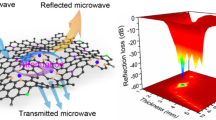
Abstract
Light-weight and exceptional microwave absorption are two vital characteristics for microwave absorbers in practical applications, but still face challenges. Herein, we employ a sacrificial template strategy to fabricate heteroatoms-doped carbon nanocages (CNs) via chemical vapor deposition, in which heteroatoms are simultaneously doped into the carbon frameworks by bubbling flowing source liquid. Compared with CNs, doped heteroatoms, accompanied with the inevitably defective arrangements in the lattice, not only decrease the electrical conductivity and balance the impedance characteristics, but also introduce structural-chemical defects and trigger dominant dipolar/defect polarization. As a result, both the minimum reflection loss (RL,min) and effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) greatly increase at an ultralow filler loading of 5 wt.% owing to internal hollow void and high specific surface area. The RL,min values reach −53.6, −43.2, and −50.1 dB for N-CNs, S-CNs, and N,S-CNs with the corresponding EAB of 4.9, 2.5, and 3.1 GHz, respectively. Furthermore, this work provides an effective strategy for the construction of heteroatoms-doped hollow carbon frameworks in large-scale production and the obtained doped carbon nanocages can be used as light-weight and high-performance microwave absorbers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, L. L.; Xiang, X. L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Gu, J. W. Multifunctional wearable silver nanowire decorated leather nanocomposites for joule heating, electromagnetic interference shielding and piezoresistive sensing. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200705.
Zhu, R. Q.; Li, Z. Y.; Deng, G.; Yu, Y. H.; Shui, J. L.; Yu, R. H.; Pan, C. F.; Liu, X. F. Anisotropic magnetic liquid metal film for wearable wireless electromagnetic sensing and smart electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106700.
Zhang, Y. L.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. W. New generation electromagnetic materials: Harvesting instead of dissipation solo. Sci. Bull., in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2022.06.017.
Li, W. C.; Cai, H. W.; Kang, Y.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J. W.; Qiao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Che, S. L. High permeability and low loss bioinspired soft magnetic composites with nacre-like structure for high frequency applications. Acta Mater. 2019, 167, 267–274.
Kang, Y.; Li, W. C.; Ma, T.; Huang, X. C.; Mo, Y. P.; Chu, Z. Y.; Zhang, Z. J.; Feng, G. T. Microwave-constructed honeycomb architectures of h-BN/rGO nano-hybrids for efficient microwave conversion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 184–193.
Niu, H. H.; Tu, X. Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Y.; Wang, H. L.; Shao, G.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. X.; Zhao, B.; Fan, B. B. Engineered core-shell SiO2@Ti3C2Tx composites: Towards ultra-thin electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137260.
Wu, Z. C.; Cheng, H. W.; Jin, C.; Yang, B. T.; Xu, C. Y.; Pei, K.; Zhang, H. B.; Yang, Z. Q.; Che, R. C. Dimensional design and core-shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107538.
Zhang, X. J.; Zhu, J. Q.; Yin, P. G.; Guo, A. P.; Huang, A. P.; Guo, L.; Wang, G. S. Tunable high-performance microwave absorption of Co1−xS hollow spheres constructed by nanosheets within ultralow filler loading. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800761.
Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H. H.; Huang, Z. Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, P. S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. S. Composition and structure control of ultralight graphene foam for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 2016, 105, 438–447.
Ye, F.; Song, Q.; Zhang, Z. C.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Y.; Yin, X. W.; Zhou, Y. Z.; Tao, H. W.; Liu, Y. S.; Cheng, L. F. et al. Direct growth of edge-rich graphene with tunable dielectric properties in porous Si3N4 ceramic for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707205.
Li, C.; Li, Z. H.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Chen, Y. L.; Peng, Q.; Deng, C. Y.; Jing, T.; Zhong, W. A generalizable strategy for constructing ultralight three-dimensional hierarchical network heterostructure as high-efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2022, 605, 13–22.
Liu, P. B.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, W. J.; Huang, W. H.; Luo, J. H. Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122653.
Zhao, H. H.; Xu, X. Z.; Wang, Y. H.; Fan, D. G.; Liu, D. W.; Lin, K. F.; Xu, P.; Han, X. J.; Du, Y. C. Heterogeneous interface induced the formation of hierarchically hollow carbon microcubes against electromagnetic pollution. Small 2020, 16, 2003407.
Li, T.; Zhi, D. D.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, Z. W.; Meng, F. B. Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 477–484.
Wu, Z. C.; Pei, K.; Xing, L. S.; Yu, X. F.; You, W. B.; Che, R. C. Enhanced microwave absorption performance from magnetic coupling of magnetic nanoparticles suspended within hierarchically tubular composite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901448.
