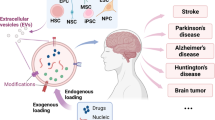
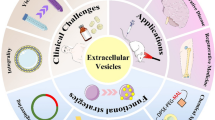
Abstract
Despite noteworthy technological progress and promising preclinical trials, brain disorders are still the leading causes of death globally. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), nano-/micro-sized membrane vesicles carrying bioactive molecules, are involved in cellular communication. Based on their unique properties, including superior biocompatibility, non-immunogenicity, and blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration, EVs can shield their cargos from immune clearance and transport them to specific site, which have attracted increasing interests as novel nanocarriers for brain disorders. However, considering the limitations of native EVs, such as poor encapsulation efficiency, inadequate targeting capability, uncontrolled drug release, and limited production, researchers bioengineer EVs to fully exploit the clinical potential. Herein, this review initially describes the basic properties, biogenesis, and uptake process of EVs from different subtypes. Then, we highlight the application of EVs derived from different sources for personalized therapy and novel strategies to construct bioengineered EVs for enhanced diagnosis and treatment of brain disorders. Besides, it also presents a systematic comparison between EVs and other brain-targeted nanocarriers. Finally, existing challenges and future perspectives of EVs have been discussed, hoping to bolster the research from benchtop to bedside.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feigin, V. L.; Vos, T.; Nichols, E.; Owolabi, M. O.; Carroll, W. M.; Dichgans, M.; Deuschl, G.; Parmar, P.; Brainin, M.; Murray, C. The global burden of neurological disorders: Translating evidence into policy. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 255–265.
Charabati, M.; Rabanel, J. M.; Ramassamy, C.; Prat, A. Overcoming the brain barriers: From immune cells to nanoparticles. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 42–54.
Cui, J. W.; Xu, Y. X.; Tu, H. Y.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, H. L.; Di, L. Q.; Wang, R. N. Gather wisdom to overcome barriers: Well-designed nano-drug delivery systems for treating gliomas. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1100–1125.
Croese, T.; Castellani, G.; Schwartz, M. Immune cell compartmentalization for brain surveillance and protection. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 1083–1092.
Wu, P. P.; Zhang, B.; Ocansey, D. K. W.; Xu, W. R.; Qian, H. Extracellular vesicles: A bright star of nanomedicine. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120467.
Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228.
Morad, G.; Carman, C. V.; Hagedorn, E. J.; Perlin, J. R.; Zon, L. I.; Mustafaoglu, N.; Park, T. E.; Ingber, D. E.; Daisy, C. C.; Moses, M. A. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles breach the intact blood-brain barrier via transcytosis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13853–13865.
Qiao, L.; Hu, S. Q.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Li, Z. H.; Vandergriff, A.; Cores, J.; Dinh, P. U.; Allen, T.; Shen, D. L. et al. Tumor cell-derived exosomes home to their cells of origin and can be used as Trojan horses to deliver cancer drugs. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3474–3487.
Wang, S. A.; Li, F.; Ye, T.; Wang, J. H.; Lyu, C. L.; Qing, S.; Ding, Z. W.; Gao, X. Y.; Jia, R. R.; Yu, D. et al. Macrophage-tumor chimeric exosomes accumulate in lymph node and tumor to activate the immune response and the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb6981.
Cong, M. H.; Tan, S. Y.; Li, S. M.; Gao, L. N.; Huang, L. Q.; Zhang, H. G.; Qiao, H. Z. Technology insight: Plant-derived vesicles-how far from the clinical biotherapeutics and therapeutic drug carriers? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 182, 114108.
Zhang, J. H.; Ji, C.; Zhang, H. B.; Shi, H.; Mao, F.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. R.; Wang, D. Q.; Pan, J. M.; Fang, X. J. et al. Engineered neutrophil-derived exosome-like vesicles for targeted cancer therapy. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj8207.
Ma, M. M.; Gao, N.; Sun, Y. H.; Du, X. B.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Redox-activated near-infrared-responsive polyoxometalates used for photothermal treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800320.
Zan, G. T.; Wu, Q. S. Biomimetic and bioinspired synthesis of nanomaterials/nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2099–2147.
Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V. S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977.
He, C. J.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Exosome theranostics: Biology and translational medicine. Theranostics 2018, 8, 237–255.
Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17.
Herrmann, I. K.; Wood, M. J. A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759.
Dinkla, S.; Van Cranenbroek, B.; Van Der Heijden, W. A.; He, X. H.; Wallbrecher, R.; Dumitriu, I. E.; Van Der Ven, A. J.; Bosman, G. J. C. G. M.; Koenen, H. J. P. M.; Joosten, I. Platelet microparticles inhibit IL-17 production by regulatory T cells through P-selectin. Blood 2016, 127, 1976–1986.
Bodega, G.; Alique, M.; Puebla, L.; Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R. M. Microvesicles: ROS scavengers and ROS producers. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1626654.
Gudbergsson, J. M.; Jønsson, K.; Simonsen, J. B.; Johnsen, K. B. Systematic review of targeted extracellular vesicles for drug delivery—Considerations on methodological and biological heterogeneity. J. Control. Release 2019, 306, 108–120.
Atkin-Smith, G. K.; Poon, I. K. H. Disassembly of the dying: Mechanisms and functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 151–162.
Chen, C. C.; Liu, L. N.; Ma, F. X.; Wong, C. W.; Guo, X. E.; Chacko, J. V.; Farhoodi, H. P.; Zhang, S. X.; Zimak, J.; Ségaliny, A. et al. Elucidation of exosome migration across the blood-brain barrier model in vitro. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2016, 9, 509–529.
Wang, J.; Tang, W.; Yang, M.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, F. F.; Tang, L.; Ma, X. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Z. Inflammatory tumor microenvironment responsive neutrophil exosomes-based drug delivery system for targeted glioma therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 273, 120784.
Cheng, H.; Fan, J. H.; Zhao, L. P.; Fan, G. L.; Zheng, R. R.; Qiu, X. Z.; Yu, X. Y.; Li, S. Y.; Zhang, X. Z. Chimeric peptide engineered exosomes for dual-stage light guided plasma membrane and nucleus targeted photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2019, 211, 14–24.
Saint-Pol, J.; Gosselet, F.; Duban-Deweer, S.; Pottiez, G.; Karamanos, Y. Targeting and crossing the blood-brain barrier with extracellular vesicles. Cells 2020, 9, 851.
