Abstract
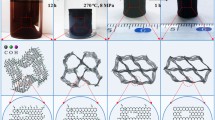
Graphene aerogels are desirable for energy storage and conversion, as catalysis supports, and as adsorbents for environmental remediation. To produce graphene aerogels with low density, while maintaining high electrical conductivity and strong mechanic performance, we synthesized graphene aerogels by the magnesiothermic reduction of a freeze-dried graphene oxide (GO) self-assembly and subsequent etching of the formed MgO in acid solution. The reduced graphene oxide (rGO) aerogel samples exhibited densities as low as 1.1 mg·cm−3. The rGO aerogel was very resilient, exhibiting full recoveryeven after being compressed by strains of up to 80%; its elastic modulus (E) scaled with density (ρ) as E∼ρ2. The rGO aerogels also exhibited high conductivities (e.g., 27.7 S·m−1 at 3.6 mg·cm−3) and outperformed many rGO aerogels fabricated by other reduction processes. Such outstanding properties were ascribed to the microstructures inherited from the freeze-dried GO self-assembly and the magnesiothermic reduction process.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K.; Morozov, S. V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S. V.; Grigorieva, I. V.; Firsov, A. A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669.
Ferrari, A. C.; Meyer, J. C.; Scardaci, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Novoselov, K. S.; Roth, S. et al. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 187401.
Geim, A. K. Graphene: Status and prospects. science 2009, 324, 1530–1534.
Lee, C.; Wei, X. D.; Kysar, J. W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388.
Balandin, A. A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W. Z.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C. N. Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907.
Zhu, Y. W.; Murali, S.; Stoller, M. D.; Ganesh, K. J.; Cai, W. W.; Ferreira, P. J.; Pirkle, A.; Wallace, R. M.; Cychosz, K. A.; Thommes, M. et al. Carbon-based supercapacitors produced by activation of graphene. Science 2011, 332, 1537–1541.
Novoselov, K. S.; Fal’ko, V. I.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P. R.; Schwab, M. G.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2012, 490, 192–200.
Orlita, M.; Faugeras, C.; Plochocka, P.; Neugebauer, P.; Martinez, G.; Maude, D. K.; Barra, A. L.; Sprinkle, M.; Berger, C.; de Heer, W. A. et al. Approaching the dirac point in high-mobility multilayer epitaxial graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 267601.
Xu, Y. X.; Sheng, K. X.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Q. Self-assembled graphene hydrogel via a one-step hydrothermal process. Acs Nano 2010, 4, 4324–4330.
Zhang, X. T.; Sui, Z. Y.; Xu, B.; Yue, S. F.; Luo, Y. J.; Zhan, W. C.; Liu, B. Mechanically strong and highly conductive graphene aerogel and its use as electrodes for electrochemical power sources. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6494–6497.
Wu, Z.-S.; Yang, S. B.; Sun, Y.; Parvez, K.; Feng, X. L.; Muellen, K. 3D nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel-supported Fe3O4 nanoparticles as efficient eletrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9082–9085.
Zhao, Y.; Hu, C. G.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. H.; Shi, G. Q.; Qu, L. T. A versatile, ultralight, nitrogen-doped graphene framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11371–11375.
Sun, H. Y.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Multifunctional, ultra-flyweight, synergistically assembled carbon aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2554–2560.
Zhao, J. P.; Ren, W. C.; Cheng, H.-M. Graphene sponge for efficient and repeatable adsorption and desorption of water contaminations. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20197–20202.
Nardecchia, S.; Carriazo, D.; Ferrer, M. L.; Gutiérrez, M. C.; del Monte, F. Three dimensional macroporous architectures and aerogels built of carbon nanotubes and/or graphene: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 794–830.
Chabot, V.; Higgins, D.; Yu, A. P.; Xiao, X. C.; Chen, Z. W.; Zhang, J. J. A review of graphene and graphene oxide sponge: Material synthesis and applications to energy and the environment. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1564–1596.
Qiu, L.; Liu, J. Z.; Chang, S. L. Y.; Wu, Y. Z.; Li, D. Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1241.
Hu, H.; Zhao, Z. B.; Wan, W. B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Qiu, J. S. Ultralight and highly compressible graphene aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2219–2223.
