Abstract
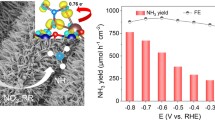
Electrochemical nitrate reduction reaction (NO3RR) has great potential for ammonia (NH3) synthesis benefiting from its environmental friendliness and sustainability. Cu-based alloys with elemental diversity and adsorption tunability are widely used as electrocatalyst to lower the reaction overpotential for NO3RR catalysis. However, phase separation commonly found in alloys leads to uneven distribution of elements, which limits the possibility of further optimizing the catalytic activity. Herein, an electro-triggered Joule heating method, possessing unique superiority of flash heating and cooling that lead to well-dispersed nanoparticles and uniform mixing of various elements, was adopted to synthesize a single-phase CuNi nano-alloy catalyst evenly dispersed on carbon fiber paper, CFP-Cu1Ni1, which exhibited a more positive NO3RR initial potential of 0.1 V versus reversible hydrogen electrode (vs. RHE) than that of pure copper nanoparticles at 10 mA·cm−2 in 0.5 mol·L−1 Na2SO4 + 0.1 mol·L−1 KNO3 solution. Importantly, CFP-Cu1Ni1 presented high electrocatalytic activity with a Faradaic efficiency of 95.7% and NH3 yield rate of 180.58 µmol·h−1·cm−2 (2550 µmol·h−1·mg −1cat ) at −0.22 V vs. RHE. Theoretical calculations showed that alloying Cu with Ni into single-phase caused an upshift of its d-band center, which promoted the adsorption of NO −3 and weakened the adsorption of NH3. Moreover, the competitive adsorption of hydrogen ions was restrained until −0.24 V. This work offers a rational design concept with clear guidance for rapid synthesis of uniformly dispersed single-phase nano-alloy catalyst for efficient electrochemical NO3RR toward ammonia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, G. F.; Yuan, Y. F.; Jiang, H. F.; Ren, S. Y.; Ding, L. X.; Ma, L.; Wu, T. P.; Lu, J.; Wang, H. H. Electrochemical reduction of nitrate to ammonia via direct eight-electron transfer using a copper-molecular solid catalyst. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 605–613.
Li, Z. R.; Deng, Z. Q.; Ouyang, L.; Fan, X. Y.; Zhang, L. C.; Sun, S. J.; Liu, Q.; Alshehri, A. A.; Luo, Y. L.; Kong, Q. Q. et al. CeO2 nanoparticles with oxygen vacancies decorated N-doped carbon nanorods: A highly efficient catalyst for nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8914–8921.
Wen, G. L.; Liang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, T. S.; An, X. G.; Zhang, F.; Alshehri, A. A.; Alzahrani, K. A.; Luo, Y. L.; Kong, Q. Q. et al. Ambient ammonia production via electrocatalytic nitrite reduction catalyzed by a CoP nanoarray. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 972–977.
Zhang, L. C.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y. Y.; Mou, T.; Lin, Y. T.; Yue, L. C.; Li, T. S.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Y. L.; Li, N. et al. High-performance electrochemical NO reduction into NH3 by MoS2 nanosheet. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25263–25268.
Liu, Q.; Xie, L. S.; Liang, J.; Ren, Y. C.; Wang, Y. Y.; Zhang, L. C.; Yue, L. C.; Li, T. S.; Luo, Y. S.; Li, N. et al. Ambient ammonia synthesis via electrochemical reduction of nitrate enabled by NiCo2O4 nanowire array. Small 2022, 18, e2106961.
Fan, X. Y.; Xie, L. S.; Liang, J.; Ren, Y. C.; Zhang, L. C.; Yue, L. C.; Li, T. S.; Luo, Y. L.; Li, N.; Tang, B. et al. In situ grown Fe3O4 particle on stainless steel: A highly efficient electrocatalyst for nitrate reduction to ammonia. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3050–3055.
Xu, H.; Wu, J.; Luo, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W. X.; Yang, J. P. Dendritic cell-inspired designed architectures toward highly efficient electrocatalysts for nitrate reduction reaction. Small 2020, 16, 2001775.
Murphy, E.; Liu, Y. C.; Matanovic, I.; Guo, S. Y.; Tieu, P.; Huang, Y.; Ly, A.; Das, S.; Zenyuk, I.; Pan, X. Q. et al. Highly durable and selective Fe- and Mo-based atomically dispersed electrocatalysts for nitrate reduction to ammonia via distinct and synergized NO −2 pathways. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 6651–6662.
Xu, H.; Ma, Y. Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. X.; Yang, J. P. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate—A step towards a sustainable nitrogen cycle. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 2710–2758.