Gao, X. F.; Zhang, Z. H.; Mashimo, T.; Shen, B.; Nyagilo, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. H.; Liu, Z. D.; Mulgaonkar, A.; Hu, X. L. et al. Gliomas interact with non-glioma brain cells via extracellular vesicles. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2489–2500.E5.
Holm, M. M.; Kaiser, J.; Schwab, M. E. Extracellular vesicles: Multimodal envoys in neural maintenance and repair. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 360–372.
Shi, M.; Liu, C. Q.; Cook, T. J.; Bullock, K. M.; Zhao, Y. C.; Ginghina, C.; Li, Y. F.; Aro, P.; Dator, R.; He, C. M. et al. Plasma exosomal α-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 639–650.
Gagliardi, D.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G. P.; Corti, S. Extracellular vesicles and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: From misfolded protein vehicles to promising clinical biomarkers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 561–572.
Lapointe, S.; Perry, A.; Butowski, N. A. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 2018, 392, 432–446.
Zhong, J.; Xia, B. Z.; Shan, S. B.; Zheng, A. P.; Zhang, S. W.; Chen, J. G.; Liang, X. J. High-quality milk exosomes as oral drug delivery system. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121126.
Han, L.; Lam, E. W. F.; Sun, Y. Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: Old stories, but new tales. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 59.
Pan, Z. W.; Zhao, R. R.; Li, B. Y.; Qi, Y. H.; Qiu, W.; Guo, Q. D.; Zhang, S. J.; Zhao, S. L.; Xu, H.; Li, M. et al. EWSR1-induced CircNEIL3 promotes glioma progression and exosome-mediated macrophage immunosuppressive polarization via stabilizing IGF2BP3. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 16.
Yekula, A.; Minciacchi, V. R.; Morello, M.; Shao, H. L.; Park, Y.; Zhang, X.; Muralidharan, K.; Freeman, M. R.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. et al. Large and small extracellular vesicles released by glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 9, 1689784.
Lang, F. M.; Hossain, A.; Gumin, J.; Momin, E. N.; Shimizu, Y.; Ledbetter, D.; Shahar, T.; Yamashita, S.; Kerrigan, B. P.; Fueyo, J. et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as natural biofactories for exosomes carrying MiR-124a in the treatment of gliomas. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 20, 380–390.
Zhu, Q. W.; Ling, X. Z.; Yang, Y. L.; Zhang, J. T.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Hu, G. W.; Chen, B.; Li, H. Y.; Wang, Y. et al. Embryonic stem cells-derived exosomes endowed with targeting properties as chemotherapeutics delivery vehicles for glioblastoma therapy. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801899.
Pegtel, D. M.; Peferoen, L.; Amor, S. Extracellular vesicles as modulators of cell-to-cell communication in the healthy and diseased brain. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130516.
Wang, J.; Ma, P.; Kim, D. H.; Liu, B. F.; Demirci, U. Towards microfluidic-based exosome isolation and detection for tumor therapy. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101066.
Zhang, Y.; Bi, J. Y.; Huang, J. Y.; Tang, Y. N.; Du, S. Y.; Li, P. Y. Exosome: A review of its classification, isolation techniques, storage, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 6917–6934.
Yang, D. B.; Zhang, W. H.; Zhang, H. Y.; Zhang, F. Q.; Chen, L. M.; Ma, L. X.; Larcher, L. M.; Chen, S. X.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Q. X. et al. Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation—Efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3684–3707.
Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P. R. M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A. B.; Borràs, F. E.; Buzas, E. I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J. et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066.
Sisirak, V.; Sally, B.; D’Agati, V.; Martinez-Ortiz, W.; Özçakar, Z. B.; David, J.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Yeste, A.; Panea, C.; Chida, A. S. et al. Digestion of chromatin in apoptotic cell microparticles prevents autoimmunity. Cell 2016, 166, 88–101.
Li, M. J.; Liao, L.; Tian, W. D. Extracellular vesicles derived from apoptotic cells: An essential link between death and regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 573511.
Jamjoom, A. A. B.; Rhodes, J.; Andrews, P. J. D.; Grant, S. G. N. The synapse in traumatic brain injury. Brain 2021, 144, 18–31.
Gill, J.; Mustapic, M.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Lange, R.; Gulyani, S.; Diehl, T.; Motamedi, V.; Osier, N.; Stern, R. A.; Kapogiannis, D. Higher exosomal tau, amyloid-beta 42 and IL-10 are associated with mild TBIs and chronic symptoms in military personnel. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1359–1366.
Manek, R.; Moghieb, A.; Yang, Z. H.; Kumar, D.; Kobessiy, F.; Sarkis, G. A.; Raghavan, V.; Wang, K. K. W. Protein biomarkers and neuroproteomics characterization of microvesicles/exosomes from human cerebrospinal fluid following traumatic brain injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6112–6128.
McBride, J. D.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; Guzman, W.; Candanedo, A.; Garcia-Contreras, M.; Badiavas, E. V. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived CD63+ exosomes transport Wnt3a exteriorly and enhance dermal fibroblast proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2017, 26, 1384–1398.
Upadhya, R.; Madhu, L. N.; Attaluri, S.; Gitaí, D. L. G.; Pinson, M. R.; Kodali, M.; Shetty, G.; Zanirati, G.; Kumar, S.; Shuai, B. et al. Extracellular vesicles from human IPSC-derived neural stem cells: MiRNA and protein signatures, and anti-inflammatory and neurogenic properties. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1809064.
Pan, W.; Xu, X. H.; Zhang, M.; Song, X. Y. Human urine-derived stem cell-derived exosomal MiR-21-5p promotes neurogenesis to attenuate Rett syndrome via the EPha4/TEK axis. Lab. Invest. 2021, 101, 824–836.
Tian, T.; Cao, L.; He, C.; Ye, Q.; Liang, R. Y.; You, W. Y.; Zhang, H. X.; Wu, J. H.; Ye, J. H.; Tannous, B. A. et al. Targeted delivery of neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6507–6521.
Dugger, B. N.; Dickson, D. W. Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a028035.
Reddy, P. H.; Oliver, D. M. A. Amyloid beta and phosphorylated tau-induced defective autophagy and mitophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Cells 2019, 8, 488.
