Abstract
Eutrophication and water pollution have become serious aquatic environmental problems worldwide. In this study, four different water quality indexing methods, the Canadian Council of Ministers of Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI), the revised Comprehensive Pollution Index (CPI), the Eutrophication Index (EI), and the Trophic State Index (TSI), were used to investigate water quality and trophic status in the Tri An Reservoir (TAR), Vietnam. Nineteen water variables were monitored bimonthly between February 2018 and December 2019 to calculate these four indices. Although different input data sets were used, all the indices showed similar results in terms of water quality and eutrophic state. The CCME WQI ranged from 32 to 68 (median 36–48), which indicated that the water quality was classified between poor and marginal and was insufficient for domestic purposes. Similarly, the water quality was ranked between slightly polluted and medium polluted based on the revised CPI index, with the median values ranging from 0.72 to 0.94. In the CCME WQI and the CPI, the major parameters that contributed to water pollution in the TAR were turbidity, dissolved oxygen (DO), total suspended solids (TSS), chemical and biological oxygen demand (BOD5), ammonium (NH4+), nitrite (NO2−), iron (Fe), lead (Pb), and coliforms. Regarding the trophic status of water, the EI ranged from 10 to 464, indicating that the reservoir was eutrophic, and the TSI values ranged from 53 to 89, indicating that the water quality was classified between light-eutrophic and hypereutrophic conditions. A temporal variation in water quality was found, with the highest levels of pollution recorded in June during the study period. Our results show that the combination of different water quality indices provides a comprehensive assessment of water quality in the TAR.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in the paper or their Supplementary Information.
References
Ahmed MS, Raknuzzaman M, Akther H, Ahmed S (2007) The role of cyanobacteria blooms in Cholera epidemic in Bangladesh. J Appl Sci 7:1785–1789
American Public Health Association (APHA) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association. Water Environment Federation, Washington DC, pp 1–2671
Brusseau ML, Walker DB, Fitzsimmons K (2019) Chapter 3—physical-chemical characteristics of water. In: Brusseau ML, Pepper IL, Gerba CP (eds) Environmental and pollution science, 3rd edn. Academic Press, pp 23–45
Bwire G, Sack DA, Kagirita A, Obala T, Debes AK, Ram M, Komakech H, George CM, Orach CG (2020) The quality of drinking and domestic water from the surface water sources (lakes, rivers, irrigation canals and ponds) and springs in Cholera prone communities of Uganda: an analysis of vital physicochemical parameters. BMC Public Health 20(1):1128
Calmuc M, Calmuc V, Arseni M, Topa C, Timofti M, Georgescu LP, Iticescu C (2020) A comparative approach to a series of physico-chemical quality indices in assessing water quality in the Lower Danube. Water 12(11):3239
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (2017) Canadian water quality (CCME WQI) guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: CCME Water Quality Index, User’s Manual–2017 Update. In: Canadian environmental quality guidelines, 1999. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg
Carlson RE (1977) A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 22(2):361–369
Chislock MF, Doster E, Zitomer RA, Wilson AE (2013) Eutrophication: causes, consequences, and controls in aquatic ecosystems. Nat Educ Knowl 4(4):10
Cuevas MH, Lugo VA, Peralta SL, Morlán MJ, Vilaclara FG, Sánchez RM, Escobar OMA, Carmona JJ (2020) Identification of key factors affecting the trophic state of four tropical small water bodies. Water 12(5):1454
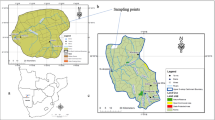
Dao TS, Nimptsch J, Wiegand C (2016) Dynamics of cyanobacteria and cyanobacterial toxins and their correlation with environmental parameters in Tri An Reservoir Vietnam. J Water Health 14:669–712
DOF (2000) Diario Oficial de la Federación, Secretaría de Salud, Modificación a la Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-127-SSA1-1994, salud ambiental. Agua para uso y consumo humano. Límites permisibles de calidad y tratamientos a que debe someterse el agua para su potabilización 22 de Noviembre de 2000. http://www.siapa.gob.mx/sites/default/files/norma_oficial.pdf. Accessed 21 Aug 2021
Duong T, Jähnichen S, Le T, Ho C, Hoang T, Nguyen T, Vu T, Dang D (2014) The occurrence of cyanobacteria and microcystins in the Hoan Kiem Lake and the Nui Coc reservoir (North Vietnam). Environ Earth Sci 71(5):2419–2427
Horton RK (1965) An index number system for rating water quality. J Water Pollu Cont Fed 37(3):300–305
Hunter PR, MacDonald AM, Carter RC (2010) Water supply and health. PLoS Med 7(11):e1000361
Ji X, Dahlgren RA, Zhang M (2016) Comparison of seven water quality assessment methods for the characterization and management of highly impaired river systems. Environ Monit Assess 188:15
Liu S, Lou S, Kuang C, Huang W, Chen W, Zhang J, Zhong G (2011) Water quality assessment by pollution-index method in the coastal waters of Hebei Province in western Bohai Sea, China. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2220–2229
