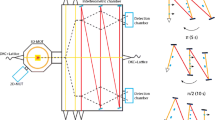
Abstract
We propose a concept for future space gravity missions using cold atom interferometers for measuring the diagonal elements of the gravity gradient tensor and the spacecraft angular velocity. The aim is to achieve better performance than previous space gravity missions due to a very low white noise spectral behavior and a very high common mode rejection, with the ultimate goals of determining the fine structures of the gravity field with higher accuracy than GOCE and detecting time-variable signals in the gravity field better than GRACE.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tapley, B., et al.: GRACE measurements of mass variability in the Earth system, Science (New York NY) 305(5683), 503505 (2004)
Reigber, C., et al.: The CHAMP geopotential mission. Bolletino di Geosica Teorica ed Applicata 40, 285–289 (1999)
Floberghagen, R., et al.: Mission design, operation and exploitation of the gravity field and steady-state ocean circulation explorer mission. J. Geodesy 85, 749–758 (2011)
Sheard, B., et al.: Intersatellite laser ranging instrument for the GRACE follow-on mission. J. Geodesy 86(12), 1083–1095 (2012)
Silvestrin, P., et al.: The future of the satellite gravimetry after the GOCE mission. Int. Assoc. Geodesy Symp. 136, 223–230 (2012)
Zhu, Z., et al.: Electrostatic gravity gradiometer design for the future mission. Adv. Space Res. 51, 2269–2276 (2013)
Peters, A., et al.: High-precision gravity measurements using atom interferometry. Metrologia 38, 25–61 (2001)
Sorrentino, F., et al.: Sensitivity limits of a Raman atom interferometer as a gravity gradiometer. Phys. Rev. A 89, 023607 (2014)
Wu, X.: Gravity gradient survey with a mobile atom interferometer, Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University (2009)
Bidel, Y., et al.: Compact cold atom gravimeter for field applications. App. Phys. Let. 102 (2013)
Yu, N., et al.: Development of an atom-interferometer gravity gradiometer for gravity measurement from space. Appl. Phys. B 84, 647 (2006)
Sorrentino, F., et al.: A compact atom interferometer for future space missions. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 22(4), 551–561 (2010)
Geiger, R., et al.: Detecting inertial effects with airborne matter-wave interferometry. Nat. Commun. 2, 474 (2011)
Müntinga, H., et al.: Interferometry with bose-einstein condensates in microgravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 093602 (2013)
Jiang, Z., et al.: On the gravimetric contribution to the redefinition of the kilogram. Metrologia 50, 452–471 (2013)
Bonin, A., et al.: Simultaneous dual-species matter-wave accelerometer. Phys. Rev. A 88, 043615 (2013)
Barrett, B., et al.: Mobile and Remote Inertial Sensing with Atom Interferometers, Proceedings of the Enrico Fermi International School of Physics Enrico Fermi, Course 188,Varenna (2013)
Dickerson, S.M., et al.: Multiaxis Inertial Sensing with Long-Time Point Source Atom Interferometry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 083001 (2013)
Canuel, B., et al.: Six-Axis Inertial Sensor Using Cold-Atom Interferometry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 010402 (2006)
Kasevich, M.A., Chu, S.: Atomic interferometry using stimulated Raman transitions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 181–184 (1991)
Lévèque, T., et al.: Enhancing the area of a Raman atom interferometer using a versatile double-diffraction technique. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 080405 (2009)
Giese, E., et al.: Double Bragg diffraction: A tool for atom optics. Phys. Rev. A 88, 053608 (2013)
Tino, G.M., et al.: Precision Gravity Tests with Atom Interferometry in Space. Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) 243-244, 203–217 (2013)
Bordé, C.J.: Theoretical tools for atom optics and interferometry. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris, t.2 Srie IV, 509–530 (2001)
Roura, A., et al.: Overcoming loss of contrast in atom interferometry due to gravity gradients (2014). arXiv:1401.7699v1
Biedermann, G.W., et al.: Low-noise simultaneous fluorescence detection of two atomic states. Opt. Lett. 34, 3 (2009)
Schoser, J., et al.: Intense source of cold Rb atoms from a pure two-dimensional magneto-optical trap. Phys. Rev. A 66, 023410 (2002)
Chiow, S.W., et al.: 102hk large area atom interferometers. PRL 107, 130403 (2011)
van Zoest, T., et al.: Bose-Einstein Condensation in Microgravity. Science 328(5985), 1540–1543 (2010)
Louchet-Chauvet, A., et al.: The influence of transverse motion within an atomic gravimeter. New. J. Phys. 13, 065025 (2011)
Gross, C.: Spin, squeezing entanglement and quantum metrology with Bose-Einstein condensates. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 45, 103001 (2012)
Haine, S.A.: Information-recycling beam splitters for quantum enhanced atom interferometry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 053002 (2013)
Vanier, J.: Transfer of frequency stability from an atomic frequency reference to a quartz-crystal oscillator. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 28, 3 (1979)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge useful discussions with Bruno Leone during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carraz, O., Siemes, C., Massotti, L. et al. A Spaceborne Gravity Gradiometer Concept Based on Cold Atom Interferometers for Measuring Earth’s Gravity Field. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 26, 139–145 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-014-9385-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-014-9385-x