Blauwendraat, C.; Heilbron, K.; Vallerga, C. L.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Von Coelln, R.; Pihlstrøm, L.; Simón-Sánchez, J.; Schulte, C.; Sharma, M.; Krohn, L. et al. Parkinson’s disease age at onset genome-wide association study: Defining heritability, genetic loci, and α-synuclein mechanisms. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 866–875.
Van Es, M. A.; Hardiman, O.; Chio, A.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Pasterkamp, R. J.; Veldink, J. H.; Van Den Berg, L. H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 2084–2098.
Sinha, M. S.; Ansell-Schultz, A.; Civitelli, L.; Hildesjö, C.; Larsson, M.; Lannfelt, L.; Ingelsson, M.; Hallbeck, M. Alzheimer’s disease pathology propagation by exosomes containing toxic amyloid-beta oligomers. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 41–56.
Ruan, Z.; Pathak, D.; Kalavai, S. V.; Yoshii-Kitahara, A.; Muraoka, S.; Bhatt, N.; Takamatsu-Yukawa, K.; Hu, J. Q.; Wang, Y. Z.; Hersh, S. et al. Alzheimer’s disease brain-derived extracellular vesicles spread tau pathology in interneurons. Brain 2021, 144, 288–309.
Agosta, F.; Libera, D. D.; Spinelli, E. G.; Finardi, A.; Canu, E.; Bergami, A.; Chiavetto, L. B.; Baronio, M.; Comi, G.; Martino, G. et al. Myeloid microvesicles in cerebrospinal fluid are associated with myelin damage and neuronal loss in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 813–825.
Stuendl, A.; Kunadt, M.; Kruse, N.; Bartels, C.; Moebius, W.; Danzer, K. M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Schneider, A. Induction of α-synuclein aggregate formation by CSF exosomes from patients with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain 2016, 139, 481–494.
Westergard, T.; Jensen, B. K.; Wen, X. M.; Cai, J. L.; Kropf, E.; Iacovitti, L.; Pasinelli, P.; Trotti, D. Cell-to-cell transmission of dipeptide repeat proteins linked to C9orf72-ALS/FTD. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 645–652.
Gratpain, V.; Mwema, A.; Labrak, Y.; Muccioli, G. G.; Van Pesch, V.; Des Rieux, A. Extracellular vesicles for the treatment of central nervous system diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 535–552.
Fiandaca, M. S.; Kapogiannis, D.; Mapstone, M.; Boxer, A.; Eitan, E.; Schwartz, J. B.; Abner, E. L.; Petersen, R. C.; Federoff, H. J.; Miller, B. L. et al. Identification of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease by a profile of pathogenic proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes: A case-control study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 600–607.E1.
Zhao, Z. H.; Chen, Z. T.; Zhou, R. L.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Q. Y.; Wang, Y. Z. Increased DJ-1 and α-synuclein in plasma neural-derived exosomes as potential markers for Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 10, 438.
Verderio, C.; Muzio, L.; Turola, E.; Bergami, A.; Novellino, L.; Ruffini, F.; Riganti, L.; Corradini, I.; Francolini, M.; Garzetti, L. et al. Myeloid microvesicles are a marker and therapeutic target for neuroinflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 610–624.
Minagar, A.; Jy, W.; Jimenez, J. J.; Sheremata, W. A.; Mauro, L. M.; Mao, W. W.; Horstman, L. L.; Ahn, Y. S. Elevated plasma endothelial microparticles in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2001, 56, 1319–1324.
Yuyama, K.; Sun, H.; Usuki, S.; Sakai, S.; Hanamatsu, H.; Mioka, T.; Kimura, N.; Okada, M.; Tahara, H.; Furukawa, J. I. et al. A potential function for neuronal exosomes: Sequestering intracerebral amyloid-β peptide. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 84–88.
Trotta, T.; Panaro, M. A.; Cianciulli, A.; Mori, G.; Di Benedetto, A.; Porro, C. Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease: A double-edged sword. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 148, 184–192.
Calabria, E.; Scambi, I.; Bonafede, R.; Schiaffino, L.; Peroni, D.; Potrich, V.; Capelli, C.; Schena, F.; Mariotti, R. ASCs-exosomes recover coupling efficiency and mitochondrial membrane potential in an in vitro model of ALS. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1070.
Kim, J.; Inoue, K.; Ishii, J.; Vanti, W. B.; Voronov, S. V.; Murchison, E.; Hannon, G.; Abeliovich, A. A microRNA feedback circuit in midbrain dopamine neurons. Science 2007, 317, 1220–1224.
Zhang, Z. G.; Chopp, M. Exosomes in stroke pathogenesis and therapy. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 1190–1197.
Zhang, Z. G.; Buller, B.; Chopp, M. Exosomes—Beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 193–203.
Witwer, K. W.; Van Balkom, B. W. M.; Bruno, S.; Choo, A.; Dominici, M.; Gimona, M.; Hill, A. F.; De Kleijn, D.; Koh, M.; Lai, R. C. et al. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1609206.
Betzer, O.; Perets, N.; Angel, A.; Motiei, M.; Sadan, T.; Yadid, G.; Offen, D.; Popovtzer, R. In vivo neuroimaging of exosomes using gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10883–10893.
Perets, N.; Betzer, O.; Shapira, R.; Brenstein, S.; Angel, A.; Sadan, T.; Ashery, U.; Popovtzer, R.; Offen, D. Golden exosomes selectively target brain pathologies in neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disorders. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3422–3431.
Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, W. H.; Zhao, R. C.; Lu, Z. G.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y. Y.; Wang, J. Z.; Hao, Q. L.; Wang, J. W. et al. Intranasal administration of self-oriented nanocarriers based on therapeutic exosomes for synergistic treatment of Parkinson’s disease. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 869–884.
Liu, C. P.; Wang, Y. C.; Li, L. M.; He, D. Y.; Chi, J. X.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y. X.; Zhao, Y. X.; Zhang, S. H.; Wang, L. et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles and their mimetics for cancer immunotherapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 679–698.
Zhu, L. Y.; Oh, J. M.; Gangadaran, P.; Kalimuthu, S.; Baek, S. H.; Jeong, S. Y.; Lee, S. W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B. C. Targeting and therapy of glioblastoma in a mouse model using exosomes derived from natural killer cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 824.
Xing, Y.; Sun, X.; Dou, Y. M.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y. M.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y. H. The immuno-modulation effect of macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles in chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 785728.
