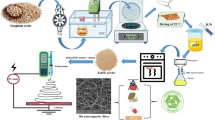
Abstract
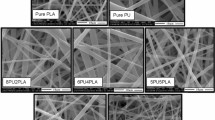
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) acquires excellent properties while possessing poor processability. Blending low molecular weight polyethylene disentangles the molecular chain of UHMWPE and improves its processability, improving fiber productivity. In the present study, UHMWPE and its HDPE-blended fibers were produced by a high-temperature electrospinning process, and the effect of HDPE content on fiber properties was investigated in depth. Analysis of fiber surface morphology revealed the formation of uniformly distributed nano- to microscopic pores/pits, wrinkles, and grooves on the surface of blended fibers, unlike neat UHMWPE fibers containing irregular surface bulges and pits. It suggested that the blending of HDPE affected the surface topography and the thermal and mechanical properties of electrospun fibers. The tensile strength and Young’s modulus of UHMWPE fiber improved by 142 and 102% at a 67:33 mass ratio of UHMWPE and HDPE and by 84 and 132% in the case of a 50:50 composition ratio, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of thdoneis study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Data Transparency
Authors will ensure all data transparency.
References
H.X. Wang, P.J. Hazell, K. Shankar, E.V. Morozov, J.P. Escobedo, The effectiveness of combined gripping method in tensile testing of UHMWPE single yarn. Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng Iop (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/87/1/012109
P. Smith, P.J. Lemstra, Ultra-high-strength polyethylene filaments by solution spinning/drawing. J. Mater. Sci. 15, 505–514 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02396802
P. Nayak, A.K. Ghosh, N. Bhatnagar, Study of dynamic compressive responses of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene felt impregnated with shear thickening fluid. Polym. Compos. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26335
Y. Cai, Q. Wei, F. Huang, Processing of composite functional nanofibers. Woodhead Publ Ltd (2012). https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857095640.1.38
R.V. Gundloori, A. Singam, N. Killi, Nanobased intravenous and transdermal drug delivery systems, in Applications of targeted nano drugs and delivery systems. ed. by R.V. Gundloori (Elsevier Inc, USA, 2019)
I.C. Um, D. Fang, B.S. Hsiao, A. Okamoto, B. Chu, Electro-spinning and electro-blowing of hyaluronic acid. Biomacromol 5, 1428–1436 (2004)
S.Y. Gu, Q.L. Wu, J. Ren, G.J. Vancso, Mechanical properties of a single electrospun fiber and its structures. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 26, 716–720 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.200400667
M. Forouharshad, O. Saligheh, R. Arasteh, R.E. Farsani, Manufacture and characterization of poly (butylene terephthalate) nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 49, 833–842 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/00222341003609377
Z.M. Huang, Y.Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, S. Ramakrishna, A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 63, 2223–2253 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00178-7
R. Nayak, R. Padhye, L. Arnold, Melt-electrospinning of nanofibers. Elsevier Ltd. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100907-9.00002-7
R. Casasola, N.L. Thomas, A. Trybala, S. Georgiadou, Electrospun poly lactic acid (PLA) fibres: Effect of different solvent systems on fibre morphology and diameter. Polymer (Guildf). 55, 4728–4737 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.06.032
X. Shi, W. Zhou, D. Ma, Q. Ma, D. Bridges, Y. Ma, A. Hu, Electrospinning of nanofibers and their applications for energy devices. J. Nanomater. 2015, 20 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/140716
T. Subbiah, G.S. Bhat, R.W. Tock, S. Parameswaran, S.S. Ramkumar, Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 96, 557–569 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.21481
S. Ramakrishna, K. Fujihara, W.E. Teo, T. Yong, Z. Ma, R. Ramaseshan, Electrospun nanofibers: solving global issues. Mater. Today. 9, 40–50 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(06)71389-X
K. Molnar, L.M. Vas, T. Czigany, Determination of tensile strength of electrospun single nanofibers through modeling tensile behavior of the nanofibrous mat. Compos. Part B Eng. 43, 15–21 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.04.024
J.M. Deitzel, J. Kleinmeyer, D. Harris, N.C. Beck Tan, The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun. Polymer 42, 261–272 (2001)
C. Zhang, T. Zhai, L.S. Turng, Electrospinning of poly(lactic acid)/polycaprolactone blends: Investigation of the governing parameters and biocompatibility. J. Polym. Eng. 38, 409–417 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2017-0194
B.K. Tarus, N. Fadel, A. Al-Oufy, M. El-Messiry, Investigation of mechanical properties of electrospun poly (vinyl chloride) polymer nanoengineered composite. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1558925020982569
P. Chavoshnejad, O. Alsmairat, C. Ke, M.J. Razavi, Effect of interfiber bonding on the rupture of electrospun fibrous mats. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 54, 025302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abba95
A.M. Azam, A. Ali, H. Khan, T. Yasin, M.S. Mehmood, Analysis of degradation in UHMWPE a comparative study among the various commercial and laboratory grades UHMWPE. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 146, 012025 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/146/1/012025
Y. Li, H. He, Y. Ma, Y. Geng, J. Tan, Rheological and mechanical properties of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/high density polyethylene/polyethylene glycol blends. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2, 51–60 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aiepr.2018.08.004
M. Hussain, R.A. Naqvi, N. Abbas, S.M. Khan, S. Nawaz, A. Hussain, N. Zahra, M.W. Khalid, Ultra-high-molecular-weight-polyethylene (UHMWPE) as a promising polymer material for biomedical applications: a concise review. Polymers (Basel). 12, 1–28 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020323
