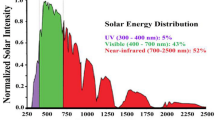
Abstract
Solar-driven water evaporation is a sustainable method to purify seawater. Nevertheless, traditional volumetric water-evaporation systems suffer from the poor sunlight absorption and inefficient light-to-thermal conversion. Also, their anti-bacterial and anti-fouling performances are crucial for the practical application. Herein, we introduce reduced graphene oxide (RGO) with broadband absorbance across the entire solar spectrum, and polypyrrole (PPy), an antibacterial polymer with efficient solar absorption and low thermal conductivity, to develop integrated RGO/PPy aerogel as both the solar absorber and evaporator for highly efficient solar-driven steam generation. As a result, the RGO/PPy aerogel shows strong absorption and good photothermal performance, leading to an evaporation rate of 1.44 kg·m−2·h−1 and high salt rejection (up to 99.99%) for real seawater, with photothermal conversion efficiency > 90% under one sun irradiation. The result is attributed to the localized heat at the air—water interface by the RGO/PPy and its porous nature with functional groups that facilitates the water evaporation. Moreover, the RGO/PPy demonstrates excellent durability and antibacterial efficiency close to 100% for 12 h, crucial characteristics for long-term application. Our well-designed RGO/PPy aerogel with efficient water desalination performance and antibacterial property provides a straightforward approach to improve the solar-driven evaporation performance by multifunctional materials integration, and offers a viable route towards practical seawater desalination.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, S. S.; Jiang, Q. S.; Wu, X. H.; Ghim, D.; Derami, H. G.; Chou, P. I.; Jun, Y. S.; Singamaneni, S. Advances in solar evaporator materials for freshwater generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 24092–24123.
Zhao, H. Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Z. L.; Chen, L. F.; Zhan, H. J.; Zhu, H. W.; Huang, J.; Shi, L. A.; Yu, S. H. Lotus-inspired evaporator with Janus wettability and bimodal pores for solar steam generation. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100074.
Gao, M. M.; Zhu, L. L.; Peh, C. K.; Ho, G. W. Solar absorber material and system designs for photothermal water vaporization towards clean water and energy production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 841–864.
Zhao, F.; Zhou, X.; Shi, Y.; Qian, X.; Alexander, M.; Zhao, X.; Mendez, S.; Yang, R.; Qu, L.; Yu, G. Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 489–495.
Zhou, X. Y.; Zhao, F.; Guo, Y. H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G. H. A hydrogel-based antifouling solar evaporator for highly efficient water desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1985–1992.
Tao, P.; Ni, G.; Song, C. Y.; Shang, W.; Wu, J. B.; Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Deng, T. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 1031–1041.
Zhang, Y. X.; Xiong, T.; Nandakumar, D. K.; Tan, S. C. Structure architecting for salt-rejecting solar interfacial desalination to achieve high-performance evaporation with in situ energy generation. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903478.
Zhu, L. L.; Gao, M. M.; Peh, C. K. N.; Ho, G. W. Recent progress in solar-driven interfacial water evaporation: Advanced designs and applications. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 507–518.
Li, H. R.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; Hong, W. P. Latest development in salt removal from solar-driven interfacial saline water evaporators: Advanced strategies and challenges. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115770.
Liu, F. H.; Lai, Y. J.; Zhao, B. Y.; Bradley, R.; Wu, W. P. Photothermal materials for efficient solar powered steam generation. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 636–653.
Zhu, L. L.; Gao, M. M.; Peh, C. K. N.; Ho, G. W. Solar-driven photothermal nanostructured materials designs and prerequisites for evaporation and catalysis applications. Mater. Horiz. 2018, 5, 323–343.
Ding, T. P.; Zhou, Y.; Ong, W. L.; Ho, G. W. Hybrid solar-driven interfacial evaporation systems: Beyond water production towards high solar energy utilization. Mater. Today 2021, 42, 178–191.
Zhou, Y.; Ding, T. P.; Gao, M. M.; Chan, K. H.; Cheng, Y.; He, J. Q.; Ho, G. W. Controlled heterogeneous water distribution and evaporation towards enhanced photothermal water-electricity-hydrogen production. Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105102.
Liu, Z. X.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, N. Y.; Zhang, R. Q.; Zhu, B.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Y. M.; Zhu, M. F.; Chen, Z. G. Hierarchical photothermal fabrics with low evaporation enthalpy as heliotropic evaporators for efficient, continuous, salt-free desalination. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13007–13018.
Zhang, Y. X.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, T.; Qu, H.; Koh, J. J.; Nandakumar, D. K.; Wang, J.; Tan, S. C. Manipulating unidirectional fluid transportation to drive sustainable solar water extraction and brine-drenching induced energy generation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4891–4902.
Shao, Y.; Tang, J. B.; Li, N. B.; Sun, T. Y.; Yang, L. P.; Chen, D.; Zhi, H.; Wang, D. J.; Liu, H.; Xue, G. B. Designing a bioinspired synthetic tree by unidirectional freezing for simultaneous solar steam generation and salt collection. Eco. Mat. 2020, 2, e12018.
