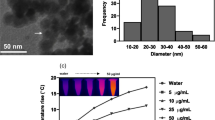
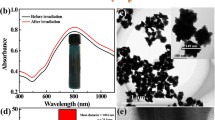
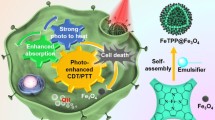
Abstract
Achieving efficient integration of cancer diagnosis and therapy is of great significance to human health, but the construction of a multifunctional intelligent therapy system still faces great challenges. In this study, we report an integrated multifunctional nanocomposite constructed by a simple modular assembly technology. The nanocomposites are composed of three different nanomaterials: Fe3O4, Au, and NaErF4:0.5%Tm@NaYF4 upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs). In this design, Fe3O4 nanoparticles have nanozyme effect of peroxidase-like activity, which can react with H2O2 in the tumor microenvironment to generate hydroxyl radicals. Because of its magnetic properties, it can help the nanocomposites to aggregate under the induction of magnetic fields. Au nanoparticles exhibit nanozyme effect of glucose oxidase-like activity. It can catalyze the conversion of glucose to gluconic acid and H2O2. Ingeniously, the generated H2O2 provides a source of reactants for the reaction of the Fe3O4 nanozyme. In addition, the photothermal effect of Au nanoparticles under 808 nm irradiation further enhanced the nanozyme activity of Fe3O4 and Au nanoparticles. Besides, UCNPs can emit near-infrared (NIR)-II fluorescence under 808 nm irradiation, which can provide imaging-guided during cancer treatment. Then, the nanocomposites were further modified by poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) to obtain UCNPs/Au/Fe3O4-PVP with good biocompatibility and high-efficiency cancer treatment ability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waks, A. G.; Winer, E. P. Breast cancer treatment: A review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300.
Wang, Y. G.; Xia, G. M.; Tan, M. M.; Wang, M. D.; Li, Y. Z.; Wang, H. M. H-dimeric nanospheres of amphipathic squaraine dye with an 81. 2% photothermal conversion efficiency for photothermal therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113098.
Chang, M. Y.; Hou, Z. Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, C. Z.; Wang, R. F.; Li, F.; Liu, D. L.; Peng, T. L.; Li, C. X.; Lin, J. Single-atom Pd nanozyme for ferroptosis-boosted mild-temperature photothermal therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12971–12979.
Chen, Y. J.; Wang, P. X.; Hao, H. G.; Hong, J. J.; Li, H. J.; Ji, S. F.; Li, A.; Gao, R.; Dong, J. C.; Han, X. D. et al. Thermal atomization of platinum nanoparticles into single atoms: An effective strategy for engineering high-performance nanozymes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18643–18651.
Feng, W.; Han, X. G.; Hu, H.; Chang, M. Q.; Ding, L.; Xiang, H. J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. H. 2D vanadium carbide MXenzyme to alleviate ROS-mediated inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2203.
Ji, S. F.; Jiang, B.; Hao, H. G.; Chen, Y. J.; Dong, J. C.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Z. D.; Gao, R.; Chen, W. X.; Zhang, R. F. et al. Matching the kinetics of natural enzymes with a single-atom Iron nanozyme. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 407–417.
Kalashnikova, I.; Chung, S. J.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Hill, M. L.; Siziba, M. E.; Contag, C. H.; Kim, T. Ceria-based nanotheranostic agent for rheumatoid arthritis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11863–11880.
Li, Y. H.; Sun, Y.; Cao, T. Y.; Su, Q. Q.; Li, Z. L.; Huang, M. X.; Ouyang, R. Z.; Chang, H. Z.; Zhang, S. P.; Miao, Y. Q. A cation-exchange controlled core-shell MnS@Bi2S3 theranostic platform for multimodal imaging guided radiation therapy with hyperthermia boost. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14364–14375.
Liang, M. M.; Yan, X. Y. Nanozymes: From new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2190–2200.
Liu, J. M.; Wang, A. Z.; Liu, S. H.; Yang, R. Q.; Wang, L. W.; Gao, F. E.; Zhou, H. G.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, C. Y. A titanium nitride nanozyme for PH-responsive and irradiation-enhanced cascade-catalytic tumor therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25328–25338.
Liu, Q. Q.; Tian, J. W.; Liu, J. J.; Zhu, M. S.; Gao, Z. X.; Hu, X. Y.; Midgley, A. C.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Y.; Kong, D. L. et al. Modular assembly of tumor-penetrating and oligomeric nanozyme based on intrinsically self-assembling protein nanocages. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103128.
Wang, D. D.; Jana, D.; Zhao, Y. L. Metal-organic framework derived nanozymes in biomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1389–1400.
Wang, D. D.; Wu, H. H.; Wang, C. L.; Gu, L.; Chen, H. Z.; Jana, D.; Feng, L. L.; Liu, J. W.; Wang, X. Y.; Xu, P. P. et al. Self-assembled single-site nanozyme for tumor-specific amplified cascade enzymatic therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3001–3007.
Wei, H.; Wang, E. K. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093.
Wen, M.; Ouyang, J.; Wei, C. W.; Li, H.; Chen, W. S.; Liu, Y. N. Artificial enzyme catalyzed cascade reactions: Antitumor immunotherapy reinforced by NIR-II light. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17425–17432.
Weng, Q. J.; Sun, H.; Fang, C. Y.; Xia, F.; Liao, H. W.; Lee, J.; Wang, J. C.; Xie, A.; Ren, J. F.; Guo, X. et al. Catalytic activity tunable ceria nanoparticles prevent chemotherapy-induced acute kidney injury without interference with chemotherapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1436.
