Abstract
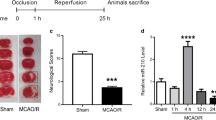
Brain ischemia is the second leading cause of death and the third leading cause of disability in the world. Systemic delivery of microRNA, a class of molecules that regulate the expression of cellular proteins associated with angiogenesis, cell growth, proliferation and differentiation, holds great promise for the treatment of brain ischemia. However, their therapeutic efficacy has been hampered by poor delivery efficiency of microRNA. We report herein a platform technology based on microRNA nanocapsules, which enables their effective delivery to the disease sites in the brain. Exemplified by microRNA-21, intravenous injection of the nanocapsules into a rat model of cerebral ischemia could effectively ameliorate the infarct volume, neurological deficit and histopathological severity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isner, J. M. Tissue responses to ischemia: Local and remote responses for preserving perfusion of ischemic muscle. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 106, 615–619.
Semenza, G. L. Series introduction: Tissue ischemia: Pathophysiology and therapeutics. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 106, 613–614.
Eltzschig, H. K.; Eckle, T. Ischemia and reperfusion-From mechanism to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1391–1401.
Upadhyay, R. K. Drug delivery systems, CNS protection, and the blood brain barrier. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 869269.
Rosenberg, G. A. Neurological diseases in relation to the blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1139–1151.
Gállego, J.; Muñoz, R.; Martínez-Vila, E. Emergent cerebrovascular disease risk factor weighting: Is transient ischemic attack an imminent threat? Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 27, 88–96.
Luengo-Fernandez, R.; Gray, A. M.; Rothwell, P. M. Costs of stroke using patient-level data: A critical review of the literature. Stroke 2009, 40, e18–e23.
Novakovic, R.; Toth, G.; Purdy, P. D. Review of current and emerging therapies in acute ischemic stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2009, 1, 13–26.
Hankey, G. J. Stroke. Lancet 2017, 389, 641–654.
Lee, J. M.; Grabb, M. C.; Zipfel, G. J.; Choi, D. W. Brain tissue responses to ischemia. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 106, 723–731.
Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Bluhmki, E.; Brozman, M.; Dávalos, A.; Guidetti, D.; Larrue, V.; Lees, K. R.; Medeghri, Z.; Machnig, T. et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1317–1329.
Goyal, M.; Yu, A. Y. X.; Menon, B. K.; Dippel, D. W. J.; Hacke, W.; Davis, S. M.; Fisher, M.; Yavagal, D. R.; Turjman, F.; Ross, J. et al. Endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 548–553.
Del Zoppo, G. J.; Saver, J. L.; Jauch, E. C.; Adams, H. P., Jr.; American Heart Association Stroke Council. Expansion of the time window for treatment of acute ischemic stroke with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator: A science advisory from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2009, 40, 2945–2948.
Emberson, J.; Lees, K. R.; Lyden, P.; Blackwell, L.; Albers, G.; Bluhmki, E.; Brott, T.; Cohen, G.; Davis, S.; Donnan, G. et al. Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 384, 1929–1935.
Mead, G. E.; Hsieh, C. F.; Lee, R.; Kutlubaev, M. A.; Claxton, A.; Hankey, G. J.; Hackett, M. L. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for stroke recovery. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD009286.
Mortensen, J. K.; Andersen, G. Safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment in recovering stroke patients. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2015, 14, 911–919.
Prasad, K.; Sharma, A.; Garg, A.; Mohanty, S.; Bhatnagar, S.; Johri, S.; Singh, K. K.; Nair, V.; Sarkar, R. S.; Gorthi, S. P. et al. Intravenous autologous bone marrow mononuclear stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke: A multicentric, randomized trial. Stroke 2014, 45, 3618–3624.
Kalladka, D.; Sinden, J.; Pollock, K.; Haig, C.; McLean, J.; Smith, W.; McConnachie, A.; Santosh, C.; Bath, P. M.; Dunn, L. et al. Human neural stem cells in patients with chronic ischaemic stroke (PISCES): A phase 1, first-in-man study. Lancet 2016, 388, 787–796.
