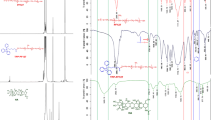
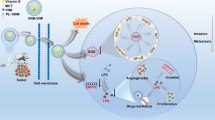
Abstract
Mitochondria are highly involved in the metastasis of cancer cells. However, tumor cells impede the efficiency of mitochondrial targeted drugs by protecting mitochondria through an intrinsic and adaptive antioxidant mechanism. We aim to disturb the redox homeostasis by prolyl-isomerase PIN1 inhibitor all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) to improve the therapeutic efficacy of mitochondrial targeted lonidamine (TL). The combination of ATRA and TL with a ratio of 2:1 was found to have the best synergistic effect in inhibiting the proliferation and metastasis of metastatic 4T1 breast cancer cells. Dual-drug loaded nanoparticles (TL-ATRA NPs) were further developed by self-assembly and were observed to disturb the redox homeostasis drastically and triggered a robust mitochondrial disruption on metastatic 4T1 breast cancer cells. The molecular mechanism was related to the downregulation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (NRF2), a critical transcription factor that regulated antioxidant responses, and its downstream molecules. As a result, TL-ATRA NPs significantly suppressed the growth of primary tumors and the formation of lung metastasis nodes. Collectively, our findings showed that sensitizing mitochondria to anti-cancer drugs by disturbing redox homeostasis achieved a satisfactory therapeutic effect to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steeg, P. S. Targeting metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 201–218.
Kalyanaraman, B.; Cheng, G.; Hardy, M.; Ouari, O.; Lopez, M.; Joseph, J.; Zielonka, J.; Dwinell, M. B. A review of the basics of mitochondrial bioenergetics, metabolism, and related signaling pathways in cancer cells: Therapeutic targeting of tumor mitochondria with lipophilic cationic compounds. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 316–327.
Lin, X.; Li, L.; Li, S. J.; Li, Q. Y.; Xie, D. D.; Zhou, M. L.; Huang, Y. Targeting the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores potentiates nanoparticle drug delivery and mitigates cancer metastasis. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002834.
Bhandary, B.; Marahatta, A.; Kim, H. R.; Chae, H. J. Mitochondria in relation to cancer metastasis. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2012, 44, 623–627.
Li, Q. Y.; Yang, J. T.; Chen, C.; Lin, X.; Zhou, M. L.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y. A novel mitochondrial targeted hybrid peptide modified HPMA copolymers for breast cancer metastasis suppression. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 38–51.
Huang, Y. X.; Sun, G. H.; Sun, X. D.; Li, F. F.; Zhao, L. J.; Zhong, R. G.; Peng, Y. Z. The potential of lonidamine in combination with chemotherapy and physical therapy in cancer treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3332.
Cheng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Lee, Y.; Ouari, O.; Hardy, M.; Zielonka, M.; Myers, C. R.; Zielonka, J.; Weh, K. et al. Targeting lonidamine to mitochondria mitigates lung tumorigenesis and brain metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2205.
Bansal, A.; Simon, M. C. Glutathione metabolism in cancer progression and treatment resistance. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2291–2298.
Rao, V. A.; Klein, S. R.; Bonar, S. J.; Zielonka, J.; Mizuno, N.; Dickey, J. S.; Keller, P. W.; Joseph, J.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Shacter, E. The antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 negatively regulates autophagy and growth arrest induced by the anticancer redox agent mitoquinone. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 34447–34459.
Bollong, M. J.; Lee, G.; Coukos, J. S.; Yun, H.; Zambaldo, C.; Chang, J. W.; Chin, E. N.; Ahmad, I.; Chatterjee, A. K.; Lairson, L. L. et al. A metabolite-derived protein modification integrates glycolysis with KEAP1-NRF2 signalling. Nature 2018, 562, 600–604.
