Abstract
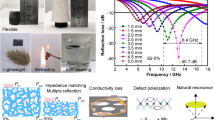
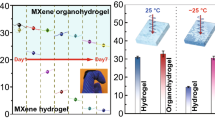
Rapid advancements in flexible electronics and military applications necessitate high-performance electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorbers. While huge breakthroughs in achieving high-attenuation microwave absorption, conventional EMW absorbing materials have single function and ambiguous absorption mechanisms. Herein, numerous gel-type absorbers are fabricated by introducing “regulators” into poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) (P(AM-co-AA)) networks through radical polymerization in a glycerol-water mixed solvent. The dielectric constant and EMW absorption performance of the gels are precisely predicted by adjusting monomer concentration, the ratio of glycerol/water, and the content of the regulators. Notably, A6G20T20-2 exhibits promising absorption performance with a minimum reflection loss (RLmin) of −33.8 dB at 12.4 GHz. The effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) covers the entire X-band (8.2–12.4 GHz) at a thickness of 2.7 mm. A6G20T20-2 also has sensitive deformation responses and excellent tensile strength, adhesiveness, self-healing and anti-freezing properties. Overall, this work not only provides insight into the polarization loss mechanism of the gels as the result of high correlation between EMW absorbing properties and molecular polarization, but also offers an important reference for developing functional protective materials because of the rich functionalities and efficient protective capabilities of the gels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, H. Y.; Sun, X. B.; Yang, S. H.; Zhao, P. Y.; Zhang, X. J.; Wang, G. S.; Huang, Y. 3D ultralight hollow NiCo compound@MXene composites for tunable and high-efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 206.
Liu, Q. H.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C. Y.; Yuan, K. P.; She, W.; Yang, Y. J.; Che, R. C. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490.
Liu, Y. J.; He, X. X.; Wang, Y. C.; Cheng, Z. Y.; Yao, Z. J.; Zhou, J. T.; Zuo, Y. X.; Chen, R. X.; Lei, Y. M.; Tan, R. Y.; Chen, P. Controlled synthesis of MOF-derived nano-microstructure toward lightweight and wideband microwave absorption. Small 2023, 19, 2302633.
Wei, M. M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. W.; Zhang, G. X.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Zhang, B. L. Rational construction of magnetic core-shell structural carbon nanotubes@mesoporous N-doped carbon nanofibers for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 213, 118254.
Liu, J. L.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. A competitive reaction strategy toward binary metal sulfides for tailoring electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105018.
Liu, P. J.; Ng, V. M. H.; Yao, Z. J.; Zhou, J. T.; Lei, Y. M.; Yang, Z. H.; Lv, H. L.; Kong, L. B. Facile synthesis and hierarchical assembly of flowerlike NiO structures with enhanced dielectric and microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16404–16416.
Zhang, X.; Tian, X. L.; Qin, Y. T.; Qiao, J.; Pan, F.; Wu, N.; Wang, C. X.; Zhao, S. Y.; Liu, W.; Cui, J. et al. Conductive metal-organic frameworks with tunable dielectric properties for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 12510–12518.
Lin, M. Y.; Liu, P.; Wu, F.; Zhang, B. L. Theee-dimensional RGO/CNTs/GDY assembled microsphere: Bridging-induced electron transport enhanced microwave absorbing mechanism. Carbon 2023, 214, 118351.
Zhang, R. N.; Li, B.; Yang, Y. F.; Wu, N.; Sui, Z. Y.; Ban, Q. F.; Wu, L. L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R.; Zeng, Z. H. Ultralight aerogel sphere composed of nanocellulose-derived carbon nanofiber and graphene for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 7931–7940.
Zhang, Y. L.; Wang, X. X.; Cao, M. S. Confinedly implanted NiFe2O4-rGO: Cluster tailoring and highly tunable electromagnetic properties for selective-frequency microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1426–1436.
Yang, Y. F.; Wu, N.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Pan, F.; Zeng, Z. H.; Liu, J. R. Biomimetic porous MXene sediment-based hydrogel for high-performance and multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 15042–15052.
Wei, B.; Wang, M. Q.; Yao, Z. J.; Chen, Z. P.; Chen, P.; Tao, X. W.; Liu, Y. J.; Zhou, J. T. Bimetallic nanoarrays embedded in three-dimensional carbon foam as lightweight and efficient microwave absorbers. Carbon 2022, 191, 486–501.