Beavers, K. R.; Nelson, C. E.; Duvall, C. L. MiRNA inhibition in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 88, 123–137.
Inui, M.; Martello, G.; Piccolo, S. MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 252–263.
Caputo, M.; Saif, J.; Rajakaruna, C.; Brooks, M.; Angelini, G. D.; Emanueli, C. MicroRNAs in vascular tissue engineering and postischemic neovascularization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 88, 78–91.
Liang, T. Y.; Lou, J. Y. Increased expression of mir-34a-5p and clinical association in acute ischemic stroke patients and in a rat model. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2950–2955.
Zhao, H. P.; Wang, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, R. L.; Liu, X. R.; Gao, Z.; Tao, Z.; Xu, C. M.; Song, J. X.; Ji, X. M. et al. MiRNA-424 protects against permanent focal cerebral ischemia injury in mice involving suppressing microglia activation. Stroke 2013, 44, 1706–1713.
Buller, B.; Liu, X. S.; Wang, X. L.; Zhang, R. L.; Zhang, L.; Hozeska-Solgot, A.; Chopp, M.; Zhang, Z. G. MicroRNA-21 protects neurons from ischemic death. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 4299–4307.
Chen, Y. C.; Gao, D. Y.; Huang, L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: Challenges and strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 128–141.
Kim, J.; Cao, L.; Shvartsman, D.; Silva, E. A.; Mooney, D. J. Targeted delivery of nanoparticles to ischemic muscle for imaging and therapeutic angiogenesis. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 694–700.
Pecot, C. V.; Calin, G. A.; Coleman, R. L.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A. K. RNA interference in the clinic: Challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 59–67.
Vickers, K. C.; Remaley, A. T. Lipid-based carriers of microRNAs and intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2012, 23, 91–97.
Crooke, S. T.; Graham, M. J.; Zuckerman, J. E.; Brooks, D.; Conklin, B. S.; Cummins, L. L.; Greig, M. J.; Guinosso, C. J.; Kornbrust, D.; Manoharan, M. et al. Pharmacokinetic properties of several novel oligonucleotide analogs in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 277, 923–937.
Cheng, C. J.; Bahal, R.; Babar, I. A.; Pincus, Z.; Barrera, F.; Liu, C.; Svoronos, A.; Braddock, D. T.; Glazer, P. M.; Engelman, D. M. et al. MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour microenvironment. Nature 2015, 518, 107–110.
Davis, M. E.; Zuckerman, J. E.; Choi, C. H. J.; Seligson, D.; Tolcher, A.; Alabi, C. A.; Yen, Y.; Heidel, J. D.; Ribas, A. Evidence of RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted nanoparticles. Nature 2010, 464, 1067–1070.
Gibbings, D. J.; Ciaudo, C.; Erhardt, M.; Voinnet, O. Multivesicular bodies associate with components of miRNA effector complexes and modulate miRNA activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1143–1149.
Yang, Y. P.; Chien, Y.; Chiou, G. Y.; Cherng, J. Y.; Wang, M. L.; Lo, W. L.; Chang, Y. L.; Huang, P. I.; Chen, Y. W.; Shih, Y. H. et al. Inhibition of cancer stem cell-like properties and reduced chemoradioresistance of glioblastoma using microRNA145 with cationic polyurethane-short branch PEI. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1462–1476.
Chiou, G. Y.; Cherng, J. Y.; Hsu, H. S.; Wang, M. L.; Tsai, C. M.; Lu, K. H.; Chien, Y.; Hung, S. C.; Chen, Y. W.; Wong, C. I. et al. Cationic polyurethanes-short branch PEI-mediated delivery of Mir145 inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation and cancer stem-like properties and in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 240–250.
Kanasty, R.; Dorkin, J. R.; Vegas, A.; Anderson, D. Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 967–977.
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. J.; Gemeinhart, R. A. Progress in microRNA delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 962–974.
Hwang, D. W.; Son, S.; Jang, J.; Youn, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y. S.; Jeong, J. M.; Kim, W. J.; Lee, D. S. A brain-targeted rabies virus glycoprotein-disulfide linked PEI nanocarrier for delivery of neurogenic microRNA. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4968–4975.
