Abstract
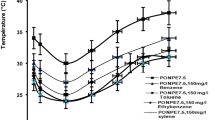
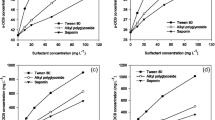
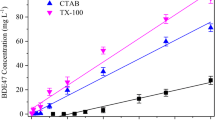
The biodegradation of diphenyl ethers (DEs) in the environment is limited by their high hydrophobicity. The enhancement of DE bioavailability by a cloud point system (CPS) was investigated in this study. Three CPSs (i.e., Triton X-114, Triton X-114 + Triton X-45, and Brij30 + TMN-3) were tested to promote DE biodegradation. Biocompatibility tests showed that the biodegradation of DE and 4-bromodiphenyl ether (4-BDE) was inhibited by TX-114, unaffected by TX-114 + TX-45, and promoted by Brij30 + TMN-3 over 48 h of cultivation with Cupriavidus basilensis and 4% (w/v) nonionic surfactants. Further optimization with 2% (w/v) Brij30 + TMN-3 yielded residual DE and 4-BDE quantities of 143 and 154 mg/L, respectively, lower than quantities in the control. During degradation, DE content did not decrease in the dilute phase, but sharply decreased in the coacervate phase, indicating that the DEs gradually diffused and transferred from the coacervate phase to the dilute phase for degradation by microbial cells. This behavior also enhanced the bioavailability of DEs in the CPS. By removing the cell-rich dilute phase and adding fresh degradation medium and DE to the coacervate phase, surfactants were successfully recovered and reused twice without affecting DE biodegradation. Results demonstrated that a CPS with 2% (w/v) Brij30 + TMN-3 not only enhanced the bioavailability of DEs, but also decreased the treatment cost through surfactant recycling, which is beneficial for large-scale applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darnerud, P. O. (2003) Toxic effects of brominated flame retardants in man and in wildlife. Environ. Int. 29: 841–853.
Hites, R. A. (2004) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: a meta-analysis of concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38: 945–956.
Darnerud, P. O., G. S. Eriksen, T. Johannesson, P. B. Larsen, and M. Viluksela (2001) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers: occurrence, dietary exposure, and toxicology. Environ. Health Persp. 109: 49–68.
Li, Y. F., W. L. Ma, and M. Yang (2015) Prediction of gas/particle partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in global air: A theoretical study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 15: 1669–1681.
Deng, W. J., J. S. Zheng, X. H. Bi, J. M. Fu, and M. H. Wong (2007) Distribution of PBDEs in air particles from an electronic waste recycling site compared with Guangzhou and Hong Kong, South China. Environ. Int. 33: 1063–1069.
Moon, H.-B., K. Kannan, S.-J. Lee, and M. Choi (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediment and bivalves from Korean coastal waters. Chemosphere 66: 243–251.
Lv, J., Y. Zhang, X. Zhao, C. Zhou, C. Guo, Y. Luo, W. Meng, G. Zou, and J. Xu (2015) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments of Liaohe River: Levels, spatial and temporal distribution, possible sources, and inventory. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22: 4256–4264.
Moeckel, C., L. Nizzetto, A. Di Guardo, E. Steinnes, M. Freppaz, G. Filippa, P. Camporini, J. Benner, and K. C. Jones (2008) Persistent organic pollutants in boreal and montane soil profiles: Distribution, evidence of processes and implications for global cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42: 8374–8380.
Huang, H., S. Wang, J. Lv, X. Xu, and S. Zhang (2016) Influences of artificial root exudate components on the behaviors of BDE-28 and BDE-47 in soils: Desorption, availability, and biodegradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 23: 7702–7711.
Zhao, Y., Y. Li, X. Qin, Q. Lou, and Z. Qin (2016) Accumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the brain compared with the levels in other tissues among different vertebrates from an ewaste recycling site. Environ. Pollut. 218: 1334–1341.
Kim, Y.-M., K. Murugesan, Y.-Y. Chang, E.-J. Kim, and Y.-S. Chang (2012) Degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by a sequential treatment with nanoscale zero valent iron and aerobic biodegradation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 87: 216–224.
Pan, Y., D. C. W. Tsang, Y. Wang, Y. Li, and X. Yang (2016) The photodegradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in various environmental matrices: Kinetics and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 297: 74–96.
Tang, S., H. Yin, S. Chen, H. Peng, J. Chang, Z. Liu, and Z. Dang (2016) Aerobic degradation of BDE-209 by Enterococcus casseliflavus: Isolation, identification and cell changes during degradation process. J. Hazard Mater. 308: 335–342.
Chen, X., G. Chen, M. Qiu, G. Sun, J. Guo, and M. Xu (2014) Synergistic degradation of deca-BDE by an enrichment culture and zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 21: 7856–7862.
Gerecke, A. C., P. C. Hartmann, N.V. Heeb, H.-P. E. Kohler, W. Giger, P. Schmid, M. Zennegg, and M. Kohler (2005) Anaerobic degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39: 1078–1083.
Zhu, B., X. Xia, S. Wu, X. Lu, and X. A. Yin (2016) Microbial bioavailability of 2,2',4,4'-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) in natural sediments from major rivers of China. Chemosphere 153: 386–393.