Huo, Q. H.; Shi, Y. J.; Qi, Y.; Huang, L. J.; Sui, H. J.; Zhao, L. Biomimetic silibinin-loaded macrophage-derived exosomes induce dual inhibition of Aβ aggregation and astrocyte activation to alleviate cognitive impairment in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 129, 112365.
Jiang, H. L.; Zhou, L.; Shen, N.; Ning, X. H.; Wu, D. Q.; Jiang, K. L.; Huang, X. S. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes and their key molecule LncRNA HOTTIP suppress head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by upregulating the TLR5/NF-ΚB pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 183.
Giese, M. A.; Hind, L. E.; Huttenlocher, A. Neutrophil plasticity in the tumor microenvironment. Blood 2019, 133, 2159–2167.
Grozdanov, V.; Bousset, L.; Hoffmeister, M.; Bliederhaeuser, C.; Meier, C.; Madiona, K.; Pieri, L.; Kiechle, M.; McLean, P. J.; Kassubek, J. et al. Increased immune activation by pathologic α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 593–606.
Lindenbergh, M. F. S.; Wubbolts, R.; Borg, E. G. F.; Van’ T Veld, E. M.; Boes, M.; Stoorvogel, W. Dendritic cells release exosomes together with phagocytosed pathogen; potential implications for the role of exosomes in antigen presentation. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1798606.
Liu, L. Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, R. Y.; Ji, W. H.; Shi, Z. Y.; Shen, J.; Ma, G. H.; Zhang, X. Targeted exosome coating gene-chem nanocomplex as “nnnocavenngrr” for clearing α-synuclein and immune activation of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, aba3967.
Qiu, Y. F.; Yang, Y.; Yang, R. Y.; Liu, C. X.; Hsu, J. M.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, L. L.; Wei, Y. K.; Li, C. W.; Yu, D. H. et al. Activated T cell-derived exosomal PD-1 attenuates PD-L1-induced immune dysfunction in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4992–5001.
Mashouri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Aref, A. R.; Ahadi, A. M.; Molaei, F.; Alahari, S. K. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 75.
Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S. D.; Zhou, J. H.; Tan, Y. L.; Song, J.; Xing, H. K.; Yi, K. K.; Zhan, Q. et al. Glioma-derived exosomes hijack the blood-brain barrier to facilitate nanocapsule delivery via LCN2. J. Control. Release 2022, 345, 537–548.
Dou, G.; Tian, R.; Liu, X. M.; Yuan, P. Y.; Ye, Q. W.; Liu, J.; Liu, S. Y.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Z. H.; Chen, X. et al. Chimeric apoptotic bodies functionalized with natural membrane and modular delivery system for inflammation modulation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba2987.
Wang, Y. L.; Pang, J. Y.; Wang, Q. Y.; Yan, L. C.; Wang, L. T.; Xing, Z.; Wang, C. M.; Zhang, J. F.; Dong, L. Delivering antisense oligonucleotides across the blood-brain barrier by tumor cell-derived small apoptotic bodies. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004929.
Jang, Y.; Kim, H.; Yoon, S.; Lee, H.; Hwang, J.; Jung, J.; Chang, J. H.; Choi, J.; Kim, H. Exosome-based photoacoustic imaging guided photodynamic and immunotherapy for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 293–304.
Zhou, X.; Miao, Y. Q.; Wang, Y.; He, S. F.; Guo, L. M.; Mao, J. S.; Chen, M. S.; Yang, Y. T.; Zhang, X. X.; Gan, Y. Tumour-derived extracellular vesicle membrane hybrid lipid nanovesicles enhance SiRNA delivery by tumour-homing and intracellular freeway transportation. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12198.
Kim, D. K.; Rhee, W. J. Antioxidative effects of carrot-derived nanovesicles in cardiomyoblast and neuroblastoma cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1203.
Logozzi, M.; Di Raimo, R.; Mizzoni, D.; Fais, S. Nanovesicles from organic agriculture-derived fruits and vegetables: Characterization and functional antioxidant content. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8170.
Zeng, L. P.; Wang, H. Y.; Shi, W. H.; Chen, L. F.; Chen, T. T.; Chen, G. Y.; Wang, W. S.; Lan, J. M.; Huang, Z. H.; Zhang, J. et al. Aloe derived nanovesicle as a functional carrier for indocyanine green encapsulation and phototherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 439.
Zhao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, J. Z.; Ye, D.; Mu, S.; Yang, X. D.; Zhang, W. D.; Ma, B. L. Natural nano-drug delivery system in Coptidis rhizoma extract with modified berberine hydrochloride pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 6297–6311.
Zhai, K. F.; Duan, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S. Y.; Khan, G. J.; Wang, M. T.; Zhang, Y. H.; Thakur, K.; Fang, X. M.; Wu, C. et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption and traumatic brain injury via attenuating macrophages derived exosomes MiR-21 release. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3493–3507.
Xu, X. H.; Yuan, T. J.; Dad, H. A.; Shi, M. Y.; Huang, Y. Y.; Jiang, Z. H.; Peng, L. H. Plant exosomes as novel nanoplatforms for microRNA transfer stimulate neural differentiation of stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 8151–8159.
Han, X.; Wei, Q.; Lv, Y.; Weng, L.; Huang, H. Y.; Wei, Q. Y.; Li, M. Y.; Mao, Y. J.; Hua, D.; Cai, X. T. et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles potentiate immune checkpoint antibody efficacy by reprogramming the cold tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 327–340.
Long-Smith, C.; O’Riordan, K. J.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T. G.; Cryan, J. F. Microbiota-gut-brain axis: New therapeutic opportunities. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 477–502.
Cui, G. H.; Guo, H. D.; Li, H.; Zhai, Y.; Gong, Z. B.; Wu, J.; Liu, J. S.; Dong, Y. R.; Hou, S. X.; Liu, J. R. RVG-modified exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells rescue memory deficits by regulating inflammatory responses in a mouse model of Alzheimer’ s disease. Immun. Ageing 2019, 16, 10.
Guo, S. W.; Perets, N.; Betzer, O.; Ben-Shaul, S.; Sheinin, A.; Michaelevski, I.; Popovtzer, R.; Offen, D.; Levenberg, S. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes loaded with phosphatase and tensin homolog SiRNA repairs complete spinal cord injury. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10015–10028.