Zhang, Y. X.; Xiong, T.; Suresh, L.; Qu, H.; Zhang, X. P.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J. C.; Tan, S. C. Guaranteeing complete salt rejection by channeling saline water through fluidic photothermal structure toward synergistic zero energy clean water production and in situ energy generation. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 3397–3404.
Wang, Y. D.; Wu, X.; Shao, B.; Yang, X. F.; Owens, G.; Xu, H. L. Boosting solar steam generation by structure enhanced energy management. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1380–1388.
Wu, X.; Wu, Z. Q.; Wang, Y. D.; Gao, T.; Li, Q.; Xu, H. L. All-cold evaporation under one sun with zero energy loss by using a heatsink inspired solar evaporator. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002501.
Shao, B.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. D.; Gao, T.; Liu, Z. Q.; Owens, G.; Xu, H. L. A general method for selectively coating photothermal materials on 3D porous substrate surfaces towards cost-effective and highly efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 24703–24709.
Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Z.; Zhu, J. Solar thermophotovoltaics: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 080906.
Zhang, Q.; Yang, H. J.; Xiao, X. F.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Shi, Z. X.; Chen, Y. L.; Xu, W. L.; Wang, X. B. A new self-desalting solar evaporation system based on a vertically oriented porous polyacrylonitrile foam. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 14620–14628.
Wang, X. Q.; Ou, G.; Wang, N.; Wu, H. Graphene-based recyclable photo-absorbers for high-efficiency seawater desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 9194–9199.
Hu, X. Z.; Xu, W. C.; Zhou, L.; Tan, Y. L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S. N.; Zhu, J. Tailoring graphene oxide-based aerogels for efficient solar steam generation under one sun. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604031.
Salam, M. A.; Obaid, A. Y.; El-Shishtawy, R. M.; Mohamed, S. A. Synthesis of nanocomposites of polypyrrole/carbon nanotubes/silver Nano particles and their application in water disinfection. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16878–16884.
Varesano, A.; Vineis, C.; Aluigi, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Tonetti, C.; Mazzuchetti, G. Antibacterial efficacy of polypyrrole in textile applications. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 36–42.
Li, X. Q.; Xu, W. C.; Tang, M. Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, S. N.; Zhu, J. Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one sun with a confined 2D water path. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13953–13958.
Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D. A.; Piner, R. D.; Kohlhaas, K. A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y. Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S. T.; Ruoff, R. S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565.
Li, C. X.; Yang, J.; Pachfule, P.; Li, S.; Ye, M. Y.; Schmidt, J.; Thomas, A. Ultralight covalent organic framework/graphene aerogels with hierarchical porosity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4712.
Fu, Y.; Wang, G.; Mei, T.; Li, J. H.; Wang, J. Y.; Wang, X. B. Accessible graphene aerogel for efficiently harvesting solar energy. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4665–4671.
Wang, X.; Liu, Q. C.; Wu, S. Y.; Xu, B. X.; Xu, H. X. Multilayer polypyrrole nanosheets with self-organized surface structures for flexible and efficient solar-thermal energy conversion. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807716.
Chen, J. X.; Li, B.; Hu, G. X.; Aleisa, R.; Lei, S.; Yang, F.; Liu, D. L.; Lyu, F. L.; Wang, M. Z.; Ge, X. W. et al. Integrated evaporator for efficient solar-driven interfacial steam generation. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 6051–6058.
Xiao, C. H.; Liang, W. D.; Hasi, Q. M.; Chen, L. H.; He, J. X.; Liu, F.; Wang, C. J.; Sun, H. X.; Zhu, Z. Q.; Li, A. Ag/polypyrrole co-modified poly(ionic liquid)s hydrogels as efficient solar generators for desalination. Mater. Today Energy 2020, 16, 100417.
Li, X. Q.; Li, J. L.; Lu, J. Y.; Xu, N.; Chen, C. L.; Min, X. Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, H. X.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, S. N. et al. Enhancement of interfacial solar vapor generation by environmental energy. Joule 2018, 2, 1331–1338.
Li, X. Q.; Ni, G.; Cooper, T.; Xu, N.; Li, J. L.; Zhou, L.; Hu, X. Z.; Zhu, B.; Yao, P. C.; Zhu, J. Measuring conversion efficiency of solar vapor generation. Joule 2019, 3, 1798–1803.
Jang, H.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.; Jeon, S. Corrugated wood fabricated using laser-induced graphitization for salt-resistant solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 30320–30327.
Cheng, G.; Wang, X. Z.; Liu, X.; He, Y. R.; Balakin, B. V. Enhanced interfacial solar steam generation with composite reduced graphene oxide membrane. Sol. Energy 2019, 194, 415–430.
Bai, B. L.; Yang, X. H.; Tian, R.; Ren, W. C.; Suo, R.; Wang, H. B. High-efficiency solar steam generation based on blue brick-graphene inverted cone evaporator. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 163, 114379.
Deng, X.; Nie, Q. C.; Wu, Y.; Fang, H. S.; Zhang, P. X.; Xie, Y. S. Nitrogen-doped unusually superwetting, thermally insulating, and elastic graphene aerogel for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 26200–26212.