Zhao, Y. L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. J.; Mo, Z. K.; Wang, C. Y.; Gao, S. Y. Flower-like open-structured polycrystalline copper with synergistic multi-crystal plane for efficient electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107124.
Wang, J.; Feng, T.; Chen, J. X.; He, J. H.; Fang, X. S. Flexible 2D Cu metal: Organic framework@MXene film electrode with excellent durability for highly selective electrocatalytic NH3 synthesis. Research 2022, 2022, 9837012.
Hu, T.; Wang, C. H.; Wang, M. T.; Li, C. M.; Guo, C. X. Theoretical insights into superior nitrate reduction to ammonia performance of copper catalysts. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 14417–14427.
He, W. H.; Zhang, J.; Dieckhöfer, S.; Varhade, S.; Brix, A. C.; Lielpetere, A.; Seisel, S.; Junqueira, J. R. C.; Schuhmann, W. Splicing the active phases of copper/cobalt-based catalysts achieves high-rate tandem electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1129.
Wang, Y. H.; Xu, A. N.; Wang, Z. Y.; Huang, L. S.; Li, J.; Li, F. W.; Wicks, J.; Luo, M. C.; Nam, D. H.; Tan, C. S. et al. Enhanced nitrate-to-ammonia activity on copper-nickel alloys via tuning of intermediate adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5702–5708.
Sun, Y. F.; Dai, S. High-entropy materials for catalysis: A new frontier. Science Advances 2021, 7, 1–24.
Li, T. Y.; Yao, Y. G.; Huang, Z. N.; Xie, P. F.; Liu, Z. Y.; Yang, M. H.; Gao, J. L.; Zeng, K. Z.; Brozena, A. H.; Pastel, G. et al. Denary oxide nanoparticles as highly stable catalysts for methane combustion. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 62–70.
Yao, Y. G.; Liu, Z. Y.; Xie, P. F.; Huang, Z. N.; Li, T. Y.; Morris, D.; Finfrock, Z.; Zhou, J. H.; Jiao, M. L.; Gao, J. L. et al. Computationally aided, entropy-driven synthesis of highly efficient and durable multi-elemental alloy catalysts. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz0510.
Zhang, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S. C.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Y. W.; Huang, Z. D.; Ma, L. T.; Li, P.; Yang, Q.; Liang, G. J. et al. Efficient ammonia electrosynthesis and energy conversion through a Zn-nitrate battery by iron doping engineered nickel phosphide catalyst. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103872.
Mattarozzi, L.; Cattarin, S.; Comisso, N.; Guerriero, P.; Musiani, M.; Vázquez-Gómez, L.; Verlato, E. Electrochemical reduction of nitrate and nitrite in alkaline media at CuNi alloy electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 488–496.
Yao, Y. G.; Huang, Z. N.; Xie, P. F.; Lacey, S. D.; Jacob, R. J.; Xie, H.; Chen, F. J.; Nie, A. M.; Pu, T. C.; Rehwoldt, M. et al. Carbothermal shock synthesis of high-entropy-alloy nanoparticles. Science 2018, 359, 1489–1494.
Li, T. Y.; Yao, Y. G.; Ko, B. H.; Huang, Z. N.; Dong, Q.; Gao, J. L.; Chen, W.; Li, J. G.; Li, S. K.; Wang, X. Z. et al. Carbon-supported high-entropy oxide nanoparticles as stable electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010561.
Dong, Q.; Yao, Y. G.; Cheng, S. C.; Alexopoulos, K.; Gao, J. L.; Srinivas, S.; Wang, Y. F.; Pei, Y.; Zheng, C. L.; Brozena, A. H. et al. Programmable heating and quenching for efficient thermochemical synthesis. Nature 2022, 605, 470–476.
Liu, H. M.; Lang, X. Y.; Zhu, C.; Timoshenko, J.; Rüscher, M.; Bai, L. C.; Guijarro, N.; Yin, H. B.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. H. et al. Efficient electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia with copper-supported rhodium cluster and single-atom catalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202556.
Zhang, N.; Shang, J.; Deng, X.; Cai, L. J.; Long, R.; Xiong, Y. J.; Chai, Y. Governing interlayer strain in bismuth nanocrystals for efficient ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate reduction. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 4795–4804.
Deng, X. H.; Yang, Y. P.; Wang, L.; Fu, X. Z.; Luo, J. L. Metallic Co nanoarray catalyzes selective NH3 production from electrochemical nitrate reduction at current densities exceeding 2 A cm−2. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004523.