Li, B.; Wu, N.; Yang, Y. F.; Pan, F.; Wang, C. X.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R.; Zeng. Z. H. Graphene oxide-assisted multiple cross-linking of MXene for large-area, high-strength, oxidation-resistant, and multifunctional films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213357.
Xiang, Z. N.; He, Q. C.; Wang, Y. Q.; Yin, X. M.; Xu, B. K. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of SiC/SiO2 nanocomposites with different special structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 599, 153968.
Song, L. M.; Chen, Y. Q.; Gao, Q. C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wang, H. L.; Guan, L.; Yu, Z. J.; Zhang, R.; Fan, B. B. Low weight, low thermal conductivity, and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption of three-dimensional graphene/SiC-nanosheets aerogel. Compos. Part A 2022, 158, 106980.
Guan, H. T.; Wang, Q. Y.; Wu, X. F.; Pang, J.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Chen, G.; Dong, C. J.; Wang, L. H.; Gong, C. H. Biomass derived porous carbon (BPC) and their composites as lightweight and efficient microwave absorption materials. Compos. Part B 2021, 207, 108562.
Zeng, Z. H.; Wang, G.; Wolan, B. F.; Wu, N.; Wang, C. X.; Zhao, S. Y.; Yue, S. Y.; Li, B.; He, W. D.; Liu, J. R. et al. Printable aligned single-walled carbon nanotube film with outstanding thermal conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 179.
Li, B.; Wu, N.; Wu, Q. L.; Yang, Y. F.; Pan, F.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R.; Zeng, Z. H. From “100%” utilization of MAX/MXene to direct engineering of wearable, multifunctional E-textiles in extreme environments. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2307301.
Qian, Y. X.; Tao, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Luo, Y. N.; Jiang, Q. H.; Luo, Y. B.; Yang, J. Y. High electromagnetic wave absorption and thermal management performance in 3D CNF@C-Ni/epoxy resin composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131608.
Li, B.; Yang, Y. F.; Wu, N.; Zhao, S. Y.; Jin, H.; Wang, G. L.; Li, X. Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R.; Zeng, Z. H. Bicontinuous, high-strength, and multifunctional chemical-cross-linked MXene/superaligned carbon nanotube film. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19293–19304.
Wu, N.; Yang, Y. F.; Wang, C. X.; Wu, Q. L.; Pan, F.; Zhang, R. N.; Liu, J. R.; Zeng, Z. H. Ultrathin cellulose nanofiber assisted ambient-pressure-dried, ultralight, mechanically robust, multifunctional MXene aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207969.
Song, M. L.; Yu, H. Y.; Zhu, J. Y.; Ouyang, Z. F.; Abdalkarim, S. Y. H.; Tam, K. C.; Li, Y. Z. Constructing stimuli-free self-healing, robust and ultrasensitive biocompatible hydrogel sensors with conductive cellulose nanocrystals. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125547.
Yang, Y. F.; Han, M. R.; Li, W.; Wu, N.; Liu, J. R. Hydrogel-based composites beyond the porous architectures for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9614–9630.
Yu, L. J.; Yang, Q. X.; Liao, J. L.; Zhu, Y. F.; Li, X.; Yang, W. T.; Fu, Y. Q. A novel 3D silver nanowires@polypyrrole sponge loaded with water giving excellent microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 490–500.
Huang, X.; Wang, L. B.; Shen, Z. H.; Ren, J. F.; Chen, G. X.; Li, Q. F.; Zhou, Z. Super-stretchable and self-healing hydrogel with a three-dimensional silver nanowires network structure for wearable sensor and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137136.
Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. T.; Yang, X. H.; Li, F. F.; Liang, Z.; Yong, Y.; Dai, S. B.; Li, Z. J. A stretchable, environmentally stable, and mechanically robust nanocomposite polyurethane organohydrogel with anti-freezing, anti-dehydration, and electromagnetic shielding properties for strain sensors and magnetic actuators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 6603–6614.
Zhu, Y. Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. J.; Tang, X. Z.; Nicolosi, V. Multifunctional Ti3C2Tx MXene composite hydrogels with strain sensitivity toward absorption-dominated electromagnetic-interference shielding. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1465–1474.
