Abstract
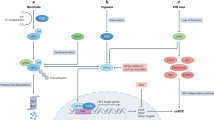
Renal cell carcinoma is the most common form of the kidney cancer accounting for more than 85% of the cases of which clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the major histological subtype. The central molecular signature for ccRCC pathogenesis is the biallelic inactivation of VHL gene due to the presence of mutations/hyper-methylation/complete gene loss, which results in the downstream HIF activation. These events lead to increased tyrosine kinase receptor signalling pathways (RAS/MEK/ERK pathway, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and NF-κB pathway), which through their downstream effector proteins causes the cell to proliferate and migrate. Recent studies have shown that VHL inactivation alone is not sufficient to induce the tumor. Mutations in numerous other genes that codes for chromatin modifiers (PBRM1, SETD2 and BAP1) and signalling proteins (PTEN and mTOR) have been identified along with activation of alternate signalling pathways like STAT and Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) pathway. It has also been shown that STAT pathway also works cooperatively with HIF to enhance the tumor progression. However, SHH pathway reactivation resulted in tumor regardless of the VHL status, indicating the complex nature of the tumor at the molecular level. Therefore, understanding the complete aetiology of ccRCC is important for future therapeutics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeng Z, Que T, Zhang J, Hu Y. A study exploring critical pathways in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2014;7:121–30.
Lopez-Beltran A, Carrasco JC, Cheng L, Scarpelli M, Kirkali Z, Montironi R. 2009 Update on the classification of renal epithelial tumors in adults. Int J Urol. 2009;16:432–43.
Kovacs G, Akhtar M, Beckwith BJ, Bugert P, Cooper CS, Delahunt B, et al. The heidelberg classification of renal cell tumors. J Pathol. 1997;183:131–3.
Pavlovich CP, Schmidt LS, Phillips JL. The genetic basis of renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin N Am. 2003;30:437–54.
Shen C, Kaelin WG Jr. The VHL/HIF axis in clear cell renal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013;23:18–25.
Beroukhim R, Brunet JP, Di Napoli A, Mertz KD, Seeley A, Pires MM, et al. Patterns of gene expression and copy number alterations in von Hippel–Lindau disease associated and sporadic clear cell carcinoma of the kidney. Can Res. 2009;69:4674–81.
Furge KA, Tan MH, Dykema K, Kort E, Stadler W, Yao X, et al. Identification of deregulated oncogenic pathways in renal cell carcinoma: an integrated oncogenomic approach based on gene expression profiling. Oncogene. 2007;26:1346–50.
Sato Y, Yoshizato T, Shiraishi Y, Maekawa S, Okuno Y, Kamura T, et al. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2013;45:860–7.
Baldewijns MM, van Vlodrop IJ, Vermeulen PB, Soetekouw PM, van Engeland M, de Bruine AP. VHL and HIF signalling in renal cell carcinogenesis. J Pathol. 2010;221:125–38.
Semenza GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:721–32.
Koul H, Huh JS, Rove KO, Crompton L, Koul S, Meacham RB, et al. Molecular aspects of renal cell carcinoma: a review. Am J Cancer Res. 2011;1:240–54.
Cuadros T, Trilla E, Sarro E, Vila MR, Vilardell J, Torres ID, et al. HAVCR/KIM-1 activates the IL-6/STAT-3 pathway in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and determines tumor progression and patient outcome. Cancer Res. 2014;74:1416–28.
Dormoy V, Danilin S, Lindner V, Thomas L, Rothhut S, Coquard C, et al. The sonic hedgehog signalling pathway is reactivated in human renal cell carcinoma and plays orchestral role in tumor growth. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:123–39.
Pavlovich CP, Schmidt LS. Searching for the hereditary causes of renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:381–93.
Cohen AJ, Li FP, Berg S, Marchetto DJ, Tsai S, Jacob SC, et al. Hereditary renal cell carcinoma associated with a chromosomal translocation. N Engl J Med. 1979;301:592–5.
Brugarolas J. Molecular genetics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:1968–76.
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA, editors. Pathology and genetics of tumors of urinary system and male genital organs. Lyon: IARCPress; 2004.
Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J, Yao M, Duh FM, Orcutt ML, et al. Identification of the von Hippel–Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science. 1993;260:1317–20.
Stebbins CE, Kaelin WG Jr, Pavletich NP. Structure of the VHL-ElonginC-ElonginB complex: implications for HL tumor suppressor function. Science. 1999;284:455–61.