Gu, W. H.; Sheng, J. Q.; Huang, Q. Q.; Wang, G. H.; Chen, J. B.; Ji, G. B. Environmentally friendly and multifunctional shaddock peel-based carbon aerogel for thermal-insulation and microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 102.
Zhao, H. Q.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, L. J.; Zhang, B. S.; Wang, L. P.; Ji, G. B.; Xu, Z. J. Biomass-derived porous carbon-based nanostructures for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 24.
Liu, Z. C.; Pan, F.; Deng, B. W.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Self-assembled MoS2/3D worm-like expanded graphite hybrids for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 174, 59–69.
Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Xiang, Z.; Cai, L.; Lu, W. A hierarchical Co@mesoporous C/macroporous C sheet composite derived from bimetallic MOF and oroxylum indicum for enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 187, 477–487.
Luo, J. H.; Dai, Z. Y.; Feng, M. N.; Chen, X. W.; Sun, C. H.; Xu, Y. Hierarchically porous carbon derived from natural porphyra for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 206–214.
Li, C.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y. L.; Xie, R.; Zhong, W. Magnetic-dielectric synergy and interfacial engineering to design yolk—shell structured CoNi@void@C and CoNi@void@C@MoS2 nanocomposites with tunable and strong wideband microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6761–6771.
Zhang, J. J.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y. L.; Xie, R.; Zhong, W. Microstructure optimization of core@shell structured MSe2/FeSe2@MoSe2 (M = Co, Ni) flower-like multicomponent nanocomposites towards high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 59–70.
Liu, P. B.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G. Z.; Huang, Y.; You, W. B.; Che, R. C. Hollow engineering to Co@N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102812.
Liu, D. W.; Du, Y. C.; Xu, P.; Wang, F. Y.; Wang, Y. H.; Cui, L. R.; Zhao, H. H.; Han, X. J. Rationally designed hierarchical N-doped carbon nanotubes wrapping waxberry-like Ni@C microspheres for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 5086–5096.
Liu, P. B.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Yan, J.; Huang, Y.; Xia, L.; Guang, Z. X. Synthesis of lightweight N-doped graphene foams with open reticular structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 285–298.
Sun, Y. W.; Wang, H. L.; Wei, W. R.; Zheng, Y. L.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y. X.; Huang, M. H.; Shi, J.; Shi, Z. C.; Mitlin, D. Sulfur-rich graphene nanoboxes with ultra-high potassiation capacity at fast charge: Storage mechanisms and device performance. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1652–1665.
Luo, J. H.; Feng, M. N.; Dai, Z. Y.; Jiang, C. Y.; Yao, W.; Zhai, N. X. MoS2 wrapped MOF-derived N-doped carbon nanocomposite with wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5781–5789.
Liu, P. B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G. Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R. X.; Liu, X. H.; Zhang, X. F.; Che, R. C. Hierarchical engineering of double-shelled nanotubes toward hetero-interfaces induced polarization and microscale magnetic interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202202588.
Xu, H. X.; Zhang, G. Z.; Wang, Y.; Ning, M. Q.; Ouyang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P. B. Size-dependent oxidation-induced phase engineering for MOFs derivatives via spatial confinement strategy toward enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 102.
Wu, T. J.; Jing, M. J.; Yang, L.; Zou, G. Q.; Hou, H. S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X. Y.; Ji, X. B. Controllable chain-length for covalent sulfur-carbon materials enabling stable and high-capacity sodium storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803478.
Wang, J. J.; Yu, S. L.; Wu, Q. Q.; Li, Y.; Li, F. Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y. H.; Li, B. Z.; Liu, P. B. Heterogeneous junctions of magnetic Ni core@binary dielectric shells toward high-efficiency microwave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 115, 71–80.
Yu, Y. H.; Yi, P.; Xu, W. B.; Sun, X.; Deng, G.; Liu, X. F.; Shui, J. L.; Yu, R. H. Environmentally tough and stretchable MXene organohydrogel with exceptionally enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding performances. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 77.
Li, Y.; Liu, X. F.; Nie, X. Y.; Yang, W. W.; Wang, Y. D.; Yu, R. H.; Shui, J. L. Multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid aerogel for self-cleaning, heat-insulating, and highly efficient microwave absorbing material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 99, 1807624.
Han, Y. X.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Janus (BNNS/ANF)-(AgNWs/ANF) thermal conductivity composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4747–4755.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small 2021, 17, 2101951.
Cao, M. S.; Han, C.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. L.; Shu, J. C.; Yang, H. J.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Graphene nanohybrids: Excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4586–4602.
