Abstract
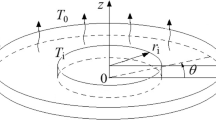
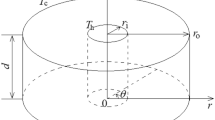
In order to understand surface heat dissipation dependence of thermocapillary convection for moderate Prandtl number fluid in a deep annular pool, a series of three-dimensional numerical simulations have been carried out by using the finite volume method. The radius ratio and the aspect ratio of an annular pool are fixed at 0.5 and 1.0, respectively. The working fluid is 0.65cSt silicone oil with Prandtl number of 6.7. Surface heat dissipation Biot (Bi) number is varied from 0 to 50. Results indicate that with the increase of Biot number, the radial temperature gradient near the inner cylindrical wall decreases, and near the outer cylindrical wall it increases, so the flow is enhanced. When 0 < Bi < 10, with the increase of Marangoni number, the axisymmetric steady flow first transits to the standing wave, and then to the azimuthal waves. The standing wave should be attributed to Marangoni-Bénard instability. However, the azimuthal waves should be corresponded to hydraulic instability, which is mainly driven by the azimuthal motion of temperature fluctuation from the sudden change of flow direction near the bottom and the inner cylindrical wall. When Bi ≥ 10, when the flow destabilizes, the axisymmetric steady flow transits directly to the azimuthal waves. With the increase of Biot number, the critical Marangoni number of the flow destabilization increases. Furthermore, the fundamental frequency and the wave number of three-dimensional oscillatory flow increase gradually with the increase of Biot number.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bi :
-
Biot number
- d :
-
Depth of annular pool, m
- f :
-
Oscillatory frequency, Hz
- F :
-
Dimensionless oscillatory frequency
- h :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient, W/(m2·K)
- m :
-
Wave number
- Ma :
-
Marangoni number
- p :
-
Pressure, Pa
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- r :
-
Radius, m
- R :
-
Dimensionless radius
- t :
-
Time, s
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- u :
-
Radial velocity, m/s
- U :
-
Dimensionless radial velocity
- v :
-
Azimuthal velocity, m/s
- V :
-
Dimensionless azimuthal velocity
- V :
-
Dimensionless velocity vector
- w :
-
Axial velocity, m/s
- W :
-
Dimensionless axial velocity
- z :
-
Axial coordinate, m
- Z :
-
Dimensionless axial coordinate
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity, m2/s
- ε :
-
Aspect ratio
- γ T :
-
Temperature coefficient of surface tension, N/(m·K)
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity, W/(m·K)
- η :
-
Radius ratio
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity, kg/(m·s)
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity, m2/s
- Θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- ρ :
-
Density, kg/m3
- τ :
-
Dimensionless time
- ψ :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- 0:
-
Ambient
- c:
-
Cold
- h:
-
Hot
- i:
-
Inner
- o:
-
Outer
- p:
-
Period
References
Burguete, J., Mukolobwiez, N., Daviaud, F., Garnier, N., Chiffaudel, A.: Buoyant-thermocapillary instabilities in extended liquid layers subjected to a horizontal temperature gradient. Phys. Fluids. 13, 2773–2787 (2001)
Carpenter, B.M., Homsy, G.M.: High Marangoni number convection in a square cavity. Phys. Fluids. 2, 137–149 (1989)
Chen, J.C., Li, Y.R., Yu, J.J., Zhang, L., Wu, C.M.: Flow pattern transition of thermal-solutal capillary convection with the capillary ratio of −1 in a shallow annular pool. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 95, 1–6 (2016)
Colinet, P., Legros, J.C., Velarde, M.G.: Nonlinear Dynamics of Surface-Tension-Driven Instabilities. Wiley-VCH Verlag Berlin GmbH, Berlin (2001)
Daviaud, F., Vince, J.M.: Traveling waves in a fluid layer subjected to a horizontal temperature gradient. Phys. Rev. E. 48, 4432–4436 (1993)
Duan, L.S., Duan, L., Jiang, L., Kang, Q.: Oscillation transition routes of buoyant-thermocapillary convection in annular liquid layers. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 865–876 (2018)
Garnier, N., Chiffaudel, A.: Two dimensional hydrothermal waves in an extend cylindrical vessel. Eur. Phys. J. B. 19, 87–95 (2001)
Gillon, P., Homsy, G.M.: Combined thermocapillary-buoyancy convection in a cavity: an experimental study. Phys. Fluids. 8, 2953–2963 (1996)
Hoyas, S., Fajardo, P., Gil, A., Perez-Quiles, M.J.: Analysis of bifurcations in a Bénard-Marangoni problem: gravitational effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 73, 33–41 (2014)
Hoyas, S., Fajardo, P., Gil, A., Perez-Quiles, M.J.: Influence of geometrical parameters on the linear stability of a Bénard-Marangoni problem. Phys. Rev. E. 93, 043105 (2016)
Jing, C.J., Imaishi, N., Yasuhiro, S., Miyazawa, Y.: Three-dimensional numerical simulation of spoke pattern in oxide melt. J. Cryst. Growth. 200, 204–212 (1999)
Kamotani, Y., Ostrach, S., Masud, J.: Microgravity experiments on oscillatory thermocapillary flow in cylindrical containers. J. Fluid Mech. 410, 211–233 (2000)