Wu, S. H.; Gong, B. Y.; Yang, H. C.; Tian, Y. K.; Xu, C. X.; Guo, X. Z.; Xiong, G. P.; Luo, T. F.; Yan, J. H.; Cen, K. F. et al. Plasmamade graphene nanostructures with molecularly dispersed f and Na sites for solar desalination of oil-contaminated seawater with complete in-water and in-air oil rejection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38512–38521.
Wang, F.; Mu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, T.; Li, Y. Z.; Sun, H. X.; Zhu, Z. Q.; Liang, W. D.; Li, A. Reduced graphene oxide coated hollow polyester fibers for efficient solar steam generation. Energy Technol. 2019, 7, 1900265.
Ren, H. Y.; Tang, M.; Guan, B. L.; Wang, K. X.; Yang, J. W.; Wang, F. F.; Wang, M. Z.; Shan, J. Y.; Chen, Z. L.; Wei, D. et al. Hierarchical graphene foam for efficient omnidirectional solar-thermal energy conversion. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702590.
Wang, Y. C.; Wang, C. Z.; Song, X. J.; Megarajan, S. K.; Jiang, H. Q. A facile nanocomposite strategy to fabricate a rGO-MWCNT photothermal layer for efficient water evaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 963–971.
Mohsenpour, M.; Motahari, S.; Tajabadi, F.; Najafi, M. Preparation and application of sunlight absorbing ultra-black carbon aerogel/graphene oxide membrane for solar steam generation systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41780–41790.
Shan, X. L.; Lin, Y. W.; Zhao, A. Q.; Di, Y. S.; Hu, Y. J.; Guo, Y. J.; Gan, Z. X. Porous reduced graphene oxide/nickel foam for highly efficient solar steam generation. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 425403.
Xiong, Z. C.; Zhu, Y. J.; Qin, D. D.; Yang, R. L. Flexible salt-rejecting photothermal paper based on reduced graphene oxide and hydroxyapatite nanowires for high-efficiency solar energy-driven vapor generation and stable desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 32556–32565.
Kuang, Y. D.; Chen, C. J.; He, S. M.; Hitz, E. M.; Wang, Y. L.; Gan, W. T.; Mi, R. Y.; Hu, L. B. A high-performance self-regenerating solar evaporator for continuous water desalination. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900498.
Wang, Y. C.; Sun, X. Y.; Tao, S. Y. Rational 3D coiled morphology for efficient solar-driven desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 16240–16248.
Zhang, Y. X.; Ravi, S. K.; Tan, S. C. Food-derived carbonaceous materials for solar desalination and thermo-electric power generation. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104006.
Li, X.; Pang, R. Z.; Li, J. S.; Sun, X. Y.; Shen, J. Y.; Han, W. Q.; Wang, L. J. In situ formation of ag nanoparticles in PVDF ultrafiltration membrane to mitigate organic and bacterial fouling. Desalination 2013, 324, 48–56.
Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Li, M. F.; Li, K.; Liao, X. P.; Shi, B. Immobilization of ytterbium by plant polyphenols for antibiofilm materials with highly effective activity and long-term stability. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 18558–18566.
Hui, L. W.; Piao, J. G.; Auletta, J.; Hu, K.; Zhu, Y. W.; Meyer, T.; Liu, H. T.; Yang, L. H. Availability of the basal planes of graphene oxide determines whether it is antibacterial. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13183–13190.
Zheng, H. Z.; Ma, R. L.; Gao, M.; Tian, X.; Li, Y. Q.; Zeng, L. W.; Li, R. B. Antibacterial applications of graphene oxides: Structure-activity relationships, molecular initiating events and biosafety. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 133–142.
Farid, M. U.; Jeong, S.; Seo, D. H.; Ahmed, R.; Lau, C.; Gali, N. K.; Ning, Z.; An, A. K. Mechanistic insight into the in vitro toxicity of graphene oxide against biofilm forming bacteria using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4475–4487.
Da Silva, F. A. G. Jr.; Queiroz, J. C.; Macedo, E. R.; Fernandes, A. W.; Freire, N. B.; Da Costa, M. M.; De Oliveira, H. P. Antibacterial behavior of polypyrrole: The influence of morphology and additives incorporation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 317–322.
Facchi, D. P.; Facchi, S. P.; Martins, A. F. N, N, N-trimethyl chitosan and its potential bactericidal activity: Current aspects and technological applications. J. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2016, 4, 291.
Berendjchi, A.; Khajavi, R.; Yousefi, A. A.; Yazdanshenas, M. E. Improved continuity of reduced graphene oxide on polyester fabric by use of polypyrrole to achieve a highly electro-conductive and flexible substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 363, 264–272.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2018YFA0209500 and 2018YFA0306900) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21872114 and 21627811).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Xu, F., Liu, W. et al. Antibacterial evaporator based on reduced graphene oxide/polypyrrole aerogel for solar-driven desalination. Nano Res. 16, 4219–4224 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-4041-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-4041-4