C.R. Silva, R.M. Lago, H.S. Veloso, P.S.O. Patricio, Use of amphiphilic composites based on clay/carbon nanofibers as fillers in UHMWPE. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 29, 278–284 (2018). https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20170138
F. Wang, L. Liu, P. Xue, M. Jia, Crystal structure evolution of UHMWPE/HDPE blend fibers prepared by melt spinning. Polymers (Basel). 9, 96 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030096
G. Shi, Z. Cao, X. Yan, Q. Wang, In-situ fabrication of a UHMWPE nanocomposite reinforced by SiO2 nanospheres and its tribological performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 236, 121778 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121778
H. Shen, L. He, C. Fan, B. Xie, W. Yang, M. Yang, Effective dissolution of UHMWPE in HDPE improved by high temperature melting and subsequent shear. Polym. Eng. Sci. 55, 270–276 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.23898
S.S. Khasraghi, M. Rezaei, Preparation and characterization of UHMWPE/HDPE/MWCNT melt-blended nanocomposites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 28, 305–326 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705713484745
K. Ravi, Y. Ichikawa, T. Deplancke, K. Ogawa, O. Lame, J.Y. Cavaille, Development of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) coating by cold spray technique. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 24, 1015–1025 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0276-5
W. Yang, Y. Bin, H. Wang, Z. Ge, Rheological properties of UHMWPE/HDPE blend gels and morphology and mechanical properties of gel-spun fibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 61, 2127–2136 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25740
J.K. Keum, F. Zuo, B.S. Hsiao, Formation and stability of shear-induced shish-kebab structure in highly entangled melts of UHMWPE/HDPE blends. Macromolecules 41, 4766–4776 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma800063e
P. Nayak, A.K. Ghosh, N. Bhatnagar, Investigation of Solution Rheology in Electrospinning of Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Fibers Polym. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-0374-6
T.J. Sill, H.A. von Recum, Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 29, 1989–2006 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.01.011
Y.C. Zeng, Z.G. Pei, X.H. Wang, Numerical simulation of whipping process in electrospinning, Proc. 8th Wseas Int. Conf. Appl. Comput. Appl. Comput. Sci. 2, 309–317 (2009)
M.A. Ghalia, Y. Dahman, Advanced nanobiomaterials in tissue engineering: Synthesis, properties, and applications, in Advanced nanobiomaterials in tissue engineering. ed. by M.A. Ghalia (Elsevier Inc, USA, 2016)
H. Tang, B. Yi, X. Wang, Y. Shen, Y. Zhang, Understanding the cellular responses based on low-density electrospun fiber networks. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 119, 111470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111470
Y. Tang, R. Yang, Z. Du, F. Zeng, Experimental study of formation damage caused by complete water vaporization and salt precipitation in sandstone reservoirs. Transp. Porous Media. 107, 205–218 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-014-0433-1
D. Li, M.W. Frey, Y.L. Joo, Characterization of nanofibrous membranes with capillary flow porometry. J. Memb. Sci. 286, 104–114 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.09.020
J.M. Ameer, P.R. Anil Kumar, N. Kasoju, Strategies to tune electrospun scaffold porosity for effective cell response in tissue engineering. J. Funct. Biomater. 10, 1–21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb10030030
M. Ahmad, M.U. Wahit, M.R.A. Kadir, K.Z.M. Dahlan, M. Jawaid, Thermal and mechanical properties of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/high-density polyethylene/polyethylene glycol blends. J. Polym. Eng. 33, 599–614 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2012-0142
H. Zhang, Y. Liang, Extrusion Processing of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Extrus. Met. Polym. Food Prod. (2018). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.72212
A. De, A. Lucas, J.D. Ambrósio, H. Otaguro, L.C. Costa, J.A.M. Agnelli, Abrasive wear of HDPE/UHMWPE blends. Wear 270, 576–583 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.011
J.M. Sustaita-Rodríguez, F.J. Medellín-Rodríguez, D.C. Olvera-Mendez, A.J. Gimenez, G. Luna-Barcenas, Thermal stability and early degradation mechanisms of high-density polyethylene, polyamide 6 (Nylon 6), and polyethylene terephthalate. Polym. Eng. Sci. 59, 2016–2023 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25201
J. Diani, K. Gall, Finite Strain 3D thermoviscoelastic constitutive model. Society. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen
P. Nayak, A.K. Ghosh, N. Bhatnagar, Enhancement of electrospun UHMWPE fiber performance through post-processing treatment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 140, e54221 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.54221
K.L.K. Lim, Z.A.M. Ishak, U.S. Ishiaku, A.M.Y. Fuad, A.H. Yusof, T. Czigany, B. Pukanszky, D.S. Ogunniyi, High-density polyethylene/ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene blend. I. The processing, thermal, and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 97, 413–425 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.21298
T.U. Rashid, R.E. Gorga, W.E. Krause, Mechanical properties of electrospun fibers a critical review. Adv. Eng. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202100153
R. Erdem, I. Usta, M. Akalin, O. Atak, M. Yuksek, A. Pars, The impact of solvent type and mixing ratios of solvents on the properties of polyurethane based electrospun nanofibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 334, 227–230 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.10.123
Funding
No funding was received to conduct this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, P., Ghosh, A.K. & Bhatnagar, N. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Mat of Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene/High-Density Polyethylene Blends. Fibers Polym 24, 3421–3433 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00286-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00286-6