Worsley, M. A.; Pauzauskie, P. J.; Olson, T. Y.; Biener, J.; Satcher, J. H.; Baumann, T. F. Synthesis of graphene aerogel with high electrical conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14067–14069.
Pham, H. D.; Pham, V. H.; Cuong, T. V.; Nguyen-Phan, T. D.; Chung, J. S.; Shin, E. W.; Kim, S. Synthesis of the chemically converted graphene xerogel with superior electrical conductivity. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9672–9674.
Li, Y. R.; Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Li, C.; Hong, J.-D.; Shi, G. Q. Highly compressible macroporous graphene monoliths via an improved hydrothermal process. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4789–4793.
Lin, Y. R.; Ehlert, G. J.; Bukowsky, C.; Sodano, H. A. Superhydrophobic functionalized graphene aerogels. ACSAppl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2200–2203.
Bao, Z. H.; Weatherspoon, M. R.; Shian, S.; Cai, Y.; Graham, P. D.; Allan, S. M.; Ahmad, G.; Dickerson, M. B.; Church, B. C.; Kang, Z. T. Chemical reduction of three-dimensional silica micro-assemblies into microporous silicon replicas. Nature 2007, 446, 172–175.
Xing, A.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Z. H.; Mei, Y. F.; Gordin, A. S.; Sandhage, K. H. A magnesiothermic reaction process for the scalable production of mesoporous silicon for rechargeable lithium batteries. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6743–6745.
Hummers, W. S.; Offeman, R. E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339–1339.
Cote, L. J.; Kim, F.; Huang, J. X. Langmuir-blodgett assembly of graphite oxide single layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1043–1049.
Eda, G.; Fanchini, G.; Chhowalla, M. Large-area ultrathin films of reduced graphene oxide as a transparent and flexible electronic material. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 270–274.
Warner, J. H.; Rümmeli, M. H.; Gemming, T.; Büchner, B.; Briggs, G. A. D. Direct imaging of rotational stacking faults in few layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 102–106.
Nguyen, S. T.; Ruoff, R. S.; Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D. A.; Piner, R. D.; Kohlhaas, K. A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y. Y.; Wu, Y. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565.
Kudin, K. N.; Ozbas, B.; Schniepp, H. C.; Prud’homme, R. K.; Aksay, I. A.; Car, R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 36–41.
Liu, H. T.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y. L.; Cheng, C.; Yang, L. J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, G.; Hu, W. P.; Liu, Y. G.; Zhu, D. B. Reduction of graphene oxide to highly conductive graphene by lawesson’s reagent and its electrical applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 3104–3109.
Fernandez-Merino, M. J.; Guardia, L.; Paredes, J. I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Solis-Fernandez, P.; Martinez-Alonso, A.; Tascon, J. M. D. Vitamin C is an ideal substitute for hydrazine in the reduction of graphene oxide suspensions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6426–6432.
Salari-Sharif, L.; Schaedler, T. A.; Valdevit, L. Energy dissipation mechanisms in hollow metallic microlattices. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 1755–1770.
Schaedler, T. A.; Jacobsen, A. J.; Torrents, A.; Sorensen, A. E.; Lian, J.; Greer, J. R.; Valdevit, L.; Carter, W. B. Ultralight metallic microlattices. Science 2011, 334, 962–965.
Worsley, M. A.; Kucheyev, S. O.; Satcher, J. H.; Hamza, A. V.; Baumann, T. F. Mechanically robust and electrically conductive carbon nanotube foams. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 073115.
Liu, S. Y.; Chen, K.; Fu, Y.; Yu, S. Y.; Bao, Z. H. Reduced graphene oxide paper by supercritical ethanol treatment and itselectrochemical properties. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2012, 258, 5299–5303.
Abouimrane, A.; Compton, O. C.; Amine, K.; Nguyen, S. T. Non-annealed graphene paper as a binder-free anode forlithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 12800–12804.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material, approximately 1.86 MB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Gao, P., Bao, Z. et al. Conductive resilient graphene aerogel via magnesiothermic reduction of graphene oxide assemblies. Nano Res. 8, 1710–1717 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0672-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0672-z