Dar, G. H.; Mendes, C. C.; Kuan, W. L.; Speciale, A. A.; Conceição, M.; Görgens, A.; Uliyakina, I.; Lobo, M. J.; Lim, W. F.; El Andaloussi, S. et al. GAPDH controls extracellular vesicle biogenesis and enhances the therapeutic potential of EV mediated SiRNA delivery to the brain. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6666.
Jahangard, Y.; Monfared, H.; Moradi, A.; Zare, M.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J.; Mowla, S. J. Therapeutic effects of transplanted exosomes containing MiR-29b to a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 564.
Haney, M. J.; Klyachko, N. L.; Zhao, Y. L.; Gupta, R.; Plotnikova, E. G.; He, Z. J.; Patel, T.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A. V. et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 18–30.
Wang, H.; Sui, H. J.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, Y. B.; Shi, Y. J.; Liang, J.; Zhao, L. Curcumin-primed exosomes potently ameliorate cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting hyperphosphorylation of the tau protein through the AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7481–7496.
Yuan, D. F.; Zhao, Y. L.; Banks, W. A.; Bullock, K. M.; Haney, M.; Batrakova, E.; Kabanov, A. V. Macrophage exosomes as natural nanocarriers for protein delivery to inflamed brain. Biomaterials 2017, 142, 1–12.
Wu, T. T.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z. H. Engineering macrophage exosome disguised biodegradable nanoplatform for enhanced sonodynamic therapy of glioblastoma. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2110364.
Izco, M.; Blesa, J.; Schleef, M.; Schmeer, M.; Porcari, R.; Al-Shawi, R.; Ellmerich, S.; De Toro, M.; Gardiner, C.; Seow, Y. et al. Systemic exosomal delivery of ShRNA minicircles prevents parkinsonian pathology. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 2111–2122.
Zhang, C.; Song, J.; Lou, L.; Qi, X. J.; Zhao, L.; Fan, B.; Sun, G. Z.; Lv, Z. Q.; Fan, Z. Z.; Jiao, B. H. et al. Doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticle coated with endothelial cells-derived exosomes for immunogenic chemotherapy of glioblastoma. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 6, e10203.
Tian, T.; Liang, R. Y.; Erel-Akbaba, G.; Saad, L.; Obeid, P. J.; Gao, J.; Chiocca, E. A.; Weissleder, R.; Tannous, B. A. Immune checkpoint inhibition in GBM primed with radiation by engineered extracellular vesicles. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1940–1953.
Didiot, M. C.; Hall, L. M.; Coles, A. H.; Haraszti, R. A.; Godinho, B. M. D. C.; Chase, K.; Sapp, E.; Ly, S.; Alterman, J. F.; Hassler, M. R. et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of hydrophobically modified SiRNA for huntingtin MRNA silencing. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1836–1847.
Qu, M. K.; Lin, Q.; Huang, L. Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L. Y.; He, S. S.; Fu, Y.; Yang, S. Y.; Zhang, Z. R.; Zhang, L. et al. Dopamine-loaded blood exosomes targeted to brain for better treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Control. Release 2018, 287, 156–166.
Qi, Y.; Guo, L.; Jiang, Y. B.; Shi, Y. J.; Sui, H. J.; Zhao, L. Brain delivery of quercetin-loaded exosomes improved cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting phosphorylated tau-mediated neurofibrillary tangles. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 745–755.
Kojima, R.; Bojar, D.; Rizzi, G.; Hamri, G. C. E.; El-Baba, M. D.; Saxena, P.; Ausländer, S.; Tan, K. R.; Fussenegger, M. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1305.
Niu, W. B.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, X. J.; Zhu, J. Q.; Li, J. H.; Liang, X. M.; Peng, Y. M.; Wu, C. T.; Lu, R. J.; Pan, Y. et al. A biomimetic drug delivery system by integrating grapefruit extracellular vesicles and doxorubicin-loaded heparin-based nanoparticles for glioma therapy. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1484–1492.
You, J. Y.; Kang, S. J.; Rhee, W. J. Isolation of cabbage exosome-like nanovesicles and investigation of their biological activities in human cells. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4321–4332.
Lee, R.; Ko, H. J.; Kim, K.; Sohn, Y.; Min, S. Y.; Kim, J. A.; Na, D.; Yeon, J. H. Anti-melanogenic effects of extracellular vesicles derived from plant leaves and stems in mouse melanoma cells and human healthy skin. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1703480.
Yang, M.; Liu, X. Y.; Luo, Q. Q.; Xu, L. L.; Chen, F. X. An efficient method to isolate lemon derived extracellular vesicles for gastric cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 100.
Yang, M.; Luo, Q. Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, F. X. Bitter melon derived extracellular vesicles enhance the therapeutic effects and reduce the drug resistance of 5-fluorouracil on oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 259.
Chen, X. Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J. J. Exosome-like nanoparticles from ginger rhizomes inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2019, 16, 2690–2699.
Sundaram, K.; Miller, D. P.; Kumar, A.; Teng, Y.; Sayed, M.; Mu, J. Y.; Lei, C.; Sriwastva, M. K.; Zhang, L. F.; Yan, J. et al. Plant-derived exosomal nanoparticles inhibit pathogenicity of Porphyromonas gingivalis. iScience 2020, 23, 100869.
Liu, B. L.; Lu, Y. Z.; Chen, X. Y.; Muthuraj, P. G.; Li, X. Z.; Pattabiraman, M.; Zempleni, J.; Kachman, S. D.; Natarajan, S. K.; Yu, J. J. Protective role of shiitake mushroom-derived exosome-like nanoparticles in D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury in mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 477.
Liu, B. L.; Li, X. Z.; Yu, H.; Shi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Alvarez, S.; Naldrett, M. J.; Kachman, S. D.; Ro, S. H.; Sun, X. H. et al. Therapeutic potential of garlic chive-derived vesicle-like nanoparticles in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory diseases. Theranostics 2021, 11, 9311–9330.
Cao, M.; Yan, H. J.; Han, X.; Weng, L.; Wei, Q.; Sun, X. Y.; Lu, W. G.; Wei, Q. Y.; Ye, J.; Cai, X. T. et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles alter macrophage polarization to inhibit melanoma growth. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 326.
Zhang, L.; He, F. J.; Gao, L. N.; Cong, M. H.; Sun, J.; Xu, J. L.; Wang, Y. T.; Hu, Y.; Asghar, S.; Hu, L. H. et al. Engineering exosome-like nanovesicles derived from Asparagus cochinchinensis can inhibit the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells with better safety profile. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 1575–1586.