Wang, L.; Ma, Z. L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Chen, L. X.; Cao, D. P.; Gu, J. W. Polymer-based EMI shielding composites with 3D conductive networks: A mini-review. SusMat 2021, 1, 413–431.
Huang, W. H.; Gao, W. M.; Zuo, S. W.; Zhang, L. X.; Pei, K.; Liu, P. B.; Che, R. C.; Zhang, H. B. Hollow MoC/NC sphere for electromagnetic wave attenuation: Direct observation of interfacial polarization on nanoscale hetero-interfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1290–1298.
Liu, Q. H.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C. Y.; Yuan, K. P.; She, W.; Yang, Y. J.; Che, R. C. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490.
Li, W. J.; Li, W. C.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J. W.; Qiao, L.; Li, J.; Che, S. L. Multifunctional flower-like core-shell Fe/Fe4N@SiO2 composites for broadband and high-efficiency ultrathin electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 90–99.
Song, L. M.; Chen, Y. Q.; Gao, Q. C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wang, H. L.; Guan, L.; Yu, Z. J.; Zhang, R.; Fan, B. B. Low weight, low thermal conductivity, and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption of three-dimensional graphene/SiC-nanosheets aerogel. Compos. Part A 2022, 158, 106980.
Song, P.; Ma, Z. L.; Qiu, H.; Ru, Y. F.; Gu, J. W. High-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding of rGO@FeNi/epoxy composites with regular honeycomb structures. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 51.
Du, H.; Zhang, Q. P.; Zhao, B.; Marken, F.; Gao, Q. C.; Lu, H. X.; Guan, L.; Wang, H. L.; Shao, G.; Xu, H. L. et al. Novel hierarchical structure of MoS2/TiO2/Ti3C2Tx composites for dramatically enhanced electromagnetic absorbing properties. J. Add. Ceram. 2021, 10, 1042–1051.
Hu, F. Y.; Wang, X. H.; Bao, S.; Song, L. M.; Zhang, S.; Niu, H. H.; Fan, B. B.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. X. Tailoring electromagnetic responses of delaminated Mo2TiC2Tx MXene through the decoration of Ni particles of different morphologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 440, 135855.
Li, W. C.; Xu, L. Y.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J. W.; Qiao, L.; Che, S. L. Investigating the effect of honeycomb structure composite on microwave absorption properties. Compos. Commun. 2020, 19, 182–188.
Kuang, B. Y.; Song, W. L.; Ning, M. Q.; Li, J. B.; Zhao, Z. J.; Guo, D. Y.; Cao, M. S.; Jin, H. B. Chemical reduction dependent dielectric properties and dielectric loss mechanism of reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 2018, 127, 209–217.
Sun, L.; Shi, S. C.; He, B. L.; Wang, H. L.; Liu, S.; Huang, M. H.; Shi, J.; Dastan, D.; Wang, H. Asymmetric trilayer all-polymer dielectric composites with simultaneous high efficiency and high energy density: A novel design targeting advanced energy storage capacitors. Add. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100280.
Sun, S. B.; Shi, Z. C.; Sun, L.; Liang, L.; Dastan, D.; He, B. L.; Wang, H. L.; Huang, M. H.; Fan, R. H. Achieving concurrent high energy density and efficiency in all-polymer layered paraelectric/ferroelectric composites via introducing a moderate layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 27522–27532.
Sun, L.; Shi, Z. C.; Liang, L.; Dong, J. F.; Pan, Z. Z.; Wang, H. L.; Gao, Z.; Qin, Y.; Fan, R. H.; Wang, H. Concurrently achieving high discharged energy density and efficiency in composites by introducing ultralow loadings of core-shell structured graphene@TiO2 nanoboxes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 29292–29301.
Ma, T. B.; Ma, H.; Ruan, K. P.; Shi, X. T.; Qiu, H.; Gao, S. Y.; Gu, J. W. Thermally conductive poly(lactic acid) composites with superior electromagnetic shielding performances via 3D printing technology. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 40, 248–255.
Wang, H. Y.; Sun, X. B.; Yang, S. H.; Zhao, P. Y.; Zhang, X. J.; Wang, G. S.; Huang, Y. 3D ultralight hollow NiCo compound@MXene composites for tunable and high-efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 206.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2022JM-260), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2020ME038), and the Fundamental Research Funds of the Central Universities (No. G2022KY05109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Zhang, G., Wang, Y. et al. Heteroatoms-doped carbon nanocages with enhanced dipolar and defective polarization toward light-weight microwave absorbers. Nano Res. 15, 8705–8713 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4820-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4820-6