wang H, An T, Huang D, Liu R, Xu B, Zhang S, Deng X, Siddique KHM, Chen Y (2021a) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbioses alleviating salt stress in maize is associated with a decline in root-to-leaf gradient of Na(+)/K(+) ratio. BMC Plant Biol 21:457. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03237-6
Wang Y, Dong F, Tang M (2021b) Transcriptome analysis of arbuscular mycorrhizal Casuarina glauca in damage mitigation of roots on NaCl stress. Microorganisms 10(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010015
Wang J, Yuan J, Ren Q, Zhang B, Zhang J, Huang R, Wang GG (2022) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhanced salt tolerance of Gleditsia sinensis by modulating antioxidant activity, ion balance and P/N ratio. Plant Growth Regul 97:33–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-021-00792-8
Wu J, Shu S, Li C, Sun J, Guo S (2018) Spermidine-mediated hydrogen peroxide signaling enhances the antioxidant capacity of salt-stressed cucumber roots. Plant Physiol Biochem 128:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.05.002
Wu QS, Zou YN, Xia RX (2006) Effects of water stress and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on reactive oxygen metabolism and antioxidant production by citrus (Citrus tangerine) roots. Eur J Soil Biol 42:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2005.12.006
Ye L, Zhao X, Bao E, Cao K, Zou Z (2019) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on watermelon growth, elemental uptake, antioxidant, and photosystem II activities and stress-response gene expressions under salinity-alkalinity stresses. Front Plant Sci 10:1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00863
Zhang T, Hu Y, Zhang K, Tian C, Guo J (2018) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve plant growth of Ricinus communis by altering photosynthetic properties and increasing pigments under drought and salt stress. Ind Crops Prod 117:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.02.087
Zhang Y, Li G, Si L, Liu N, Gao T, Yang Y (2021) Effects of tea polyphenols on the activities of antioxidant enzymes and the expression of related gene in the leaves of wheat seedlings under salt stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:65447–65461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15492-z
Zulfiqar F, Ashraf M (2021) Bioregulators: unlocking their potential role in regulation of the plant oxidative defense system. Plant Mol Biol 105:11–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01077-w
Zulfiqar F, Akram NA, Ashraf M (2019) Osmoprotection in plants under abiotic stresses: new insights into a classical phenomenon. Planta 251:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03293-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ASA and HA conceived the original idea, carried out the experiment, performed the computations and verified the analytical methods. ASA compiled the data and wrote the first manuscript draft. HA revised the draft. All authors contributed to, commented, and agreed on the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Afshar, A.S., Abbaspour, H. Mycorrhizal symbiosis alleviate salinity stress in pistachio plants by altering gene expression and antioxidant pathways. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 29, 263–276 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-023-01279-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-023-01279-8