Tong, L. J.; Hao, H. N.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y. Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, Q. Q.; Liu, T. J.; Gong, P. M.; Zhang, L. W.; Cao, F. F. et al. Milk-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate ulcerative colitis by regulating the gut immunity and reshaping the gut microbiota. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8570–8586.
Lei, J. H.; Jiang, X. Y.; Li, W.; Ren, J.; Wang, D. T.; Ji, Z. J.; Wu, Z. M.; Cheng, F.; Cai, Y. S.; Yu, Z. R. et al. Exosomes from antler stem cells alleviate mesenchymal stem cell senescence and osteoarthritis. Protein Cell 2022, 13, 220–226.
Chen, X. Y.; Liu, B. L.; Li, X. Z.; An, T. T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.; Wu-Smart, J.; Alvarez, S.; Naldrett, M. J.; Eudy, J. et al. Identification of anti-inflammatory vesicle-like nanoparticles in honey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12069.
Park, K. S.; Svennerholm, K.; Crescitelli, R.; Lässer, C.; Gribonika, I.; Lötvall, J. Synthetic bacterial vesicles combined with tumour extracellular vesicles as cancer immunotherapy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12120.
Haraszti, R. A.; Miller, R.; Didiot, M. C.; Biscans, A.; Alterman, J. F.; Hassler, M. R.; Roux, L.; Echeverria, D.; Sapp, E.; DiFiglia, M. et al. Optimized cholesterol-SiRNA chemistry improves productive loading onto extracellular vesicles. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1973–1982.
Lunavat, T. R.; Jang, S. C.; Nilsson, L.; Park, H. T.; Repiska, G.; Lässer, C.; Nilsson, J. A.; Gho, Y. S.; Lötvall, J. RNAi delivery by exosome-mimetic nanovesicles—Implications for targeting c-Myc in cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 231–238.
Cooper, J. M.; Wiklander, P. B. O.; Nordin, J. Z.; Al-Shawi, R.; Wood, M. J.; Vithlani, M.; Schapira, A. H. V.; Simons, J. P.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Alvarez-Erviti, L. Systemic exosomal SiRNA delivery reduced alpha-synuclein aggregates in brains of transgenic mice. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1476–1485.
Wang, K.; Kumar, U. S.; Sadeghipour, N.; Massoud, T. F.; Paulmurugan, R. A microfluidics-based scalable approach to generate extracellular vesicles with enhanced therapeutic MicroRNA loading for intranasal delivery to mouse glioblastomas. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18327–18346.
Yang, Z. G.; Shi, J. F.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y. F.; Sun, J. Y.; Liu, T. Z.; Zhao, Y. R.; Zhao, X. T.; Wang, X. M.; Ma, Y. F. et al. Large-scale generation of functional MRNA-encapsulating exosomes via cellular nanoporation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 69–83.
Lai, C. P.; Mardini, O.; Ericsson, M.; Prabhakar, S.; Maguire, C. A.; Chen, J. W.; Tannous, B. A.; Breakefield, X. O. Dynamic biodistribution of extracellular vesicles in vivo using a multimodal imaging reporter. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 483–494.
Liu, Y.; Huang, R. Q.; Han, L.; Ke, W. L.; Shao, K.; Ye, L. Y.; Lou, J. N.; Jiang, C. Brain-targeting gene delivery and cellular internalization mechanisms for modified rabies virus glycoprotein RVG29 nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4195–4202.
Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H. F.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M. J. A. Delivery of SiRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345.
Yu, X. Y.; Bai, Y.; Han, B.; Ju, M. Z.; Tang, T. C.; Shen, L.; Li, M. Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, G. K. et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of CircDYM alleviates CUS-induced depressive-like behaviours. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12185.
Kim, G.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Byun, J. W.; Hwang, D. W.; Lee, M. Systemic delivery of MicroRNA-21 antisense oligonucleotides to the brain using T7-peptide decorated exosomes. J. Control. Release 2020, 317, 273–281.
Huang, R. X.; Rofstad, E. K. Integrins as therapeutic targets in the organ-specific metastasis of human malignant melanoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 92.
Mead, B. P.; Mastorakos, P.; Suk, J. S.; Klibanov, A. L.; Hanes, J.; Price, R. J. Targeted gene transfer to the brain via the delivery of brain-penetrating DNA nanoparticles with focused ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2016, 223, 109–117.
Du, J. B.; Wan, Z.; Wang, C.; Lu, F.; Wei, M. Y.; Wang, D. S.; Hao, Q. Designer exosomes for targeted and efficient ferroptosis induction in cancer via chemo-photodynamic therapy. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8185–8196.
Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V. S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S. J.; Ruivo, C. F.; Melo, S. A.; Lee, J. J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503.
Chen, Y. D.; Wang, L. X.; Zheng, M. F.; Zhu, C. D.; Wang, G. S.; Xia, Y. Q.; Blumenthal, E. J.; Mao, W. J.; Wan, Y. Engineered extracellular vesicles for concurrent anti-PDL1 immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 9, 251–265.
Li, L.; Yang, W. W.; Xu, D. G. Stimuli-responsive nanoscale drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 423–433.
Chen, M. C.; Lin, Z. W.; Ling, M. H. Near-infrared light-activatable microneedle system for treating superficial tumors by combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 93–101.
Donohoe, C.; Senge, M. O.; Arnaut, L. G.; Gomes-Da-Silva, L. C. Cell death in photodynamic therapy: From oxidative stress to anti-tumor immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1872, 188308.
Chang, M. Y.; Hou, Z. Y.; Wang, M.; Li, C. X.; Lin, J. Recent advances in hyperthermia therapy-based synergistic immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004788.
Chen, Q.; Xu, L. G.; Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Photothermal therapy with immune-adjuvant nanoparticles together with checkpoint blockade for effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13193.
Zhang, W.; Yu, Z. L.; Wu, M.; Ren, J. G.; Xia, H. F.; Sa, G. L.; Zhu, J. Y.; Pang, D. W.; Zhao, Y. F.; Chen, G. Magnetic and folate functionalization enables rapid isolation and enhanced tumor-targeting of cell-derived microvesicles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 277–290.
