Abstract
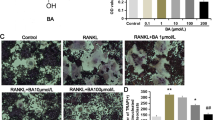
Osteoporosis is a metabolic dysregulation of bone that occurs mainly in postmenopausal women, and the hyperfunction of osteoclasts is the primary contributor to postmenopausal osteoporosis. However, the development of effective therapeutic drugs and precise delivery systems remains a challenge in the field of anti-absorption therapy. Here, we reported the α-cyperone (α-CYP) for anti-osteoporosis and developed a liposome-based nano-drug delivery system of α-CYP, that specifically targets the bone resorption interface. Firstly, we found that the α-CYP, one of the major sesquiterpenes of Cyperus rotundus L., attenuated the progression of osteoporosis in ovariectomized (OVX) mice and down-regulated the expression of phosphorylated proteins of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (Akt), causing down-regulation of osteoclast-related genes/proteins and curbing osteoclast differentiation. Furthermore, α-CYP reversed the activation of osteoclastic differentiation and enhanced osteoporosis-related proteins expression caused by PI3K/Akt agonist (YS-49). More importantly, we adopted the osteoclastic resorption surface targeting peptide Asp8 and constructed the liposome (lipaC@Asp8) to deliver α-CYP to osteoclasts and confirmed its anti-osteoporosis effect and enhanced osteoclast inhibition by blocking PI3K/Akt axis. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that α-CYP inhibits osteoclast differentiation and osteoporosis development by silencing PI3K/Akt pathway, and the liposome targeting delivery systems loaded with α-CYP might provide a novel and effective strategy to treat osteoporosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weitzmann, M. N.; Ofotokun, I. Physiological and pathophysiological bone turnover - role of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 518–532.
Eastell, R.; O’Neill, T. W.; Hofbauer, L. C.; Langdahl, B.; Reid, I. R.; Gold, D. T.; Cummings, S. R. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16069.
Sipos, W.; Pietschmann, P.; Rauner, M. Strategies for novel therapeutic approaches targeting cytokines and signaling pathways of osteoclasto- and osteoblastogenesis in the fight against immunemediated bone and joint diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 127–136.
Li, H. X.; Xiao, Z. S.; Quarles, L. D.; Li, W. Osteoporosis: Mechanism, molecular target and current status on drug development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1489–1507.
Lee, S.; Kim, G. J.; Kwon, H.; Nam, J. W.; Baek, J. Y.; Shim, S. H.; Choi, H.; Kang, K. S. Estrogenic effects of extracts and isolated compounds from belowground and aerial parts of Spartina anglica. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 210.
Zeytinoglu, M.; Naaman, S. C.; Dickens, L. T. Denosumab discontinuation in patients treated for low bone density and osteoporosis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2021, 50, 205–222.
Black, D. M.; Rosen, C. J. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 254–262.
Horn, C.; Vediyappan, G. Anticapsular and antifungal activity of α-Cyperone. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 51.
Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, D.; Ran, X.; Yan, X.; Du, J.; Meng, T.; Gao, X.; Liu, D. α-Cyperone Attenuates H(2)O(2)-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells via Activation of Nrf2. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11 281.
Huang, B. X.; He, D. W.; Chen, G. X.; Ran, X.; Guo, W. J.; Kan, X. C.; Wang, W.; Liu, D. F.; Fu, S. P.; Liu, J. X. α-Cyperone inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in BV-2 cells through activation of Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 and suppression of the NF-κB pathway. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2735–2743.
Zhang, H. W.; Li, S. L.; Lu, J. J.; Jin, J.; Zhu, G. S.; Wang, L. B.; Yan, Y. Z.; He, L. J.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. Y. et al. α-Cyperone (CYP) down-regulates NF-κB and MAPKs signaling, attenuating inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation in chondrocytes, to ameliorate osteoarthritis in mice. Aging 2021, 13, 17690–17706.
Kum, C. J.; Kim, E. Y.; Kim, J. H.; Lee, B.; Min, J. H.; Heo, J.; Kim, J. H.; Yeom, M.; Sohn, Y.; Jung, H. S. Cyperus rotundus L. extract suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through NFATc1/c-fos downregulation and prevent bone loss in OVX-induced osteoporosis rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 186–194.
Nirwan, N.; Nikita; Sultana, Y.; Vohora, D. Liposomes as multifaceted delivery system in the treatment of osteoporosis. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 761–775.
Wang, D.; Miller, S. C.; Shlyakhtenko, L. S.; Portillo, A. M.; Liu, X. M.; Papangkorn, K.; Kopečková, P.; Lyubchenko, Y.; Higuchi, W. I.; Kopeček, J. Osteotropic Peptide that differentiates functional domains of the skeleton. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1375–1378.
Zhang, G.; Guo, B. S.; Wu, H.; Tang, T.; Zhang, B. T.; Zheng, L. Z.; He, Y. X.; Yang, Z. J.; Pan, X. H.; Chow, H. et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic therapy. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 307–314.
Armas, L. A. G.; Recker, R. R. Pathophysiology of osteoporosis: New mechanistic insights. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2012, 41, 475–486.
Zhang, M. J.; Yu, J. Y.; Liu, A.; Liu, Q. Q.; Sun, T.; Li, X.; Du, Y. Y.; Li, J. M.; Wang, B.; Yang, Q. Luteolin in the Qi Bi Anshen decoction improves propionic acid-induced autism-like behavior in rats by inhibiting LRP1/MMP9. Phytomedicine 2023, 118, 154965.
Wang, T. X.; Chen, M.; Li, H. X.; Ding, G. Y.; Song, Y. F.; Hou, B.; Yao, B.; Wang, Z. X.; Hou, Y. L.; Liang, J. Q. et al. Repositioning of clinically approved drug Bazi Bushen capsule for treatment of Aizheimer’s disease using network pharmacology approach and in vitro experimental validation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17603.
