Abstract
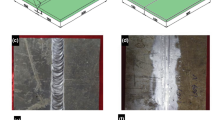
The effects of various weld geometries on the fatigue performance of T-fillet joint aluminum arc welding were investigated by conducting gas metal arc weld (GMAW) experiments using 6061-T6 material for various weld geometries. The results of the fatigue tests conducted using a 5-ton grade tester demonstrated that the fatigue performance of T-fillet joint aluminum arc welding is primarily affected by the area of the welded part and weld reinforcement. A large welded area can be obtained by full penetration, and a large weld reinforcement can be obtained by a large throat size and a small toe angle. Contrary to expectations, it was observed that optimal size and higher quantity of porosities can increase fatigue performance. This can be attributed to porosities behaving similarly to crack stop holes, which can prevent stress focusing. The deviation in fatigue performance in the case of minute penetration depth and minute throat size is not remarkable. Therefore, deeper penetration and larger weld reinforcement are crucial factors in obtaining higher fatigue performance in the industry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Cho, Weldability increase of aluminum by variable polarity arc, Journal of Welding and Joining, 32(1) (2014) 108–111.
J. Cho, J. J. Lee and S. H. Bae, Heat input analysis of variable polarity arc welding of aluminum, The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 81 (2015) 1273–1280.
H. Jeong, K. Park, S. Baek and J. Cho, Thermal efficiency decision of variable polarity aluminum arc welding through molten pool analysis, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 138 (2019) 729–737.
D. R. Askeland and W. J. Wright, Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, 4th Ed., Cengage Learning, Boston (2019) 245–247.
R. S. Florea, D. J. Bammann, A. Yeldell, K. N. Solanki and Y. Hammi, Welding parameters influence on fatigue life and microstructure in resistance spot welding of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy, Materials and Design, 45 (2013) 456–465.
A. Gean, S. A. Westgate, J. C. Kucza and J. C. Ehrstrom, Static and fatigue behavior of spot-welded 51 82-0 aluminum alloy sheet, Welding Journal, 78(3) (1999) 80s–86s.
K. V. Jata, K. K. Sankara and J. J. Ruschau, Friction stir welding effects on microstructure and fatigue of aluminum alloy 7050-T7451, Metallurgical and Materials Transaction A, 31 (2000) 2181–2192.
M. N. Ilman, Kusmono and P. T. Iswanto, Fatigue crack growth rate behaviour of friction-stir aluminium alloy AA2024-T3 welds under transient thermal tensioning, Materials and Design, 50 (2013) 235–243.
G. D’Urso, C. Giardini, S. Lorenzi and T. Pastore, Fatigue crack growth in the welding nugget of FSW joints of a 6060 aluminum alloy, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 214(10) (2014) 2075–2084.
D. G. Moghadam and K. Farhangdoost, Influence of welding parameters on fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth rate in friction stir welded nugget of 2024-T351 aluminum alloy joints, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 26(10) (2016) 2567–2585.
D. A. Wang and C. H. Chen, Fatigue lives of friction stir spot welds in aluminum 6061-T6 sheets, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 209(1) (2009) 367–375.
Y. E. Ma, Z. C. Xia, R. R. Jiang and W. Y. Li, Effect of welding parameters on mechanical and fatigue properties of friction stir welded 2198 T8 aluminum-lithium alloy joints, Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 114 (2013) 1–11.
P. C. Lin, J. Pan and T. Pan, Failure modes and fatigue life estimations of spot friction welds in lap-shear specimens of aluminum 6111-T4 sheets, part 2: welds made by a flat tool, International Journal of Fatigue, 30(1) (2008) 90–105.
H. R. Ghazvinloo, A. Honarbakhsh-Raouf and N. Shadfar, Effect of arc voltage, welding current and welding speed on fatigue life, impact energy and bead penetration of AA6061 joints produced by robotic MIG welding, Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 3(2) (2010) 156–162.
Y. Gori and R. P. Verma, Experimental fatigue life estimation of AA5083 aluminium alloys welded by two welding processes-gas metal arc (GMA) welding and friction stir welding (FSW), Journal of Graphic Era University, 5(1) (2017) 10–15.
J. da Silva, J. M. Costa, A. Loureiro and J. M. Ferreira, Fatigue behaviour of AA6082-T6 MIG welded butt joints improved by friction stir processing, Materials and Design, 51 (2013) 315–322.
C. Zhang, M. Gao and X. Zeng, Effect of microstructural characteristics on high cycle fatigue properties of laser-arc hybrid welded AA6082 aluminum alloy, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 231 (2016) 479–487.
Y. Qiao, H. Zhang, L. Zhao and Q. Feng, Fatigue crack growth properties of AA 5754 aluminum alloy gas tungsten arc welding and friction stir welding joints, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 29 (2020) 2113–2124.
J. M. Kuk, K. C. Jang, D. G. Lee and I. S. Kim, Effects of temperature and shielding gas mixture on fatigue life of 5083 aluminum alloy, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 155–156(30) (2004) 1408–1414.
P. Livieri and P. lazzarin, Fatigue strength of steel and aluminium welded joints based on generalised stress intensity factors and local strain energy values, International Journal of Fracture, 133 (2005) 247–276.
S. W. Han, H. J. Lee and S. R. Lee, Fatigue strength evaluation of butt-welded aluminum alloy component for railway vehicles, Processing of Spring Conference of Korean Society for Railway (2020) 242–249.
N. L. Person, Fatigue of aluminum alloy welded joints, Weld Journal, 50(2) (1971) 77s–87s.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No.2021R1A4A1033141) and (No.2021R1F1A1064238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jungho Cho received his Ph.D. at KAIST in 2007 and now he is a faculty of Chungbuk National University after working at Hyundai Motors and Ohio State University, USA for several years. His major is development of welding and joining techniques, welding physics and thermo-dynamical analysis of weld pool.
Sang-Woo Han is a visiting scholar of Research Institute of Industrial Science & Technology, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. He received his Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from KAIST. His research interests include arc welding, laser processing, and numerical simulation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S.W., Lee, G., Kim, H. et al. Effect of weld geometry on fatigue performance of 6061-T6 aluminum GMAW: part 3. T-fillet joint. J Mech Sci Technol 36, 5215–5221 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-022-0934-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-022-0934-8