Abstract
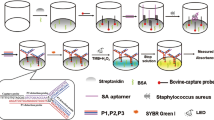
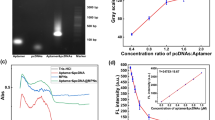
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the ubiquitous bacterial pathogens in human that are able to cause various diseases from skin infections to serious diseases. This pathogen can make seven types of bacterial toxins that are accountable for food poisoning. Moreover, the pandemic of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus has been globally dangerous for chronically infectious diseases, and nosocomial infections with life-threatening problems, because of their resistance to most antibiotics. Therefore, rapid and accurate detection of S. aureus has emerged as an urgent need in fields of clinical diagnostics, biodefense and food safety. However, the current rapid tests are challenging with being limited their capacities in on-site detection for the increase of prevention results. In this study, we report an aptamer-based sensor for fast detection of S. aureus. Instead of trying to capture bacterial cells on the substrate or nanoparticle surface, our detection method allows the DNA aptamer to detach from the silver nanoparticle when interacting with bacteria and bind to its target, leading to the aggregation of silver nanoparticle by salt. The strategy dramatically enhances the selectivity and sensitivity of whole-cell based biosensor. The results demonstrated that aptasensor could detect S. aureus with a detection limit of ~ 105 CFU/mL within 20 min. The detection method showed many advantages compared with conventional methods with respect to cost, simplicity and analysis time. This biosensor can be used as a powerful bio-analytical tool for whole-cell detection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowy FD (1998) Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 339(8):520–532
Argudín MÁ, Mendoza MC, Rodicio MR (2010) Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Toxins 2(7):1751–1773
Balaban N, Rasooly A (2000) Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Int J Food Microbiol 61(1):1–10
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2003) Outbreaks of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin infections. Los Angeles County, California, 2002–2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 52(5):88
Shahdordizadeh M, Taghdisi SM, Ansari N, Langroodi FA, Abnous K, Ramezani M (2017) Aptamer based biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sens Actuators, B Chem 241:619–635
Štěpán J, Pantůček R, Doškař J (2004) Molecular diagnostics of clinically important staphylococci. Folia Microbiol 49(4):353–386
Truong PL, Sim SJ (2015) Development of individual plasmonic nanosensors for clinical diagnosis. In: 5th international conference on biomedical engineering in Vietnam. Springer, Cham, pp 1–6
Sun Y, Long TP, Wolff A, Bang DD (2016) A novel gold nanoparticle-DNA aptamer-based plasmonic chip for rapid and sensitive detection of bacterial pathogens. In: 20th international conference on miniaturized systems for chemistry and life sciences: MicroTAS 2016. Chemical and Biological Microsystems Society, pp 1222–1223
Truong PL, Choi SP, Sim SJ (2013) Amplification of resonant Rayleigh light scattering response using immunogold colloids for detection of lysozyme. Small 9(20):3485–3492
Lai HZ, Wang SG, Wu CY, Chen YC (2015) Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by functional gold nanoparticle-based affinity surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 87(4):2114–2120
Abbaspour A, Norouz-Sarvestani F, Noori A, Soltani N (2015) Aptamer-conjugated silver nanoparticles for electrochemical dual-aptamer-based sandwich detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 68:149–155
Chang YC, Yang CY, Sun RL, Cheng YF, Kao WC, Yang PC (2013) Rapid single cell detection of Staphylococcus aureus by aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Sci Rep 3(1):1–7
Almaquer FEP, Ricacho JSY, Ronquillo RLG (2019) Simple and rapid colorimetric sensing of Ni (II) ions in tap water based on aggregation of citrate-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Sustain Environ Res 29(1):1–10
Wu WH, Li M, Wang Y, Ouyang HX, Wang L, Li CX, Cao YC, Meng QH, Lu JX (2012) Aptasensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella typhimurium. Nanoscale Res Lett 7(1):658
Li H, Rothberg L (2004) Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(39):14036–14039
Ramezani M, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2015) A novel colorimetric triple-helix molecular switch aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of tetracycline. Biosens Bioelectron 70:181–187
Paramelle D, Sadovoy A, Gorelik S, Free P, Hobley J, Fernig DG (2014) A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst 139(19):4855–4861
Balasubramanian S, Sorokulova IB, Vodyanoy VJ, Simonian AL (2007) Lytic phage as a specific and selective probe for detection of Staphylococcus aureus—a surface plasmon resonance spectroscopic study. Biosens Bioelectron 22(6):948–955
Brakstad OG, Aasbakk K, Maeland JA (1992) Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J Clin Microbiol 30(7):1654–1660
Trnčíková T, Hrušková V, Oravcová K, Pangallo D, Kaclíková E (2009) Rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food using selective enrichment and real-time PCR targeting a new gene marker. Food Anal Methods 2(4):241
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) under grant number NCM2020-28-01.
Conflicts of Interest
he authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Truong, P.L. (2022). Fast Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Using DNA Aptamer and Silver Nanoparticles. In: Van Toi, V., Nguyen, TH., Long, V.B., Huong, H.T.T. (eds) 8th International Conference on the Development of Biomedical Engineering in Vietnam. BME 2020. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 85. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75506-5_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75506-5_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-75505-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-75506-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)