Jia, X. Y.; He, Y. H.; Li, L.; Xu, D. L. Pharmacological targeting of gastric mucosal barrier with traditional Chinese medications for repairing gastric mucosal injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1091530.
Alam, S. S. M.; Samanta, A.; Uddin, F.; Ali, S.; Hoque, M. Tanshinone IIA targeting cell signaling pathways: A plausible paradigm for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 907–922.
Yang, F. G.; Zhang, S. H.; Tian, D. M.; Zhou, G. R.; Tang, X. Y.; Miao, X. L.; He, Y.; Yao, X. S.; Tang, J. S. Deciphering chemical and metabolite profiling of Chang-Kang-Fang by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and its potential active components identification. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2023, 21, 459–480.
Liu, X. S. B. J.; Jin, X. T.; Yu, D.; Liu, G. Suppression of NLRP3 and NF-κB signaling pathways by α-Cyperone via activating SIRT1 contributes to attenuation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105886.
Jung, S. H.; Kim, S. J.; Jun, B. G.; Lee, K. T.; Hong, S. P.; Oh, M. S.; Jang, D. S.; Choi, J. H. α-Cyperone, isolated from the rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus, inhibits LPS-induced COX-2 expression and PGE2 production through the negative regulation of NFκB signalling in RAW 264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 208–214.
Huang, B. X.; Hu, G. Q.; Zong, X. F.; Yang, S.; He, D. W.; Gao, X. Y.; Liu, D. F. α-Cyperone protects dopaminergic neurons and inhibits neuroinflammation in LPS-induced Parkinson’s disease rat model via activating Nrf2/HO-1 and suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 115, 109698.
Pei, X. D.; Yao, H. L.; Shen, L. Q.; Yang, Y.; Lu, L.; Xiao, J. S.; Wang, X. Y.; He, Z. L.; Jiang, L. H. α-Cyperone inhibits the proliferation of human cervical cancer HeLa cells via ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173355.
Hopkins, A. L. Network pharmacology: The next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690.
Lee, S. E.; Woo, K. M.; Kim, S. Y.; Kim, H. M.; Kwack, K.; Lee, Z. H.; Kim, H. H. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved in osteoclast differentiation. Bone 2002, 30, 71–77.
Liang, J. Y.; Wu, W. L.; Chen, Y. X.; Liu, H. C. The efficacy and potential mechanism of cnidium lactone to inhibit osteoclast differentiation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3087–3093.
Soysa, N. S.; Alles, N. Osteoclast function and bone-resorbing activity: An overview. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 476, 115–120.
Boyle, W. J.; Simonet, W. S.; Lacey, D. L. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 2003, 423, 337–342.
Dumortier, C.; Danopoulos, S.; Velard, F.; Al Alam, D. Bone cells differentiation: How CFTR mutations may rule the game of stem cells commitment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 611921.
Guo, W.; Li, H. J.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Qian, M.; Wei, H. F.; Xiao, J. R.; Xu, Y. J. Tyloxapol inhibits RANKL-stimulated osteoclastogenesis and ovariectomized-induced bone loss by restraining NF-κB and MAPK activation. J. Orthop. Translat. 2021, 28, 148–158.
Bobo, D.; Robinson, K. J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K. J.; Corrie, S. R. Nanoparticle-based medicines: A review of FDA-approved materials and clinical trials to date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387.
Dang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, F. F.; Wang, L. Y.; Li, D. F.; Guo, B. S.; He, X. J.; Jiang, F.; Liang, C.; Liu, B. et al. Targeted delivery systems for molecular therapy in skeletal disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 428.
Waldrep, J. C.; Gilbert, B. E.; Knight, C. M.; Black, M. B.; Scherer, P. W.; Knight, V.; Eschenbacher, W. Pulmonary delivery of beclomethasone liposome aerosol in volunteers: Tolerance and safety. Chest 1997, 111, 316–323.
Chang, M. L.; Lu, S. S.; Zhang, F.; Zuo, T. T.; Guan, Y. Y.; Wei, T.; Shao, W.; Lin, G. M. RGD-modified pH-sensitive liposomes for docetaxel tumor targeting. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2015, 129, 175–182.
Wieland, K.; Ramer, G.; Weiss, V. U.; Allmaier, G.; Lendl, B.; Centrone, A. Nanoscale chemical imaging of individual chemotherapeutic cytarabine-loaded liposomal nanocarriers. Nano Res 2019, 12, 197–203.
Wang, D.; Sima, M.; Lee Mosley, R.; Davda, J. P.; Tietze, N.; Miller, S. C.; Gwilt, P. R.; Kopečková, P.; Kopeček, J. Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies of a bone-targeting drug delivery system based on N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymers. Mol. Pharm. 2006, 3, 717–725.
Wang, D.; Miller, S.; Sima, M.; Kopečková, P.; Kopeček, J. Synthesis and evaluation of water-soluble polymeric bone-targeted drug delivery systems. Bioconjug. Chem. 2003, 14, 853–859.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project (No. 2021YFA1201404), Major Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81991514, 82272530), Jiangsu Province Medical Innovation Center of Orthopedic Surgery (No. CXZX202214), Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Center Foundation, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Outstanding Talent Foundation, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent Foundation, Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Talent Foundation, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 14380493 and 14380494).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., An, X., Gong, W. et al. Liposomal α-cyperone targeting bone resorption surfaces suppresses osteoclast differentiation and osteoporosis progression via the PI3K/Akt axis. Nano Res. 17, 2949–2959 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6224-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6224-7