Zhao, X.; Hu, G. Z.; Tan, F.; Zhang, S. S.; Wang, X. Z.; Hu, X.; Kuklin, A. V.; Baryshnikov, G. V.; Ågren, H.; Zhou, X. H. et al. Copper confined in vesicle-like BCN cavities promotes electrochemical reduction of nitrate to ammonia in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 23675–23686.
Zhang, Y. Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. L.; Yin, L. F.; Crittenden, J. C. Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia on defective Au1Cu (111) single-atom alloys. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 310, 121346.
Lim, J.; Liu, C. Y.; Park, J.; Liu, Y. H.; Senftle, T. P.; Lee, S. W.; Hatzell, M. C. Structure sensitivity of Pd facets for enhanced electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 7568–7577.
Liu, Z.; Yang, Y. Y.; Shao, C. J.; Ji, Z. W.; Wang, Q. L.; Wang, S. J.; Guo, Y. P.; Demeestere, K.; Van Hulle, S. Ozonation of trace organic compounds in different municipal and industrial wastewaters: Kinetic-based prediction of removal efficiency and ozone dose requirements. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 123405.
Van Langevelde, P. H.; Katsounaros, I.; Koper, M. T. M. Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction for sustainable ammonia production. Joule 2021, 5, 290–294.
Zhang, D. D.; Li, M. Y.; Yang, Y. C.; Yu, H.; Xiao, F. S.; Mao, C. Z.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y. H.; Wang, Y. F.; Wu, B. et al. Nitrite and nitrate reduction drive sediment microbial nitrogen cycling in a eutrophic lake. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118637.
Liu, H. M.; Zhang, Y. D.; Luo, J. S. The removal of inevitable NOx species in catalysts and the selection of appropriate membrane for measuring electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis accurately. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 49, 51–58.
Niu, L. J.; Wang, D. D.; Xu, K.; Hao, W. C.; An, L.; Kang, Z. H.; Sun, Z. C. Tuning the performance of nitrogen reduction reaction by balancing the reactivity of N2 and the desorption of NH3. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4093–4099.
Liu, Y.; Huang, B. M.; Chen, X. F.; Tian, Z. Q.; Zhang, X. Y.; Tsiakaras, P.; Shen, P. K. Electrocatalytic production of ammonia: Biomimetic electrode-electrolyte design for efficient electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation under ambient conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 271, 118919.
Su, X. Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gu, S. Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. Operando spectroscopic identification of active sites in NiFe prussian blue analogues as electrocatalysts: Activation of oxygen atoms for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11286–11292.
Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Xie, L. S.; Ji, Y. Y.; Li, T. S.; Zhang, B.; Li, N.; Tang, B.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S. Y. et al. High-performance electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia under ambient conditions using a FeOOH nanorod catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 17312–17318.
Clark, C. A.; Reddy, C. P.; Xu, H.; Heck, K. N.; Luo, G. H.; Senftle, T. P.; Wong, M. S. Mechanistic insights into pH-controlled nitrite reduction to ammonia and hydrazine over rhodium. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 494–509.
Bajdich, M.; García-Mota, M.; Vojvodic, A.; Nørskov, J. K.; Bell, A. T. Theoretical investigation of the activity of cobalt oxides for the electrochemical oxidation of water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13521–13530.
Nørskov, J. K.; Rossmeisl, J.; Logadottir, A.; Lindqvist, L.; Kitchin, J. R.; Bligaard, T.; Jónsson, H. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17886–17892.
Xie, P. F.; Yao, Y. G.; Huang, Z. N.; Liu, Z. Y.; Zhang, J. L.; Li, T. Y.; Wang, G. F.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R.; Hu, L. B.; Wang, C. Highly efficient decomposition of ammonia using high-entropy alloy catalysts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4011.
Sun, Q. Q.; Li, Y. B.; Wang, J. F.; Cao, B. Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, C. S.; Zhang, G. C.; Wang, Z. L.; Zhao, C. Pulsed electrodeposition of well-ordered nanoporous Cu-doped Ni arrays promotes high-efficiency overall hydrazine splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 21084–21093.
Chang, I. C.; Chen, T. T.; Yang, M. H.; Chiu, H. T.; Lee, C. Y. Self-powered electrochemical deposition of Cu@Ni(OH)2 nanobelts for high performance pseudocapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10370–10374.
Steimecke, M.; Seiffarth, G.; Schneemann, C.; Oehler, F.; Förster, S.; Bron, M. Higher-valent nickel oxides with improved oxygen evolution activity and stability in alkaline media prepared by high-temperature treatment of Ni(OH)2. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 3595–3603.
Zhu, G. H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H. Y.; Wang, H. F.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, M.; Qiu, P. P.; Luo, W. Constructing structurally ordered high-entropy alloy nanoparticles on nitrogen-rich mesoporous carbon nanosheets for high-performance oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2110128.
