Abstract
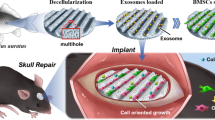
Tissue engineering scaffolds have presented effective value in bone repair. However, the integration of the diverse components, complex structures, and multifunction to impart the scaffolds with improved applicability is still a challenge. Here, we propose a novel fish-derived scaffold combined with photothermal therapy and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to promote bone regeneration. The fish-derived scaffold is composed of the decellularized fish scale and gelatin methacrylate synthesized from fish gelatin (fGelMA), which can promote the proliferation and osteogenesis of MSCs with no obvious immunological rejection. Furthermore, the black phosphorus (BP) nanosheets are incorporated into the fGelMA hydrogel network, which can endow the hydrogel with the capacity of photothermal conversion stimulated by near-infrared (NIR) light. The fish-derived scaffold can promote the osteogenesis process of MSCs with higher expression of osteogenic markers and higher mineralization assisted by the NIR light in vitro. The regeneration of mice calvarial defect has also been accelerated by the scaffold with photothermal therapy and MSCs. These results suggest that the fish-derived scaffold, photothermal therapy, and MSCs-based regenerative therapy is a promising clinical strategy in bone regeneration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie, C.; Ye, J. C.; Liang, R. J.; Yao, X. D.; Wu, X. Y.; Koh, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X. Z.; Ouyang, H. W. Advanced strategies of biomimetic tissue-engineered grafts for bone regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100408.
Sen, M. K.; Miclau, T. Autologous iliac crest bone graft: Should it still be the gold standard for treating nonunions? Injury 2007, 38 Suppl 1, S75–S80.
Quan, K.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, M. S.; Liu, X. Q.; Dai, M. Analysis of risk factors for non-union after surgery for limb fractures: A case-control study of 669 subjects. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 754150.
Stewart, S. K. Fracture non-union: A review of clinical challenges and future research needs. Malays. Orthop. J. 2019, 13, 1–10.
Krampera, M.; Le Blanc, K. Mesenchymal stromal cells: Putative microenvironmental modulators become cell therapy. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1708–1725.
Robert, A. W.; Marcon, B. H.; Dallagiovanna, B.; Shigunov, P. Adipogenesis, osteogenesis, and chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: A comparative transcriptome approach. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 561.
Fu, J. F.; Wang, Y. X.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Du, J.; Xu, J. J.; Liu, Y. Systemic therapy of MSCs in bone regeneration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 377.
Kimbrel, E. A.; Lanza, R. Next-generation stem cells—Ushering in a new era of cell-based therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 463–479.
Shafiq, M.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S. H. Insight on stem cell preconditioning and instructive biomaterials to enhance cell adhesion, retention, and engraftment for tissue repair. Biomaterials 2016, 90, 85–115.
Liu, C.; Xu, X. Y.; Cui, W. G.; Zhang, H. B. Metal-organic framework (MOF)-based biomaterials in bone tissue engineering. Eng. Regenerat. 2021, 2, 105–108.
Battafarano, G.; Rossi, M.; De Martino, V.; Marampon, F.; Borro, L.; Secinaro, A.; Del Fattore, A. Strategies for bone regeneration: From graft to tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1128.
García-Gareta, E.; Coathup, M. J.; Blunn, G. W. Osteoinduction of bone grafting materials for bone repair and regeneration. Bone 2015, 81, 112–121.
Kim, H. D.; Amirthalingam, S.; Kim, S. L.; Lee, S. S.; Rangasamy, J.; Hwang, N. S. Biomimetic materials and fabrication approaches for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700612.
Yu, Y. R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Shang, L. R. Living materials for regenerative medicine. Eng. Regenerat. 2021, 2, 96–104.
Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakazono, A.; Matsuura, T.; Yoshimura, A. Functional roles of fish collagen peptides on bone regeneration. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 1295–1302.
Kara, A.; Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F.; Havitcioglu, H. Bioactive fish scale incorporated chitosan biocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 266–279.
Mizuno, Y.; Taguchi, T. Fish gelatin-based absorbable dural sealant with anti-inflammatory properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4991–4998.
Chen, J. J.; Gao, K. L.; Liu, S.; Wang, S. J.; Elango, J.; Bao, B.; Dong, J.; Liu, N.; Wu, W. H. Fish collagen surgical compress repairing characteristics on wound healing process in vivo. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 33.