Chen, L., W. Zhang, R. Zhang, K. Lin, L. He, and L. Wu (2015) The bioavailability and adverse impacts of lead and decabromodiphenyl ether on soil microbial activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22: 12141–12149.
Liu, M., S. Tian, P. Chen, and L. Zhu (2011) Predicting the bioavailability of sediment-associated polybrominated diphenyl ethers using a 45-d sequential Tenax extraction. Chemosphere 85: 424–431.
Zamir, S. M., S. Babatabar, and S. A. Shojaosadati (2015) Styrene vapor biodegradation in single-and two-liquid phase biotrickling filters using Ralstonia eutropha. Chem. Eng. J. 268: 21–27.
Song, Y., F. Wang, Y. R. Bian, M. Ye, and X. Jiang (2015) Using a two-liquid-phase system to investigate the biodegradation of trichlorobenzenes. Pedosphere. 25: 169–176.
Zhang, Y., F. Wang, X. Yang, C. Gu, F. O. Kengara, Q. Hong, Z. Lv, and X. Jiang (2011) Extracellular polymeric substances enhanced mass transfer of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the two-liquid-phase system for biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 90: 1063–1071.
Muñoz, R., S. Villaverde, B. Guieysse, and S. Revah (2007) Two-phase partitioning bioreactors for treatment of volatile organic compounds. Biotechnol. Adv. 25: 410–422.
Liu, J. and X. Cao (2013) Biodegradation of microcrystalline cellulose in pH-pH recyclable aqueous two-phase systems with water-soluble immobilized cellulase. Biochem. Eng. J. 79: 136–143.
Pan, T., T. Deng, X. Zeng, W. Dong, and S. Yu (2016) Extractive biodegradation and bioavailability assessment of phenanthrene in the cloud point system by Sphingomonas polyaromaticivorans. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100: 431–437.
Castillo, A. S. R., S. Guiheneuf, R. Le Guevel, P.-F. Biard, L. Paquin, A. Amrane, and A. Couvert (2016) Synthesis and toxicity evaluation of hydrophobic ionic liquids for volatile organic compounds biodegradation in a two-phase partitioning bioreactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 307: 221–230.
Zhang, W., Z. Wang, W. Li, B. Zhuang, and H. Qi (2008) Production of L-phenylacetylcarbinol by microbial transformation in polyethylene glycol-induced cloud point system. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 78: 233–239.
Dai, Z., Z. Wang, J. H. Xu, and H. Qi (2010) Assessing bioavailability of the solubilization of organic compound in nonionic surfactant micelles by dose-response analysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 88: 327–339.
Wang, Z., J. H. Xu, and D. Chen (2008) Whole cell microbial transformation in cloud point system. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 35: 645–656.
Liang, R., Z. Wang, J. H. Xu, W. Li, and H. Qi (2009) Novel polyethylene glycol induced cloud point system for extraction and back-extraction of organic compounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 66: 248–256.
Dhamole, P. B., Z. Wang, Y. Liu, B. Wang, and H. Feng (2012) Extractive fermentation with non-ionic surfactants to enhance butanol production. Biomass Bioenerg. 40: 112–119.
Melchert, W. R. and F. R. P. Rocha (2016) Cloud point extraction in flow-based systems. Rev Anal. Chem. 35: 41–52.
Kaykhaii, M. and E. Ghasemi (2016) Micro-cloud point extraction for preconcentration of Aspirin in commercial tablets prior to spectrophotometric determination. J. Anal. Chem. 71: 844–848.
Hinze, W. L. and E. Pramauro (1993) A critical-review of surfactant-mediated phase separations (cloud-point extractions) -Theory and applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 24: 133–177.
Wang, Z. and Z. Dai (2010) Extractive microbial fermentation in cloud point system. Enz. Microb. Technol. 46: 407–418.
Wang, Z. (2007) The potential of cloud point system as a novel two-phase partitioning system for biotransformation. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 75: 1–10.
Wang, Z., F. Zhao, D. Chen, and D. Li (2005) Cloud point system as a tool to improve the efficiency of biotransformation. Enz. Microb. Technol. 36: 589–594.
Pan, T., Z. Wang, J.-H. Xu, Z. Wu, and H. Qi (2010) Stripping of nonionic surfactants from the coacervate phase of cloud point system for lipase separation by Winsor II microemulsion extraction with the direct addition of alcohols. Proc. Biochem. 45: 771–776.
Wang, Z., J. H. Xu, R. Liang, and H. Qi (2008) A downstream process with microemulsion extraction for microbial transformation in cloud point system. Biochem. Eng. J. 41: 24–29.
Shen, L., X. Zhang, M. Liu, and Z. Wang (2014) Transferring of red Monascus pigments from nonionic surfactant to hydrophobic ionic liquid by novel microemulsion extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 138: 34–40.
Shen, L., X. Zhang, M. Liu, and Z. Wang (2014) Microemulsion extraction of Monascus pigments from nonionic surfactant using high polarity of diethyl ether as excess oil phase. Separ. Sci. Technol. 49: 2346–2351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, T., Liu, C., Xin, Q. et al. Extractive biodegradation of diphenyl ethers in a cloud point system: Pollutant bioavailability enhancement and surfactant recycling. Biotechnol Bioproc E 22, 631–636 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-017-0085-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-017-0085-4