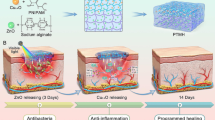
Abstract
Wound delayed healing or non-healing has seriously affected patients’ quality of life and has been a significant economic burden for public health systems worldwide. Excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) play important roles for impeding the process of wound healing. Herein, we report a hydrogel system containing low-valence-state molybdenum nanomaterials (Mo hydrogel) for wound healing by scavenging the detrimental ROS. Both in vitro and in vivo results demonstrate that the synthesized Mo hydrogel can accelerate wound healing, promote angiogenesis, and stimulate the expression of growth factors. Since the molybdenum is an essential element for the survival of all organisms, such novel Mo-hydrogel has the great potential to be clinically translated for wound healing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landén, N. X.; Li, D. Q.; Ståhle, M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885.
Malone, M.; Radzieta, M.; Schwarzer, S.; Jensen, S. O.; Lavery, L. A. Efficacy of a topical concentrated surfactant gel on microbial communities in non-healing diabetic foot ulcers with chronic biofilm infections: A proof-of-concept study. Int. Wound J. 2021, 18, 457–466.
Eming, S. A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr6.
Sanchez, M. C.; Lancel, S.; Boulanger, E.; Neviere, R. Targeting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in the treatment of impaired wound healing: A systematic review. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 98.
Dworzański, J.; Strycharz-Dudziak, M.; Kliszczewska, E.; Kiełczykowska, M.; Dworzańska, A.; Drop, B.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 infected with Epstein—Barr virus. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0230374.
Obrosova, I. G. Update on the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2003, 3, 439–445.
Rosenberger, D. C.; Blechschmidt, V.; Timmerman, H.; Wolff, A.; Treede, R. D. Challenges of neuropathic pain: Focus on diabetic neuropathy. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 589–624.
Wu, J. J. X.; Wang, X. Y.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z. P.; Li, S. R.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Qin, L.; Wei, H. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004–1076.
Zhang, R. F.; Fan, K. L.; Yan, X. Y. Nanozymes: Created by learning from nature. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1183–1200.
Lin, Y. H.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Catalytically active nanomaterials: A promising candidate for artificial enzymes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1097–1105.
Xu, J. G.; Cai, R.; Zhang, Y. G.; Mu, X. Y. Molybdenum disulfide-based materials with enzyme-like characteristics for biological applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111575.
Huang, X. Y.; Hu, D. W.; Zhao, F. J. Molybdenum: More than an essential element. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 1766–1774.
Thulabandu, V.; Chen, D. M.; Atit, R. P. Dermal fibroblast in cutaneous development and healing. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2018, 7, e307.
Niu, Y. M.; Li, Q.; Ding, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, C. M. Engineered delivery strategies for enhanced control of growth factor activities in wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 190–208.
Chen, Q. R.; Hou, H.; Wang, S. K.; Zhao, X.; Li, B. F. Effects of early enteral nutrition supplemented with collagen peptides on post-burn inflammatory responses in a mouse model. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1933–1941.
Begum, F.; Keni, R.; Ahuja, T. N.; Beegum, F.; Nandakumar, K.; Shenoy, R. R. Notch signaling: A possible therapeutic target and its role in diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2022, 16, 102542.
Kimball, A. S.; Joshi, A. D.; Boniakowski, A. E.; Schaller, M.; Chung, J.; Allen, R.; Bermick, J.; Carson, W. F. I.; Henke, P. K.; Maillard, I. et al. Notch regulates macrophage-mediated inflammation in diabetic wound healing. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 635.
Jia, C. L.; Lu, Y. Z.; Bi, B.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q. J.; Yang, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. J.; Zhu, N. W.; Liu, T. Y. Platelet-rich plasma ameliorates senescence-like phenotypes in a cellular photoaging model. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3152–3160.
Jiang, Y. H.; Zhao, W. T.; Xu, S. S.; Wei, J. J.; Lasaosa, F. L.; He, Y. Y.; Mao, H. L.; Bailo, R. M. B.; Kong, D. L.; Gu, Z. W. Bioinspired design of mannose-decorated globular lysine dendrimers promotes diabetic wound healing by orchestrating appropriate macrophage polarization. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121323.
Ma, T. F.; Zhai, X. Y.; Huang, Y. K.; Zhang, M. Z.; Zhao, X. L.; Du, Y. P.; Yan, C. H. A smart nanoplatform with photothermal antibacterial capability and antioxidant activity for chronic wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100033.
Lin, Y.; Liu, X. Y.; Liu, Z. X.; Xu, Y. H. Visible-light-driven photocatalysis-enhanced nanozyme of TiO2 nanotubes@MoS2 nanoflowers for efficient wound healing infected with multidrug-resistant bacteria. Small 2022, 17, 2201184.
Huang, H. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors: Recent advances. Sensors 2018, 18, 3249.
Da Rocha-Azevedo, B.; Ho, C. H.; Grinnell, F. PDGF stimulated dispersal of cell clusters and disruption of fibronectin matrix on three-dimensional collagen matrices requires matrix metalloproteinase-2. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 1098–1105.
Raziyeva, K.; Kim, Y.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Kassymbek, K.; Jimi, S.; Saparov, A. Immunology of acute and chronic wound healing. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 700.
Borena, B. M.; Martens, A.; Broeckx, S. Y.; Meyer, E.; Chiers, K.; Duchateau, L.; Spaas, J. H. Regenerative skin wound healing in mammals: State-of-the-art on growth factor and stem cell based treatments. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 1–23.
Komi, D. E. A.; Khomtchouk, K.; Santa Maria, P. L. A review of the contribution of mast cells in wound healing: Involved molecular and cellular mechanisms. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 298–312.
Fukushima, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Tanaka, H.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte growth factor activator: A proteinase linking tissue injury with repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3435.
Miyagi, H.; Thomasy, S. M.; Russell, P.; Murphy, C. J. The role of hepatocyte growth factor in corneal wound healing. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 166, 49–55.
Wang, X. J.; Banda, J.; Qi, H.; Chang, A. K.; Bwalya, C.; Chao, L.; Li, X. K. Scarless wound healing: Current insights from the perspectives of TGF-β, KGF-1, and KGF-2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022, 66, 26–37.
He, M.; Han, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y. H.; Qin, W. S.; Du, L. Z.; Zhao, C. Q. Effects of HGF and KGF gene silencing on vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in rat ultraviolet radiation-induced corneal neovascularization. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1888–1899.
Acknowledgements
We greatly acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82102190 and 81773347), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support (No. 20191805), and the Foundation of National Facility for Translational Medicine (Shanghai) (No. TMSK-2021-122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Jia, C., Gong, C. et al. A hydrogel system containing molybdenum-based nanomaterials for wound healing. Nano Res. 16, 5368–5375 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5255-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5255-9