Yang, Y.; Zhu, D. M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, W.; Yan, X. Y.; Fan, K. L. Platinum-carbon-integrated nanozymes for enhanced tumor photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13548–13557.
Zhu, Y.; Wang, W. Y.; Cheng, J. J.; Qu, Y. T.; Dai, Y.; Liu, M. M.; Yu, J. N.; Wang, C. M.; Wang, H. J.; Wang, S. C. et al. Stimuli-responsive manganese single-atom nanozyme for tumor therapy via integrated cascade reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9480–9488.
Lei, P. P.; An, R.; Zhang, P.; Yao, S.; Song, S. Y.; Dong, L. L.; Xu, X.; Du, K. M.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H. J. Ultrafast synthesis of ultrasmall poly(Vinylpyrrolidone)-protected bismuth nanodots as a multifunctional theranostic agent for in vivo dual-modal CT/Photothermal-imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702018.
Liu, X. Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, H. L.; Wang, P. S.; Shen, Y. H.; Xie, A. J.; Zhu, M. Z. Self-assembled Au4Cu4/Au25 NCs@liposome tumor nanotheranostics with PT/fluorescence imaging-guided synergetic PTT/PDT. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6396–6405.
Liu, X. J.; Zhang, M. Y.; Yan, D. W.; Deng, G. Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, C. L.; Zhao, L. J.; Lu, J. A smart theranostic agent based on Fe-HPPy@Au/DOX for CT imaging and PTT/chemotherapy/CDT combined anticancer therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4067–4072.
Mei, Z. H.; Gao, D. Y.; Hu, D. H.; Zhou, H. C.; Ma, T.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, R. Q.; Zheng, H. R.; Zhao, P. et al. Activatable NIR-II photoacoustic imaging and photochemical synergistic therapy of MRSA infections using miniature Au/Ag nanorods. Biomaterials 2020, 251, 120092.
Zhang, Y. Y.; Lv, F.; Cheng, Y. R.; Yuan, Z. P.; Yang, F.; Liu, C. H.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Lu, H. T.; Zada, S. et al. Pd@Au bimetallic nanoplates decorated mesoporous MnO2 for synergistic nucleus-targeted NIR-II photothermal and hypoxia-relieved photodynamic therapy. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 1901528.
Wang, J. X.; Yao, C. J.; Shen, B.; Zhu, X. H.; Li, Y.; Shi, L. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. L.; Wang, Y. L.; Sun, L. N. Upconversion-magnetic carbon sphere for near infrared light-triggered bioimaging and photothermal therapy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 608–619.
Dibaba, S. T.; Xie, Y.; Xi, W. S.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Ren, W.; Sun, L. N. Nd3+-sensitized upconversion nanoparticle coated with antimony shell for bioimaging and photothermal therapy in vitro using single laser irradiation. J. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 862–869.
De Marchi, S.; Vázquez-Iglesias, L.; Bodelón, G.; Pérez-Juste, I.; Fernández, L. Á.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I. Programmable modular assembly of functional proteins on raman-encoded Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanoparticles as SERS tags. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 5739–5749.
Guo, J. L.; Tardy, B. L.; Christofferson, A. J.; Dai, Y. L.; Richardson, J. J.; Zhu, W.; Hu, M.; Ju, Y.; Cui, J. W.; Dagastine, R. R. et al. Modular assembly of superstructures from polyphenol-functionalized building blocks. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 1105–1111.
Guo, J. M.; Yu, Y. L.; Zhu, W.; Serda, R. E.; Franco, S.; Wang, L.; Lei, Q.; Agola, J. O.; Noureddine, A.; Ploetz, E. et al. Modular assembly of red blood cell superstructures from metal-organic framework nanoparticle-based building blocks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005935.
Pazos-Perez, N.; Fitzgerald, J. M.; Giannini, V.; Guerrini, L.; Alvarez-Puebla, R. A. Modular assembly of plasmonic core-satellite structures as highly brilliant SERS-encoded nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 122–131.
Wu, H. M.; Zhang, X. R.; Wei, C. J.; Wang, C. C.; Jiang, M.; Hong, X.; Xu, Z. K.; Chen, D. J.; Huang, X. J. Modular assembly of enzyme loaded nanoparticles in 3D hollow fiber electrode for electrochemical sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129721.
Xu, L.; Xu, S. J.; Wang, H. X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Pan, L. H.; Wang, J. G.; Wei, X. Y.; Xie, H. Y.; Zhou, L. et al. Enhancing the efficacy and safety of doxorubicin against hepatocellular carcinoma through a modular assembly approach: The combination of polymeric prodrug design, nanoparticle encapsulation, and cancer cell-specific drug targeting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3229–3240.
Zhang, Z.; Jayakumar, M. K. G.; Shikha, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Modularly assembled upconversion nanoparticles for orthogonally controlled cell imaging and drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 12549–12556.
Zhou, A. W.; Du, J. J.; Jiao, M. Y.; Xie, D. P.; Wang, Q. Q.; Xue, L. J.; Ju, C. Y.; Hua, Z. C.; Zhang, C. Co-delivery of TRAIL and siHSP70 using hierarchically modular assembly formulations achieves enhanced TRAIL-resistant cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 304, 111–124.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the financial aid from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22020102003, 21834007, and 52103276), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2020YFA0712102), the Program of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province of China (No. 20220508076RC), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (No. 2022A1515010947), and Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 202201011343).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_5706_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Tumor microenvironment-responsive modular integrated nanocomposites for magnetically targeted and photothermal enhanced catalytic therapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Liu, Y., Lei, P. et al. Tumor microenvironment-responsive modular integrated nanocomposites for magnetically targeted and photothermal enhanced catalytic therapy. Nano Res. 16, 9826–9834 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5706-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5706-y