Lappa, M.: Thermal Convection: Patterns, Evolution and Stability. Wiley, Hoboken (2009)
Li, Y.R., Peng, L., Wu, S.Y., Shi, W.Y.: Effect of crystal rotation on thermocapillary flow in a shallow molten silicon pool. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 19(3–4), 163–164 (2007)
Li, Y.R., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Yu, J.J.: Experimental study on Prandtl number dependence of thermocapillary-buoyancy convection in Czochralski configuration with different depths. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 130, 168–182 (2018)
Liu, Q.S., Wang, Y., Ji, Y.: Coupling mechanism of evaporation phase change and interfacial flow. J. Eng. Thermophys. 31, 1751–1754 (2010)
Peng, L., Li, Y.R., Shi, W.Y., Imaishi, N.: Three-dimensional thermocapillary-buoyancy flow of silicone oil in a differentially heated annular pool. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 872–880 (2007)
Qin, T.R., Grigoriev, R.O.: The effect of noncondensables on buoyancy -thermocapillary convection of volatile fluids in confined geometries. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 90, 678–688 (2015)
Qin, T.R., Tukovic, Z., Grigoriev, R.O.: Buoyancy-thermocapillary convection of volatile fluids under their vapors. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 80, 38–49 (2015)
Sakhy, R.E., Omari, K.E., Le Guer, Y., Blancher, S.: Rayleigh-Bénard-Marangoni convection in an open cylindrical container heated by a non-uniform flux. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 86, 198–209 (2014)
Schwabe, D., Benz, S.: Thermocapillary flow instabilities in an annulus under microgravity - results of the experiment magia. Adv. Space Res. 29(4), 629–638 (2002)
Schwabe, D., Moeller, U., Schneider, J., Scharmann, A.: Instabilities of shallow dynamic thermocapillary liquid layers. Phys. Fluids. 4, 2368–2381 (1992)
Schwabe, D., Zebib, A., Sim, B.C.: Oscillatory thermocapillary convection in open cylindrical annuli. Part 1. Experiments under microgravity. J. Fluid Mech. 491, 239–258 (2003)
Shevtsova, V.M., Legros, J.C.: Instability in thin layer of liquid confined between rigid walls at different temperatures. Acta Astronaut. 52, 541–549 (2003)
Shevtsova, V.M., Nepomnyashchy, A.A., Legros, J.C.: Thermocapillary-buoyancy convection in a shallow cavity heated from the side. Phys. Rev. E. 67, 066308 (2003)
Sim, B.C., Zebib, A.: Effect of free surface heat loss and rotation on transition to oscillatory thermocapillary convection. Phys. Fluids. 14, 225–231 (2002)
Sim, B.C., Zebib, A., Schwabe, D.: Oscillatory thermocapillary convection in open cylindrical annuli. Part 2. Simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 491, 259–274 (2003)
Smith, M.K.: Instability mechanisms in dynamic thermocapillary liquid layers. Phys. Fluids. 29(10), 3182–3186 (1986)
Smith, M.K., Davis, S.H.: Instabilities of dynamic thermocapillary liquid layers. 1. Convective instabilities. J. Fluid Mech. 132, 119–144 (1983)
Villers, D., Platten, J.K.: Coupled buoyancy and Marangoni convection in acetone: experiments and comparison with numerical simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 234, 487–510 (1991)
Yu, J.J., Ruan, D.F., Li, Y.R., Chen, J.C.: Experimental study on thermocapillary convection of binary mixture in a shallow annular pool with radial temperature gradient. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 61, 79–86 (2015)
Yu, J.J., Zhang, L., Li, Y.R., Chen, J.C.: Numerical simulations of thermocapillary flow of a binary mixture with the Soret effect in a shallow annular pool. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 1–10 (2016)
Zhang, L., Li, Y.R., Wu, C.M.: Effect of surface evaporation on steady thermocapillary convection in an annular pool. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28(5), 499–509 (2016)
Zhang, L., Li, Y.R., Wu, C.M., Liu, Q.S.: Flow pattern transition and destabilization mechanism of thermocapillary convection for low Prandtl number fluid in a deep annular pool with surface heat dissipation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 126, 118–127 (2018a)
Zhang, L., Luo, J.Q., Wu, C.M., Yu, J.J., Li, Y.R.: Thermocapillary convection in a binary mixture with moderate Prandtl number in a shallow annular pool. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 33–42 (2018b)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51776022) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2018CDXYDL0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Thirty Years of Microgravity Research - A Topical Collection Dedicated to J. C. Legros
Guest Editor: Valentina Shevtsova
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Li, YR., Wu, CM. et al. Surface Heat Dissipation Dependence of Thermocapillary Convection of Moderate Prandtl Number Fluid in an Annular Pool. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31, 527–539 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-9680-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-9680-7