Lima-Junior, E. M.; De Moraes filho, M. O.; Costa, B. A.; Fechine, F. V.; De Moraes, M. E. A.; Silva-Junior, F. R.; Soares, M. F. A. D. N.; Rocha, M. B. S.; Leontsinis, C. M. P. Innovative treatment using tilapia skin as a xenograft for partial thickness burns after a gunpowder explosion. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2019, 2019, rjz181.
Shao, J. D.; Xie, H. H.; Huang, H.; Li, Z. B.; Sun, Z. B.; Xu, Y. H.; Xiao, Q. L.; Yu, X. F.; Zhao, Y. T.; Zhang, H. et al. Biodegradable black phosphorus-based nanospheres for in vivo photothermal cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12967.
Shao, J. D.; Ruan, C. S.; Xie, H. H.; Chu, P. K.; Yu, X. F. Photochemical activity of black phosphorus for near-infrared light controlled in situ biomineralization. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2020, 7, 2000439.
Wang, X. C.; Yu, Y. R.; Yang, C. Y.; Shao, C. M.; Shi, K. Q.; Shang, L. R.; Ye, F. F.; Zhao, Y. J. Microfluidic 3D printing responsive scaffolds with biomimetic enrichment channels for bone regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111909.
Zhang, G. W.; Chaves, A.; Huang, S. Y.; Wang, F. J.; Xing, Q. X.; Low, T.; Yan, H. G. Determination of layer-dependent exciton binding energies in few-layer black phosphorus. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9977.
Xu, D. Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. X.; Jian, Y. Y.; Wu, W. W.; Lv, R. C. Black phosphorus nanosheet with high thermal conversion efficiency for photodynamic/photothermal/immunotherapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4940–4948.
Ren, X. N.; Liu, W. L.; Zhou, H. J.; Wei, J. S.; Mu, C. P.; Wan, Y.; Yang, X. Q.; Nie, A. M.; Liu, Z. Y.; Yang, X. L. et al. Biodegradable 2D GeP nanosheets with high photothermal conversion efficiency for multimodal cancer theranostics. Chem Eng J 2022, 431, 134176.
Li, Z. M.; Yu, Y. K.; Zeng, W. F.; Ding, F.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, H. Z.; Pan, G. Q.; Mei, L. et al. Mussel-inspired ligand clicking and ion coordination on 2D black phosphorus for cancer multimodal imaging and therapy. Small 2022, 18, 2201803.
Song, H. B.; Wang, J.; Xiong, B.; Hu, J. Y.; Zeng, P.; Liu, X. M.; Liang, H. G. Biologically safe, versatile, and smart bismuthene functionalized with a drug delivery system based on red phosphorus quantum dots for cancer theranostics. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117679.
Maleki, A.; He, J. H.; Bochani, S.; Nosrati, V.; Shahbazi, M. A.; Guo, B. L. Multifunctional photoactive hydrogels for wound healing acceleration. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18895–18930.
Shahbazi, M. A.; Faghfouri, L.; Ferreira, M. P. A.; Figueiredo, P.; Maleki, H.; Sefat, F.; Hirvonen, J.; Santos, H. A. The versatile biomedical applications of bismuth-based nanoparticles and composites: Therapeutic, diagnostic, biosensing, and regenerative properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1253–1321.
Wang, X. Z.; Shao, J. D.; Abd El Raouf, M.; Xie, H. H.; Huang, H.; Wang, H. Y.; Chu, P. K.; Yu, X. F.; Yang, Y.; Abdel-Aal, A. M. et al. Near-infrared light-triggered drug delivery system based on black phosphorus for in vivo bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2018, 179, 164–174.
Qing, Y. A.; Li, R. Y.; Li, S. H.; Li, Y. H.; Wang, X. Y.; Qin, Y. G. Advanced black phosphorus nanomaterials for bone regeneration. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2045–2058.
Tan, L.; Li, M. H.; Luo, Z.; Cai, K. Y.; Hu, Y. Black phosphorus biomaterials for photo-controlled bone tissue engineering. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 246, 110245.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project (No. 2021YFA1201404), Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81730067), Major Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81991514), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82101184), Shenzhen Fundamental Research Program (No. JCYJ20210324102809024), Shenzhen PhD Start-up Program (No. RCBS20210609103713045), Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Center Foundation, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Outstanding Talent Foundation, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent Foundation, Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Talent Foundation, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 14380493 and 14380494).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, S., Liu, R., Song, C. et al. Fish scale-derived scaffolds with MSCs loading for photothermal therapy of bone defect. Nano Res. 16, 7383–7392 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5460-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5460-1