Liu S, Wang L, Guo C (2020) Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in brownfield soil from Xi’an, China: an integrated analysis of man-land interrelations. PLoS ONE 15(11):e0241398
Matta G, Naik PK, Machell J, Kumar A, Tiwari AK, Kumar A (2018) Comparative study on seasonal variation in hydro-chemical parameters of Ganga River water using comprehensive pollution index (CPI) at Rishikesh (Uttarakhand) India. Desalin Water Treat 118:87–95
Mekuria DM, Kassegne AB, Asfaw SL (2021) Assessing pollution profiles along Little Akaki River receiving municipal and industrial wastewaters, Central Ethiopia: implications for environmental and public health safety. Heliyon 7(7):e07526
Mester T, Balla D, Szabó G (2020) Assessment of groundwater quality changes in the rural environment of the Hungarian Great Plain based on selected water quality indicators. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:536
Monre (2015) QCVN 08-MT:2015/BTNMT National Technical regulation on surface water quality; MONRE, Hanoi, Vietnam
Nguyen HQ, Ha NT, Pham TL (2020) Inland harmful cyanobacterial bloom prediction in the eutrophic Tri An Reservoir using satellite band ratio and machine learning approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9135–9151
Nguyen TAD, Nguyen LT, Enright A, Pham LT, Tran HYT, Tran TT, Nguyen VHT, Tran DN (2021) Health risk assessment related to cyanotoxins exposure of a community living near Tri An Reservoir, Vietnam. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14545-7
Pham L (2017) Comparison between Water Quality Index (WQI) and biological indices, based on planktonic diatom for water quality assessment in the Dong Nai River, Vietnam. Pollution 3(2):311–323
Pham TL, Dao TS, Tran ND, Nimptsch J, Wiegand C, Motoo U (2017) Influence of environmental factors on cyanobacterial biomass and microcystin concentration in the Dau Tieng Reservoir, a tropical eutrophic water body in Vietnam. Ann Limnol Int J Lim 53:89–100
Pham TL, Tran THY, Shimizu K, Li Q (2020) Utsumi M (2020) Toxic cyanobacteria and microcystin dynamics in a tropical reservoir: assessing the influence of environmental variables. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10826-9
Salcedo-Sánchez ER, GarridoHoyos SE, EstellerAlberich MV, Morales MM (2016) Application of water quality index to evaluate groundwater quality (temporal and spatial variation) of an intensively exploited aquifer (Puebla valley, Mexico). Environ Monit Assess 188:573
Sinha E, Michalak AM, Balaji V (2017) Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 357(6349):405–408
Son CT, Giang NTH, Thao TP, Nui NH, Lam NT, Cong VH (2020) Assessment of Cau River water quality assessment using a combination of water quality and pollution indices. J Water Supply Res Technol 69(2):160–172
Suring LH (2020) Freshwater: oasis of life–an overview. In: Goldstein MI, DellaSala DA (eds) Encyclopedia of the World’s Biomes. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 1–11
Terrado M, Barceló D, Tauler R, Borrell E, de Campos S (2010) Surface-water-quality indices for the analysis of data generated by automated sampling networks. TRAC Trends Anal Chem 29:40–52
Tunc DO, Telci IT, Aral MM (2013) The use of water quality index models for the evaluation of surface water quality: a case study for Kirmir Basin, Ankara, Turkey. Water Qual Expo Health 5:41–56
Uddin MG, Nash S, Olbert AI (2021) A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol Indic 122:107218
World Health Organization (WHO) (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. Geneva: World Health Organization, Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
Xu FL, Jiao Y (2019) Trophic classification for lakes. In: Fath B (ed) Encyclopedia of ecology, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 487–494
Yan CA, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Deng C, Nie N (2015) Assessment of water quality and identification of polluted risky regions based on field observations & GIS in the Honghe River watershed China. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0119130
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the assistance by the staff the Ma Da Commune People’s Committee for their assistance in the field campaigns. We thank Nguyen Vu Linh for water sample collection. Special thanks are owed to editors and anonymous referees for their valuable comments on our manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the International Foundation for Science (IFS) under grant number “I-2-A-6054-1”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization TLP. Formal analysis THYT and TTT. Investigation TLP, THYT and TTT. Methodology TLP, TTT and XQN. Preparing original draft TLP, THYT. Writing, review and editing TLP, TTT, XQN and XDN. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, T.L., Tran, T.H.Y., Tran, T.T. et al. Assessment of surface water quality in a drinking water supply reservoir in Vietnam: a combination of different indicators. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 33, 653–662 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-022-01086-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-022-01086-5