Richards FM, Schofield PN, Fleming S, Maher ER. Expression of the von Hippel–Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene during human embryogenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:639–44.
Ohh M, Takagi Y, Aso T, Stebbins CE, Pavletich NP, Zbar B, et al. Synthetic peptides define critical contacts between elongin C, elongin B, and the von Hippel–Lindau protein. J Clin Invest. 1999;104:1583–91.
Ohh M, Park CW, Ivan M, Hoffman MA, Kim TY, Huang LE, et al. Ubiquitination of hypoxia-inducible factor requires direct binding to the beta-domain of the von Hippel–Lindau protein. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:423–7.
Razafinjatovo C, Bihr S, Mischo A, Vogl U, Schmidinger M, Moch H, et al. Characterization of VHL missense mutations in sporadic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: hotspots, affected binding domains, functional impact on pVHL and therapeutic relevance. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:638.
Pause A, Lee S, Worrell RA, Chen DY, Burgess WH, Linehan WM, et al. The von Hippel–Lindau tumor-suppressor gene product forms a stable complex with human CUL-2, a member of the Cdc53 family of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1997;94:2156–61.
Kamura T, Sato S, Iwai K, Krzeska MC, Conaway RC, Conaway JW. Activation of HIF1α ubiquitination by a reconstituted von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2000;97:10430–5.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, et al. The tumor suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature. 1999;399:271–5.
Schodel J, Grampp S, Maher ER, Moch H, Ratcliffe PJ, Russo P, et al. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and renal cancer. Eur Urol. 2016;69:646–57.
Biswas S, Troy H, Leek R, Chung YL, Li JL, Raval RR, et al. Effects of HIF-1alpha and HIF2alpha on growth and metabolism of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma 786-0 xenografts. J Oncol. 2010;2010:757908.
Shen C, Beroukhim R, Schumacher SE, Zhou J, Chang M, Signoretti S, et al. Genetic and functional studies implicate HIF1 as a 14q kidney cancer suppressorgene. Cancer Discov. 2011;1:222–35.
Godinot C, Laplanche ED, Hervouet E, Simonnet H. Actuality of Warburg’s views in our understanding of renal cancer metabolism. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2007;39:235–41.
Razorenova OV, Castellini L, Colavitti R, Edgington LE, Nicolau M, Huang X, et al. The apoptosis repressor with a CARD domain (ARC) gene is a direct hypoxia-inducible factor 1 target gene and promotes survival and proliferation of VHL-deficient renal cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:739–51.
Staller P, Sulitkova J, Lisztwan J, Moch H, Oakeley EJ, Krek W. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 downregulted by von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor pVHL. Nature. 2003;425:307–11.
Keefe SM, Hoffman-Censits J, Cohen RB, Mamtani R, Heitjan D, Eliasof S, et al. Efficacy of the nanoparticle-drug conjugate CRLX101 in combination with bevacizumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of an investigator-initiated phase I-IIa clinical trial. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:1579–85.
Jeong W, Rapisarda A, Park SR, Kinders RJ, Chen A, Melillo G, et al. Pilot trial of EZN-2968, an antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1), in patients with refractory solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;73:343–8.
Patnaik A, Papadopoulos KP, Tolcher AW, Beeram M, Urien S, Schaaf LJ, et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of EZN-2208 (PEG-SN38), a novel conjugate of poly(ethylene) glycol and SN38, administered weekly in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013;71:1499-06.
Wallace EM, Rizzi JP, Han G, Wehn PM, Cao Z, Du X, et al. A small-Molecule antagonist of HIF2 is efficacious in preclinical models of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016;76:5491-00.
Chen W, Hill H, Christie A, Kim MS, Holloman E, Pavia-Jimenez A, et al. Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. Nature. 2016;539:112–7.
Kornakiewicz A, Solarek W, Bielecka ZF, Lian F, Szczylik C, Czarnecka AM. Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors resistance mechanisms in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2014;8:210–8.
Brenner W, Farber G, Herget T, Lehr HA, Hengstler JG, Thuroff W. Loss of tumor suppressor protein PTEN during renal angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 2002;99:53–7.
Dey N, Das F, Choudhury NG, Mandal CC, Parekh DJ, Block K, et al. microRNA-21 governs TORC1 activation in renal Cancer cell proliferation and invasion. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:3–17.