Raman, M. S.; Ponnuswamy, V.; Kolandaivel, P.; Perumal, K. Ultrasonic and DFT study of intermolecular association through hydrogen bonding in aqueous solutions of glycerol. J. Mol. Liq. 2008, 142, 10–16.
Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Fan, C. C.; Zhao, X. Y.; Gao, J. S.; Jing, W. H.; Zhang, X. P.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. H. et al. An ultrasoft self-fused supramolecular polymer hydrogel for completely preventing postoperative tissue adhesion. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008395.
Zhao, Z. H.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Hydro/organo/ionogels: “Controllable” electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2205376.
Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. C.; Deng, B. W.; Cai, L.; Dong, Y. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Lu, W. Honeycomb-like NiCo2O4@MnO2 nanosheets array/3D porous expanded graphite hybrids for high-performance microwave absorber with hydrophobic and flame-retardant functions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129547.
Liu, P. B.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J. H. Core-shell CoNi@graphitic carbon decorated on B,N-codoped hollow carbon polyhedrons toward lightweight and high-efficiency microwave attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25624–25635.
Zhou, J.; Zhang, G. P.; Luo, J. L.; Hu, Y. B.; Hao, G. Z.; Guo, H.; Guo, F.; Wang, S. W.; Jiang, W. A MOFs-derived 3D superstructure nanocomposite as excellent microwave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130725.
Zhang, Y. F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou. B. Q.; Chen, H. C.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Zhang, B. L. Hierarchical 2H/1T-MoSe2@graphene on cotton fabric for multifunctional and flexible microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 205, 562–572.
Hou, T. Q.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Li, H. B.; Liu, X. H.; Bi, L.; Wu, G. L. MXene- based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2Tx as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128875.
Zhang, Y. F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, B. Q.; Ahmad, M.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Zhang, B. L. Microwave absorption and thermal conductivity properties in NPC@MoSe2/PDMS composites. Carbon 2023, 209, 117997.
Tang, Z. M.; Xu, L.; Xie, C.; Guo, L. R.; Zhang, L. B.; Guo, S. H.; Peng, J. H. Synthesis of CuCo2S4@expanded graphite with crystal/amorphous heterointerface and defects for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5951.
Kim, T.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Park, B.; Jung, B. M.; Lee, S. B. Magnetic and dispersible FeCoNi-graphene film produced without heat treatment for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1182–1189.
Xu, Y. G.; Yan, Z. Q.; Zhang, D. Y. Microwave absorbing property of a hybrid absorbent with carbonyl irons coating on the graphite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 1032–1038.
Zhang, J. X.; Feng, Y. B.; Qiu, T.; Tang, C. M. Preparation and characterization of carbonyl iron powder/millable polyurethane elastomer microwave absorbing patch. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1318–1324.
Baek, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Ban, H. W.; Gu, D. H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, F.; Lee, J.; Jung, B. M. et al. Controlled grafting of colloidal nanoparticles on graphene through tailored electrostatic interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1824–11833.
Lee, J.; Kim, T.; Lee, K.; Lee, S. B. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of graphene/FeCoNi composite materials by tuning electromagnetic parameters. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2019, 1, 015003.
Wang, Y. P.; Shi, Y. A.; Zhang, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, J. Z.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J.; Zhu, C. L. Atomically dispersed manganese sites embedded within nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2022, 198, 382–391.
Zhou, H. W.; Lai, J. L.; Zheng, B. H.; Jin, X. L.; Zhao, G. X.; Liu, H. B.; Chen, W. X.; Ma, A. J.; Li, X. S.; Wu, Y. P. From glutinous-rice-inspired adhesive organohydrogels to flexible electronic devices toward wearable sensing, power supply, and energy storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2108423.
Liu, Z. X.; Guo, W.; Wang, W. Y.; Guo, Z. J.; Yao, L. F.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Y. Healable strain sensor based on tough and eco-friendly biomimetic supramolecular waterborne polyurethane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6016–6027.
Acknowledgements
The authors were thankful for the support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22375166 and 21975206), Shaanxi Fundamental Science Research Project for Chemistry & Biology (No. 22JHZ004), and Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (No. CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX0513).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhou, B. et al. Polarization-driven multifunctional organohydrogels with strain sensitivity toward electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 17, 5688–5697 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6403-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6403-0