Jia, G.; Han, Y.; An, Y. L.; Ding, Y. N.; He, C.; Wang, X. H.; Tang, Q. S. NRP-1 targeted and cargo-loaded exosomes facilitate simultaneous imaging and therapy of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2018, 178, 302–316.
Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Dong, Y.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y. C.; Soto, F.; Ma, P.; Feng, X. J.; Du, W.; Liu, B. F. Designer exosomes enabling tumor targeted efficient chemo/gene/photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121056.
Bai, L. M.; Liu, Y. C.; Guo, K. L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q. H.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. B. Ultrasound facilitates naturally equipped exosomes derived from macrophages and blood serum for orthotopic glioma treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14576–14587.
Ji, W. H.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhao, R. C.; Zhang, X. Nature-inspired dynamic gene-loaded nanoassemblies for the treatment of brain diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 180, 114029.
Keith, B.; Simon, M. C. Hypoxia-inducible factors, stem cells, and cancer. Cell 2007, 129, 465–472.
Filipczak, N.; Joshi, U.; Attia, S. A.; Fridman, I. B.; Cohen, S.; Konry, T.; Torchilin, V. Hypoxia-sensitive drug delivery to tumors. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 431–442.
Wang, X. J.; Ding, H.; Li, Z. Y.; Peng, Y. N.; Tan, H.; Wang, C. L.; Huang, G. D.; Li, W. P.; Ma, G. H.; Wei, W. Exploration and functionalization of M1-macrophage extracellular vesicles for effective accumulation in glioblastoma and strong synergistic therapeutic effects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 74.
Niu, B. Y.; Liao, K. X.; Zhou, Y. X.; Wen, T.; Quan, G. L.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. B. Application of glutathione depletion in cancer therapy: Enhanced ROS-based therapy, ferroptosis, and chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121110.
Xiao, T. T.; He, M. J.; Xu, F.; Fan, Y.; Jia, B. Y.; Shen, M. W.; Wang, H.; Shi, X. Y. Macrophage membrane-camouflaged responsive polymer nanogels enable magnetic resonance imaging-guided chemotherapy/chemodynamic therapy of orthotopic glioma. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20377–20390.
Li, M.; Li, S. Y.; Zhou, H.; Tang, X. F.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tian, Z. G.; Zhou, X. C.; Yang, X. Z.; Wang, Y. C. Chemotaxis-driven delivery of nano-pathogenoids for complete eradication of tumors post-phototherapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1126.
D’Souza, A.; Dave, K. M.; Stetler, R. A.; Manickam, D. S. Targeting the blood-brain barrier for the delivery of stroke therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 332–351.
Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Yang, J. Y.; Zhao, Z. N.; Tan, K. Y.; Tang, S. W.; Wan, M. M.; Mao, C. Engineered exosomes with independent module/cascading function for therapy of Parkinson’s disease by multistep targeting and multistage intervention method. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201406.
Li, Y. J.; Wu, J. Y.; Liu, J. H.; Xu, W. J.; Qiu, X. H.; Huang, S.; Hu, X. B.; Xiang, D. X. Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 242.
Wu, J. Y.; Li, Y. J.; Hu, X. B.; Huang, S.; Luo, S. L.; Tang, T. T.; Xiang, D. X. Exosomes and biomimetic nanovesicles-mediated anti-glioblastoma therapy: A head-to-head comparison. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 510–521.
Kim, H. Y.; Bhang, S. H. Stem cell-engineered nanovesicles exert proangiogenic and neuroprotective effects. Materials 2021, 14, 1078.
Lee, J. R.; Kyung, J. W.; Kumar, H.; Kwon, S. P.; Song, S. Y.; Han, I. B.; Kim, B. S. Targeted delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-derived nanovesicles for spinal cord injury treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4185.
Yu, W. Y.; Yin, N.; Yang, Y.; Xuan, C. P.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Zhang, K. X.; Liu, J. J.; Shi, J. J. Rescuing ischemic stroke by biomimetic nanovesicles through accelerated thrombolysis and sequential ischemia-reperfusion protection. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 625–640.
Li, M. X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. P.; Liu, T. T.; Gu, Z. X.; Zhang, J. Q.; Gu, X. C.; Teng, G. J.; Yang, F.; Gu, N. Platelet bio-nanobubbles as microvascular recanalization nanoformulation for acute ischemic stroke lesion theranostics. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4870–4883.
Dong, X. Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, C. Y.; Hayworth, C.; Frank, M.; Wang, Z. J. Neutrophil membrane-derived nanovesicles alleviate inflammation to protect mouse brain injury from ischemic stroke. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1272–1283.
Meng, L. T.; Wang, C. R.; Lu, Y. P.; Sheng, G.; Yang, L.; Wu, Z. Y.; Xu, H.; Han, C.; Lu, Y. M.; Han, F. Targeted regulation of blood-brain barrier for enhanced therapeutic efficiency of hypoxia-modifier nanoparticles and immune checkpoint blockade antibodies for glioblastoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11657–11671.
Fernandes, M.; Lopes, I.; Magalhães, L.; Sárria, M. P.; Machado, R.; Sousa, J. C.; Botelho, C.; Teixeira, J.; Gomes, A. C. Novel concept of exosome-like liposomes for the treatment of Alzheimer’ s disease. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 130–143.
Wu, J. Y.; Li, Y. J.; Wang, J. M.; Hu, X. B.; Huang, S.; Luo, S. L.; Xiang, D. X. Multifunctional exosome-mimetics for targeted anti-glioblastoma therapy by manipulating protein corona. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 405.
Shende, P.; Trivedi, R. Biofluidic material-based carriers: Potential systems for crossing cellular barriers. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 858–870.
Tian, X.; Fan, T. J.; Zhao, W. T.; Abbas, G.; Han, B.; Zhang, K.; Li, N.; Liu, N.; Liang, W. Y.; Huang, H. et al. Recent advances in the development of nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2854–2869.
Wang, J.; Zhu, M. T.; Nie, G. J. Biomembrane-based nanostructures for cancer targeting and therapy: From synthetic liposomes to natural biomembranes and membrane-vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113974.
Gregoriadis, G.; Ryman, B. E. Liposomes as carriers of enzymes or drugs: A new approach to the treatment of storage diseases. Biochem. J. 1971, 124, 58P.
Khan, A. R.; Yang, X. Y.; Fu, M. F.; Zhai, G. X. Recent progress of drug nanoformulations targeting to brain. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 37–64.
