Abstract
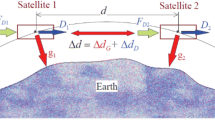
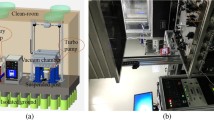
The idea of using space laser interferometer to measure the relative displacement change between two satellites has been considered for space gravitational waves detection and Earth gravity filed mapping in recent years. Some investigations on the key issues of laser interferometer in our working team have been presented in this paper. An on-ground laser interferometer prototype used for the demonstration of satellite-to-satellite ranging has been constructed, which is equipped with phasemeter, laser pointing modulation and laser phase-locking control. The experimental results show that path-length measurement sensitivity of the laser interferometer reaches 200 pm/√ Hz, and phase measurement precision achieves 2π × 10− 5 rad/√ Hz, and laser pointing modulation precision is better than 80 nrad/√ Hz, and laser phase-locking control precision attains 2π × 10− 4 rad/√ Hz within the frequency regime of 1 mHz–1 Hz. All of these demonstrate that the proposed laser interferometer has very promising feasibility to meet the requirement of the Taiji, TianQin and Space Advanced Gravity Measurement (SAGM) missions which are put forward by Chinese scientists.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, B.P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T.D., et al.: GW151226: Observation of gravitational waves from a 22-solar-mass binary black hole coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116(24), 241103 (2016a)
Abbott, B.P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T.D., et al.: Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116(6), 061102 (2016b)
Abbott, B.P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T.D., et al.: GW170104: observation of a 50-solar-mass binary black hole coalescence at Redshift 0.2. arXiv:1706.01812 (2017)
Bender, P.L.: Wavefront distortion and beam pointing for LISA. Class. Quantum Grav. 22(10), S339–S346 (2005)
Bender, P.L., Nerem, R.S., Wahr, J.M.: Possible future use of laser gravity gradiometers. In: Earth Gravity Field from Space—from Sensors to Earth Sciences, pp 385–392. Springer, Netherlands (2003)
Bender, P.L., Begelman, M.C., Gair, J.R.: Possible LISA follow-on mission scientific objectives. Class. Quantum Grav. 30(16), 165017 (2013)
Bykov, I., Delgado, J.J.E., Marín, A. F. G., Heinzel, G., Danzmann, K.: LISA phasemeter development: Advanced prototyping. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 154(1), 012017 (2009)
Cyranoski, D: Chinese gravitational-wave hunt hits crunch time. Nature 531, 150–151 (2016)
Danzmann, K., LISA Study Team: LISA: laser interferometer space antenna for gravitational wave measurements. Class. Quantum Grav. 13(11A), A247–A250 (1996)
Dehne, M., Cervantes, F.G., Sheard, B., Heinzel, G., Danzmann, K.: Laser interferometer for spaceborne mapping of the Earth’s gravity field. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 154(1), 012023 (2009)
Dong, Y.H., Liu, H.S., Luo, Z.R., Li, Y.Q., Jin, G.: Methodological demonstration of laser beam pointing control for space gravitational wave detection missions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85(7), 074501 (2014)
Gerberding, O., Sheard, B., Bykov, I., Kullmann, J., Delgado, J.J.E., Danzmann, K., Heinzel, G.: Phasemeter core for intersatellite laser heterodyne interferometry: modelling, simulations and experiments. Class. Quantum Grav. 30(23), 235029 (2013)
Gong, X., Xu, S., Bai, S., Cao, Z., Chen, G., Chen, Y., He, X., Heinzel, G., Lau, Y.K., Liu, C., Luo, J., Luo, Z., Patón, A.P., Rüdiger, A., Shao, M., Spurzem, R., Wang, Y., Xu, P., Yeh, H.C., Yuan, Y., Zhou, Z.: A scientific case study of an advanced LISA mission. Class. Quantum Grav. 28(9), 094012 (2011)
Heinzel, G.: Satellite interferometry from LTP and GRACE Follow-On to LISA. In: International Symposium on Gravitational Waves. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (2017)