White NMA, Masui O, Newsted D, Scorilas A, Romaschin AD, Bjarnason GA, et al. Galectin-1 has potential prognostic significance and is implicated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression through the HIF/mTOR signaling axis. Br J Cancer. 2010;110:1250–9.
Fiorentino M, Gruppioni E, Massari F, Giunchi F, Altimari A, Ciccarese C, et al. Wide spetcrum mutational analysis of metastatic renal cell cancer: a retrospective next generation sequencing approach. Oncotarget. 2017;31:7328–35.
Shojaei F, Lee JH, Simmons BH, Wong A, Esparza CO, Plumlee PA, et al. HGF/c-Met acts as an alternative angiogenic pathway in sunitinib-resistant tumors. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10090-00.
Cecchi F, Rabe DC, Bottaro DP. Targeting the HGF/Met signalling pathway in cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:1260–70.
Choueiri TK, Pal SK, McDermott DF, Morrissey S, Ferguson KC, Holland J. A phase I study of cabozantinib (XL184) in patients with renal cell cancer. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1603–8.
An J, Rettig MB. Mechanism of von Hippel–Lindau protein-mediated suppression of nuclear factor kappa B activity. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:7546–56.
Guttridge DC, Albanese JY, Pestell PG, Baldwin AS. NF-κB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:5785–99.
Pei X, Li M, Zhan J, Yu Y, Wei X, Guan L, et al. Enhanced IMP3 expression activates NF-кB pathway and promotes renal cell carcinoma progression. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0124338.
Peri S, Devarajan K, Yang DH, Knudson AG, Balachandran S. Meta-analysis identifies NF-κB as a therapeutic target in renal cancer. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e76746.
Labrousse-Arias D, Martínez-Alonso E, Corral-Escariz M, Bienes-Martínez R, Berridy J, Serrano-Oviedo L, et al. VHL promotes immune response against renal cell carcinoma via NF-κB-dependent regulation of VCAM-1. J Cell Biol. 2017;216:835–47.
Pawlus MR, Wang L, Hu CJ. STAT3 and HIF1α cooperatively activate HIF1 target genes in MDA-MB-231 and RCC4 cells. Oncogene. 2014;33:1670–9.
Alchanati I, Nallar SC, Sun P, Gao L, Hu J, Stein A, et al. A proteomic analysis reveals the loss of expression of the cell death regulatory gene GRIM-19 in human renal cell carcinomas. Oncogene. 2006;25:7138–47.
Qin J, Yang B, Xu BQ, Smithc A, Xu L, Yuan JL, et al. Concurrent CD44 s and STAT3 expression in human clear cell renal cellular carcinoma and its impact on survival. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:3235–44.
Zhou J, Wu K, Gao D, Zhu G, Wu D, Wang X, et al. Reciprocal regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 2α and GLI1 expression associated with the radioresistance of renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;90:942–51.
Varela I, Tarpey P, Raine K, Huang D, Ong CK, Stephens P, et al. Exome sequencing identifies frequent mutation of the SWI/SNF complex gene PBRM1 in renal carcinoma. Nature. 2011;469:539–42.
Togo Y, Yoshikawa Y, Suzuki T. Genomic profiling of the genes on chromosome 3p in sporadic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2016;48:1571–80.
Pawlowski R, Mühl SM, Sulser T, Krek W, Moch H, Schraml P. Loss of PBRM1 expression is associated with renal cell carcinoma progression. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:E11–7.
Macher-Goeppinger S, Keith M, Tagscherer KE, Singer S. PBRM1 (BAF180) protein is functionally regulated by p53-induced protein degradation in renal cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 2017;237:460–71.
Hakimi AA, Ostrovnaya I, Reva B, Schultz N, Chen YB, Gonen M, et al. Adverse outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma with mutations of 3p21 epigenetic regulators BAP1 and SETD2: a report by MSKCC and the KIRC TCGA research network. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:3259–67.
Gad S, Lefevre SH, Khoo SK, Giraud S, Vieillefond A, Vasiliu V, et al. Mutations in BHD and TP53 genes, but not in HNF1beta gene, in a large series of sporadic chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:336–40.
Delgliesh GL, Furge K, Greenman C, Chen L, Bignell G, Butler A, et al. Systematic sequencing of renal carcinoma reveals inactivation of histone modifying genes. Nature. 2010;463:360–3.
Authors contribution
All authors contributed to conception and design, manuscript preparation, read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Kumari, N., Gupta, V. et al. Renal Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Aspects. Ind J Clin Biochem 33, 246–254 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0713-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0713-y