Glasscott, M. W.; Pendergast, A. D.; Goines, S.; Bishop, A. R.; Hoang, A. T.; Renault, C.; Dick, J. E. Electrosynthesis of high-entropy metallic glass nanoparticles for designer, multi-functional electrocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2650.
Li, H. N.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Q. K.; Huang, S. D.; Lu, S. L.; Ma, P. M.; Dong, W. F.; Du, M. L. A novel synergistic confinement strategy for controlled synthesis of high-entropy alloy electrocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2637–2640.
Zhao, F. Z.; Liu, H. C.; Zhu, H. Y.; Jiang, X. Y.; Zhu, L. Q.; Li, W. P.; Chen, H. N. Amorphous/amorphous Ni-P/Ni(OH)2 heterostructure nanotubes for an efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10169–10179.
Liu, Z. J.; Zhao, Z. H.; Wang, Y. Y.; Dou, S.; Yan, D. F.; Liu, D. D.; Xia, Z. H.; Wang, S. Y. In situ exfoliated, edge-rich, oxygen-functionalized graphene from carbon fibers for oxygen electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606207.
Zhong, G.; Xu, S. M.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X. Z.; Hu, L. B. Rapid, universal surface engineering of carbon materials via microwave-induced carbothermal shock. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010968.
Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Wang, Y. A.; Yang, X. M.; Wu, D. J.; Zhu, Y. M.; Li, M. H.; Gu, M.; Shao, M. H. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia on low-cost ultrathin CoOx nanosheets. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 15135–15140.
Ye, S. H.; Chen, Z. D.; Zhang, G. K.; Chen, W. D.; Peng, C.; Yang, X. Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Li, Y. L.; Ren, X. Z.; Cao, H. Q. et al. Elucidating the activity, mechanism and application of selective electrosynthesis of ammonia from nitrate on cobalt phosphide. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 760–770.
Chen, D.; Zhang, S. C.; Bu, X. M.; Zhang, R.; Quan, Q.; Lai, Z. X.; Wang, W.; Meng, Y.; Yin, D.; Yip, S. et al. Synergistic modulation of local environment for electrochemical nitrate reduction via asymmetric vacancies and adjacent ion clusters. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107338.
Zhang, X.; Wang, C. H.; Guo, Y. M.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y. T.; Yu, Y. F. Cu clusters/TiO2−x with abundant oxygen vacancies for enhanced electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 6448–6453.
Wu, Z. Y.; Karamad, M.; Yong, X.; Huang, Q. Z.; Cullen, D. A.; Zhu, P.; Xia, C.; Xiao, Q. F.; Shakouri, M.; Chen, F. Y. et al. Electrochemical ammonia synthesis via nitrate reduction on Fe single atom catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2870.
Ye, T. N.; Park, S. W.; Lu, Y. F.; Li, J.; Sasase, M.; Kitano, M.; Hosono, H. Contribution of nitrogen vacancies to ammonia synthesis over metal nitride catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14374–14383.
Ren, H. T.; Jia, S. Y.; Zou, J. J.; Wu, S. H.; Han, X. A facile preparation of Ag2O/P25 photocatalyst for selective reduction of nitrate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176-177, 53–61.
Li, H. D.; Han, Y.; Zhao, H.; Qi, W. J.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Y. D.; Cai, W. W.; Li, S. X.; Lai, J. P.; Huang, B. L. et al. Fast site-to-site electron transfer of high-entropy alloy nanocatalyst driving redox electrocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5437.
Liu, J. X.; Richards, D.; Singh, N.; Goldsmith, B. R. Activity and selectivity trends in electrocatalytic nitrate reduction on transition metals. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 7052–7064.
Gao, Q.; Pillai, H. S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S. K.; Mu, Q. M.; Han, X.; Yan, Z. H.; Zhou, H.; He, Q.; Xin, H. L. et al. Breaking adsorption-energy scaling limitations of electrocatalytic nitrate reduction on intermetallic CuPd nanocubes by machine-learned insights. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2338.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1804255 and U22A20253) and the Key Research & Development and Promotion Projects in Henan Province (Nos. 222102520038 and 212102310060). The computational resources were provided by Shanxi Supercomputing Center of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_5402_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Electro-triggered Joule heating method to synthesize single-phase CuNi nano-alloy catalyst for efficient electrocatalytic nitrate reduction toward ammonia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Su, X. et al. Electro-triggered Joule heating method to synthesize single-phase CuNi nano-alloy catalyst for efficient electrocatalytic nitrate reduction toward ammonia. Nano Res. 16, 6632–6641 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5402-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5402-y