Zhang, S. L.; Li, J.; Lykotrafitis, G.; Bao, G.; Suresh, S. Sizedependent endocytosis of nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 419–424.
David, S.; Pitard, B.; Benoît, J. P.; Passirani, C. Non-viral nanosystems for systemic siRNA delivery. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 100–114.
Ge, X. T.; Lei, P.; Wang, H. C.; Zhang, A. L.; Han, Z. L.; Chen, X.; Li, S. H.; Jiang, R. C.; Kang, C. S.; Zhang, J. N. miR-21 improves the neurological outcome after traumatic brain injury in rats. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6718.
Shi, S. J.; Han, L.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. R.; Sun, X. Systemic delivery of microRNA-34a for cancer stem cell therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3901–3905.
Gref, R.; Domb, A.; Quellec, P.; Blunk, T.; Müller, R. H.; Verbavatz, J. M.; Langer, R. The controlled intravenous delivery of drugs using PEG-coated sterically stabilized nanospheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 16, 215–233.
White, R. E.; Giffard, R. G. MicroRNA-320 induces neurite outgrowth by targeting ARPP-1. NeuroReport 2012, 23, 590–595.
Liu, T. L.; Li, L. L.; Fu, C. H.; Liu, H. Y.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. Q. Pathological mechanisms of liver injury caused by continuous intraperitoneal injection of silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2399–2407.
Oladipupo, S.; Hu, S.; Kovalski, J.; Yao, J. J.; Santeford, A.; Sohn, R. E.; Shohet, R.; Maslov, K.; Wang, L. V.; Arbeit, J. M. VEGF is essential for hypoxia-inducible factor-mediated neovascularization but dispensable for endothelial sprouting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13264–13269.
Zhang, P.; Lei, X. H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H. T.; Chang, L.; Li, C. L.; Liu, D. M.; Bhatta, N.; Zhang, Z. R.; Jiang, C. L. Regenerative repair of Pifithrin-a in cerebral ischemia via VEGF dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26295.
Deshpande, N.; Ren, Y.; Foygel, K.; Rosenberg, J.; Willmann, J. K. Tumor angiogenic marker expression levels during tumor growth: Longitudinal assessment with molecularly targeted microbubbles and US imaging. Radiology 2011, 258, 804–811.
Yang, Z. H.; Wang, K. K. W. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: From intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 364–374.
Yan, M.; Liang, M.; Wen, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. F.; Chen, I. S. Y. Single siRNA nanocapsules for enhanced RNAi delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13542–13545.
Liang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, G.; Wen, J.; Zhang, L. L.; Li, J.; Yuan, X. B.; Chen, I. S. Y.; Chen, W. et al. Phosphorylcholine polymer nanocapsules prolong the circulation time and reduce the immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1022–1031.
Liu, C. Y.; Wen, J.; Meng, Y. B.; Zhang, K. L.; Zhu, J. L.; Ren, Y.; Qian, X. M.; Yuan, X. B.; Lu, Y. F.; Kang, C. S. Efficient delivery of therapeutic miRNA nanocapsules for tumor suppression. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 292–297.
Gu, Z.; Yan, M.; Hu, B. L.; Joo, K. I.; Biswas, A.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y. F.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y. Protein nanocapsule weaved with enzymatically degradable polymeric network. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4533–4538.
Liu, X.; An, C. Y.; Jin, P.; Liu, X. S.; Wang, L. H. Protective effects of cationic bovine serum albumin-conjugated PEGylated tanshinone IIA nanoparticles on cerebral ischemia. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 817–830.
Pignataro, G.; Scorziello, A.; Di Renzo, G.; Annunziato, L. Postischemic brain damage: Effect of ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning and identification of potential candidates for stroke therapy. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 46–57.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFA0903801), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52073015, 51773151, 52003021, and 81671169), Tianjin Municipal Health Bureau (No. 2010KY11), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (No. 2015M580212), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. ZY2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Wen, J., Li, D. et al. Systemic delivery of microRNA for treatment of brain ischemia. Nano Res. 14, 3319–3328 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3413-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3413-8