Senyuk, V.; Eskandari, N.; Jiang, Y.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Sundstrom, R.; Leanza, L.; Peruzzo, R.; Burkard, M.; Minshall, R. D.; Gentile, S. Compensatory expression of NRF2-dependent antioxidant genes is required to overcome the lethal effects of Kv11. 1 activation in breast cancer cells and PDOs. Redox Biol. 2021, 45, 102030.
Wei, S.; Kozono, S.; Kats, L.; Nechama, M.; Li, W. Z.; Guarnerio, J.; Luo, M. L.; You, M. H.; Yao, Y. D.; Kondo, A. et al. Active Pin1 is a key target of all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia and breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 457–466.
Saeidi, S.; Kim, S. J.; Han, H. J.; Kim, S. H.; Zheng, J.; Lee, H. B.; Han, W.; Noh, D. Y.; Na, H. K.; Surh, Y. J. H-Ras induces Nrf2-Pin1 interaction: Implications for breast cancer progression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 402, 115121.
Liang, C.; Shi, S.; Liu, M. Y.; Qin, Y.; Meng, Q. C.; Hua, J.; Ji, S. R.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Yang, J. X.; Xu, J. et al. PIN1 maintains redox balance via the c-Myc/NRF2 axis to counteract kras-induced mitochondrial respiratory injury in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 133–145.
Campaner, E.; Rustighi, A.; Zannini, A.; Cristiani, A.; Piazza, S.; Ciani, Y.; Kalid, O.; Golan, G.; Baloglu, E.; Shacham, S. et al. A covalent PIN1 inhibitor selectively targets cancer cells by a dual mechanism of action. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15772.
Kozono, S.; Lin, Y. M.; Seo, H. S.; Pinch, B.; Lian, X. L.; Qiu, C. X.; Herbert, M. K.; Chen, C. H.; Tan, L.; Gao, Z. J. et al. Arsenic targets Pin1 and cooperates with retinoic acid to inhibit cancer-driving pathways and tumor-initiating cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3069.
Liu, Y. Q.; Zhang, X. J.; Zhou, M. J.; Nan, X. Y.; Chen, X. F.; Zhang, X. H. Mitochondrial-targeting lonidamine-doxorubicin nanoparticles for synergistic chemotherapy to conquer drug resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 43498–43507.
Fan, J. L.; Liu, B.; Long, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tong, C. Y.; Wang, W.; You, P. D.; Liu, X. M. Sequentially-targeted biomimetic nano drug system for triple-negative breast cancer ablation and lung metastasis inhibition. Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 554–569.
Mei, L.; Liu, Y. Y.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Gao, H. L.; Zhang, Z. R.; He, Q. Enhanced antitumor and anti-metastasis efficiency via combined treatment with CXCR4 antagonist and liposomal doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2014, 196, 324–331.
Yang, D. Y.; Luo, W. S.; Wang, J. C.; Zheng, M.; Liao, X. H.; Zhang, N.; Lu, W. X.; Wang, L.; Chen, A. Z.; Wu, W. G. et al. A novel controlled release formulation of the Pin1 inhibitor ATRA to improve liver cancer therapy by simultaneously blocking multiple cancer pathways. J. Control. Release 2018, 269, 405–422.
He, S. S.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q. F.; Ding, J. X.; Liang, X. J.; Chen, X. S.; Xiao, H. H.; Chen, X. Y.; Zhou, D. F.; Huang, Y. B. Tailoring platinum(IV) amphiphiles for self-targeting all-in-one assemblies as precise multimodal theranostic nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7272–7281.
Xu, J. T.; Shi, R. P.; Chen, G. Y.; Dong, S. M.; Yang, P. P.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Niu, N.; Gai, S. L.; He, F.; Fu, Y. J. et al. All-in-one theranostic nanomedicine with ultrabright second near-infrared emission for tumor-modulated bioimaging and chemodynamic/photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9613–9625.