Gabizon, A.; Shmeeda, H.; Tahover, E.; Kornev, G.; Patil, Y.; Amitay, Y.; Ohana, P.; Sapir, E.; Zalipsky, S. Development of Promitil®, a lipidic prodrug of mitomycin c in PEGylated liposomes: From bench to bedside. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154–155, 13–26.
Zheng, Z. N.; Zhang, J. X.; Jiang, J. Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, W. Y.; Mo, X. P.; Kang, X. J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, Y. Z. Remodeling tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for glioma therapy using multi-targeting liposomal codelivery. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000207.
Skrott, Z.; Mistrik, M.; Andersen, K. K.; Friis, S.; Majera, D.; Gursky, J.; Ozdian, T.; Bartkova, J.; Turi, Z.; Moudry, P. et al. Alcohol-abuse drug disulfiram targets cancer via P97 segregase adaptor NPL4. Nature 2017, 552, 194–199.
Hou, J.; Yang, X.; Li, S. Y.; Cheng, Z. K.; Wang, Y. H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. J.; Luo, M.; Ren, H. W. et al. Accessing neuroinflammation sites: Monocyte/neutrophil-mediated drug delivery for cerebral ischemia. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau8301.
Lu, L.; Zhao, X. J.; Fu, T. W.; Li, K.; He, Y.; Luo, Z.; Dai, L. L.; Zeng, R.; Cai, K. Y. An iRGD-conjugated prodrug micelle with blood-brain-barrier penetrability for anti-glioma therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 230, 119666.
Lu, Y. F.; Li, C.; Chen, Q. J.; Liu, P. X.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X. L.; Zhang, Y. J.; Zhou, W. X.; Liang, D. H. et al. Microthrombus-targeting micelles for neurovascular remodeling and enhanced microcirculatory perfusion in acute ischemic stroke. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808361.
Israel, L. L.; Braubach, O.; Galstyan, A.; Chiechi, A.; Shatalova, E. S.; Grodzinski, Z.; Ding, H.; Black, K. L.; Ljubimova, J. Y.; Holler, E. A combination of tri-leucine and angiopep-2 drives a polyanionic polymalic acid nanodrug platform across the blood-brain barrier. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1253–1271.
Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, G. Y.; Choi, J. S.; Lee, M. Brain gene delivery using histidine and arginine-modified dendrimers for ischemic stroke therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 907–919.
Lugasi, L.; Grinberg, I.; Rudnick-Glick, S.; Okun, E.; Einat, H.; Margel, S. Designed proteinoid polymers and nanoparticles encapsulating risperidone for enhanced antipsychotic activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 149.
Mukherjee, A.; Waters, A. K.; Kalyan, P.; Achrol, A. S.; Kesari, S.; Yenugonda, V. M. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a next-generation drug delivery platform: State of the art, emerging technologies, and perspectives. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1937–1952.
Tang, F. Q.; Li, L. L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534.
Spinelli, A.; Girelli, M.; Arosio, D.; Polito, L.; Podini, P.; Martino, G.; Seneci, P.; Muzio, L.; Menegon, A. Intracisternal delivery of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles results in high brain penetrance and long-lasting stability. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 49.
Vangijzegem, T.; Stanicki, D.; Laurent, S. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery: Applications and characteristics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 69–78.
Chen, D. Q.; Dougherty, C. A.; Zhu, K. C.; Hong, H. Theranostic applications of carbon nanomaterials in cancer: Focus on imaging and cargo delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 210, 230–245.
Anfray, C.; Komaty, S.; Corroyer-Dulmont, A.; Zaarour, M.; Helaine, C.; Ozcelik, H.; Allioux, C.; Toutain, J.; Goldyn, K.; Petit, E. et al. Nanosized zeolites as a gas delivery platform in a glioblastoma model. Biomaterials 2020, 257, 120249.
Wu, V. M.; Huynh, E.; Tang, S.; Uskoković, V. Brain and bone cancer targeting by a ferrofluid composed of superparamagnetic iron-oxide/silica/carbon nanoparticles (earthicles). Acta Biomater. 2019, 88, 422–447.
Hashemi, P.; Luckau, L.; Mischnick, P.; Schmidt, S.; Stosch, R.; Wünsch, B. Biomacromolecules as tools and objects in nanometrology-current challenges and perspectives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5901–5909.
Yang, Z. Z.; Du, Y. T.; Sun, Q.; Peng, Y. W.; Wang, R. D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y. Q.; Zhang, C. L.; Qi, X. R. Albumin-based nanotheranostic probe with hypoxia alleviating potentiates synchronous multimodal imaging and phototherapy for glioma. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6191–6212.
Fang, R. H.; Kroll, A. V.; Gao, W. W.; Zhang, L. F. Cell membrane coating nanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706759.
Zhuang, J.; Gong, H.; Zhou, J. R.; Zhang, Q. Z.; Gao, W. W.; Fang, R. H.; Zhang, L. F. Targeted gene silencing in vivo by platelet membrane-coated metal-organic framework nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6108.
Chen, H. Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C. Q.; Li, X.; Dai, H. W. Hybrid cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A multifunctional biomimetic platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 112, 1–13.
He, W. X.; Mei, Q. Y.; Li, J.; Zhai, Y. T.; Chen, Y. T.; Wang, R.; Lu, E. H.; Zhang, X. Y.; Zhang, Z. W.; Sha, X. Y. Preferential targeting cerebral ischemic lesions with cancer cell-inspired nanovehicle for ischemic stroke treatment. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 3033–3043.
Zheng, T.; Wang, W. T.; Ashley, J.; Zhang, M.; Feng, X. T.; Shen, J.; Sun, Y. Self-assembly protein superstructures as a powerful chemodynamic therapy nanoagent for glioblastoma treatment. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 151.
Cully, M. Exosome-based candidates move into the clinic. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 6–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82274104, 81903557, and 82074024), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20190802), Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CACM (No. 2021-QNRC2-A01), Natural Science Foundation Youth Project of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (No. NZY81903557), College Students’ Innovative Entrepreneurial Training of Jiangsu Province (No. 202110315021), and College Students’ Innovative Entrepreneurial Training of Kangyuan School of Chinese Herbal Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (No. kyxysc12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Ma, L., Sun, D. et al. Bioengineering extracellular vesicles as novel nanocarriers towards brain disorders. Nano Res. 16, 2635–2659 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4913-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4913-2