Heinzel, G., Braxmaier, C., Schilling, R., Rüdiger, A., Robertson, D., Te Plate, M., Wand, V., Arai, K., Johann, U., Danzmann, K.: Interferometry for the LISA technology package (LTP) aboard SMART-2. Class. Quantum Grav. 20(10), S153–S161 (2003)
Heinzel, G., Wand, V., Garcia, A., Jennrich, O., Braxmaier, C., Robertson, D., Middleton, K., Hoyland, D., Rüdiger, A., Schilling, R., Johann, U., Danzmann, K.: The LTP interferometer and phasemeter. Class. Quantum Grav. 21(5), S581 (2004)
Heinzel, G., Braxmaier, C., Danzmann, K., Gath, P., Hough, J., Jennrich, O., Johann, U., Rüdiger, A., Sallusti, M., Schulte, H.: LISA interferometry: recent developments. Class. Quantum Grav. 23(8), S119 (2006)
Lhermite, J., Desfarges-Berthelemot, A., Kermene, V., Barthelemy, A.: Passive phase locking of an array of four fiber amplifiers by an all-optical feedback loop. Opt. Lett. 32(13), 1842–1844 (2007)
Li, Y.Q., Luo, Z.R., Liu, H.S., Dong, Y.H., Jin, G.: Laser interferometer used for satellite–satellite tracking: an on-ground methodological demonstration. Chin. Phys. Lett. 29(7), 079501 (2012)
Liang, Y.R., Duan, H.Z., Yeh, H.C., Luo, J.: Fundamental limits on the digital phase measurement method based on cross-correlation analysis. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83(9), 095110 (2012)
Liu, H.S., Dong, Y.H., Li, Y.Q., Luo, Z.R., Jin, G.: The evaluation of phasemeter prototype performance for the space gravitational waves detection. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85(2), 024503 (2014)
Nagano, S., Yoshino, T., Kunimori, H., Hosokawa, M., Kawamura, S., Sato, T., Ohkawa, M.: Displacement measuring technique for satellite-to-satellite laser interferometer to determine Earth’s gravity field. Meas. Sci. Technol. 15(12), 2406–2411 (2004)
Nagano, S., Hosokawa, M., Kunimori, H., Yoshino, T., Kawamura, S., Ohkawa, M., Sato, T.: Development of a simulator of a satellite-to-satellite interferometer for determination of the Earth’s gravity field. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76(12), 124501 (2005)
Olivier, C., Christian, S., Luca, M., Roger, H., Pierluigi, S.: A spaceborne gravity gradiometer concept based on cold atom interferometers for measuring Earth’s gravity field. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 26(3), 139–145 (2014)
Pierce, R., Leitch, J., Stephens, M., Bender, P., Nerem, R.: Intersatellite range monitoring using optical interferometry. Appl. Opt. 47(27), 5007–5019 (2008)
Sascha, K., Christian, V., Andreas, R., et al.: Miniaturized lab system for future cold atom experiments in microgravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29(1–2), 37–48 (2017)
Schumaker, B.L.: Disturbance reduction requirements for LISA. Class. Quantum Grav. 20(10), S239–S253 (2003)
Shaddock, D., Ware, B., Halverson, P.G., Spero, R.E., Klipstein, B.: Overview of the LISA Phasemeter. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 873(1), 654–660 (2006)
Sheard, B.S., Heinzel, G., Danzmann, K., Shaddock, D.A., Klipstein, W.M., Folkner, W.M.: Intersatellite laser ranging instrument for the GRACE follow-on mission. J. Geodyn. 86(12), 1083–1095 (2012)
Yeh, H.C., Yan, Q.Z., Liang, Y.R., Wang, Y., Luo, J.: Intersatellite laser ranging with homodyne optical phase locking for Space Advanced Gravity Measurements mission. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82(4), 044501 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDB23030200, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 61575209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Approaching the Chinese Space Station - Microgravity Research in China
Guest Editors: Jian-Fu Zhao, Shuang-Feng Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Luo, Z., Liu, H. et al. Laser Interferometer for Space Gravitational Waves Detection and Earth Gravity Mapping. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 817–829 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9624-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9624-7