Luo, T. T.; Han, J. T.; Zhao, F.; Pan, X. H.; Tian, B. C.; Ding, X. J.; Zhang, J. Redox-sensitive micelles based on retinoic acid modified chitosan conjugate for intracellular drug delivery and smart drug release in cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 8–19.
Varshosaz, J.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Aliabadi, H. S.; Nayebsadrian, M.; Banitalebi, M.; Rostami, M. Synthesis and characterization of folate-targeted dextran/retinoic acid micelles for doxorubicin delivery in acute leukemia. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 525684.
Nagar, P.; Goyal, P.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, A. K.; Kumar, P. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of retinoic acid-polyethylene glycol nanoassembly as efficient drug delivery system. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 14, 110–117.
Song, J.; Lin, C. C.; Yang, X.; Xie, Y. Q.; Hu, P.; Li, H. T.; Zhu, W. B.; Hu, H. Y. Mitochondrial targeting nanodrugs self-assembled from 9-O-octadecyl substituted berberine derivative for cancer treatment by inducing mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 27–42.
Moindjie, H.; Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Nahmias, C. Mitochondrial metabolism in carcinogenesis and cancer therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 3311.
Yang, Z. L.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. J.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X. F.; Cao, X. F.; Zhang, Y. L.; Lu, G. M. et al. Sensitive, real-time, and in-vivo oxygen monitoring for photodynamic therapy by multifunctional mesoporous nanosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 187–194.
De Oliveira, M. R.; Nabavi, S. F.; Manayi, A.; Daglia, M.; Hajheydari, Z.; Nabavi, S. M. Resveratrol and the mitochondria: From triggering the intrinsic apoptotic pathway to inducing mitochondrial biogenesis, a mechanistic view. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 727–745.
Ma, S. H.; Paiboonrungruan, C.; Yan, T. S.; Williams, K. P.; Ben Major, M.; Chen, X. L. Targeted therapy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: The NRF2 signaling pathway as target. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1434, 164–172.
Oh, E. T.; Kim, J. W.; Kim, J. M.; Kim, S. J.; Lee, J. S.; Hong, S. S.; Goodwin, J.; Ruthenborg, R. J.; Jung, M. G.; Lee, H. J. et al. NQO1 inhibits proteasome-mediated degradation of HIF-1α. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13593.
Yi, X. L.; Yan, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Q. Y.; Xiang, Y. C.; Huang, Y. Sequentially targeting cancer-associated fibroblast and mitochondria alleviates tumor hypoxia and inhibits cancer metastasis by preventing “soil” formation and “seed” dissemination. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010283.
Park, J. Y.; Park, D. H.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, Y. J.; Lee, J.; Shin, M. S.; Kang, K. S.; Hwang, G. S.; Kim, H. Y.; Yamabe, N. Eupatilin inhibits angiogenesis-mediated human hepatocellular metastasis by reducing MMP-2 and VEGF signaling. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3150–3154.
He, B.; Tan, T.; Wang, H.; Hu, H. Y.; Wang, Z. W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Sun, K. X.; Zhang, Z. W.; Li, Y. P. Rational design of tumor microenvironment-activated micelles for programed targeting of breast cancer metastasis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705622.
Sun, H. P.; Su, J. H.; Meng, Q. S.; Yin, Q.; Chen, L. L.; Gu, W. W.; Zhang, Z. W.; Yu, H. J.; Zhang, P. C.; Wang, S. L. et al. Cancer cell membrane-coated gold nanocages with hyperthermia-triggered drug release and homotypic target inhibit growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604300.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 81625023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2021_3923_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Co-delivery of mitochondrial targeted lonidamine and PIN1 inhibitor ATRA by nanoparticulate systems for synergistic metastasis suppression
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Li, Q., Xing, L. et al. Co-delivery of mitochondrial targeted lonidamine and PIN1 inhibitor ATRA by nanoparticulate systems for synergistic metastasis suppression. Nano Res. 15, 3376–3386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3923-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3923-9