Abstract
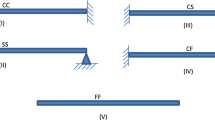
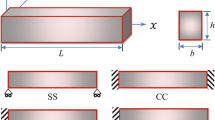
Micro/nanobeam-based resonators have found extensive applications in the micro/nanoelectromechanical system industry. Thermoelastic damping (TED) is a major energy loss issue in micro/nanobeam resonators that limits their important performance parameter, namely, the TED limited quality factor (QTED). The critical length (Lc) of a micro/nanobeam is another significant parameter that accounts for the maximum peak in the energy dissipation curve at which QTED assumes a minimum value. To evaluate QTED and Lc explicitly when the size of devices is scaled down, size effects play a decisive role and classical theories are inadequate. In this work, a higher-order theory, namely, modified couple stress theory (MCST), is used to overcome the size effects by including one internal material length scale parameter (l). The material-dependent thermoelastic coupled equations for a deflected Euler-Bernoulli microbeam are presented using variational and Hamilton principles. Moreover, the solutions for QTED are developed on the basis of a complex frequency approach with the appropriate material indices. The effects of material length scale parameters, material performance indices, mechanical boundary conditions (clamped-clamped, simply supported, and cantilever types), mode switching, and plane stress/strain conditions on QTED and Lc are analyzed. Numerical results are extracted from the analytical expressions by using MATLAB R2015a to quantify thermoelastic energy dissipation. The numerically computed QTED and Lc values are fully investigated to design high-performance resonators. The analyses verify that QTED is enhanced by optimizing the structural material and augmenting the material length scale parameter. The material order in which QTED is enhanced is the same for classical theories and MCST, i.e., it is inversely related to the TED index parameter. The influences of boundary types and mode switching on QTED are relatively less in accordance with the analysis. The effect of plane stress condition compared with that of plane strain condition on QTED is also remarkable. The Lc of the beam is determined to be dependent on the thermal diffusion length of the material used. From an adequate material point of view, poly-silicon has been proven to provide the maximum quality factor while silicon carbide yields the maximum Lc. These observations are significant and extremely helpful when designing low-loss micro/nanobeam resonators with superior performance by suitably selecting their geometry and structural materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Meinel, M. Melzer, C. Stoeckel, A. Shaporin, R. Forke, S. Zimmermann, K. Hiller, T. Otto and H. Kuhn, 2D scanning micromirror with large scan angle and monolithically integrated angle sensors based on piezoelectric thin film aluminum nitride, Sensors (MDPI), 20(22) (2020) 6599.
S. A. Razali, N. A. C. Sidik and H. Koten, Cellulose nanocrystals: a brief review on properties and general applications, Journal of Advanced Research Design, 60(1) (2019) 1–15.
Y. Li, H. Li, Y. Xiao, L. Cao and Z.-S. Guo, A compensation method for nonlinear vibration of silicon-micro resonant sensor, Sensors (MDPI), 21(7) (2021) 2545.
A. Asri, M. Izzudin, M. Hasan, M. Ahmad, Y. Yunos, M. Ali and M. Sultan, MEMS gas sensors: a review, IEEE Sensors Journal (2021) 18381–18397.
M. Mehdi, M. T. Ajani, H. Tahir, S. Tahir, Z. Alizai, F. Khan, Q. Riaz and M. Hussain, PUF-based key generation scheme for secure group communication using MEMS, Electronics, 10(14) (2021) 1691.
Z. Chen, Q. Jia, W. Liu, Q. Yuan, Y. Zhu, J. Yang and F. Yang, Dominant loss mechanisms of whispering gallery mode RFMEMS resonators with wide frequency coverage, Sensors, 20(24) (2020) 7017.
A. Persano, F. Quaranta, A. Taurino, P. A. Siciliano and J. Iannacci, Thin film encapsulation for RF MEMS in 5G and modern telecommunication systems, Sensors, 20(7) (2020) 2133.
L. Wei, X. Kuai, Y. Bao, J. Wei, L. Yang, P. Song, M. Zhang, F. Yang and X. Wang, The recent progress of MEMS/NEMS resonators, Micromachines, 12(6) (2021) 724.
R. Syms and A. Bouchaala, Mechanical synchronization of MEMS electrostatically driven coupled beam filters, Micromachines, 12(10) (2021) 1191.
R. P. Aswathy and R. Resmi, Analysis of the effects of substrate parameters on the performance of RF MEMS tunable microstrip bandpass filters, 2015 International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Communication and Computational Technologies (ICCICCT) (2015) 51–56.
Z.-Y. Tsai, P.-J. Shih, Y.-C. Tsai and C.-L. Dai, Manufacturing and testing of radio frequency MEMS switches using the complementary metal oxide semiconductor process, Sensors, 21(4) (2021) 1396.
U. S. Arathy and R. Resmi, Analysis of pull-in voltage of MEMS switches based on material properties and structural parameters, 2015 International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Communication and Computational Technologies (ICCICCT) (2015) 57–61.
Q. Bao, J. Zhang, M. Tang, Z. Huang, L. Lai, J. Huang and C. Wu, A novel PZT pump with built-in compliant structures, Sensors, 19(6) (2019) 1301.
F. Forouzandeh, A. Arevalo, A. Alfadhel and D. A. Borkholder, A review of peristaltic micropumps, Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 326 (2021) 112602.
C. Jenke, R. J. Pallejà, S. Kibler, J. Häfner, M. Richter and C. Kutter, The combination of micro diaphragm pumps and flow sensors for single stroke based liquid flow control, Sensors, 17(4) (2017) 755.
J.-S. Yoon, J. Park, H.-R. Ahn, S.-J. Yoo and Y.-J. Kim, Microfluidic airborne metal particle sensor using oil microcirculation for real-time and continuous monitoring of metal particle emission, Micromachines, 12(7) (2021) 825.
F. Xu, Y. Wei, S. Bian, H. Wang, D.-R. Chen and D. Kong, Simulation-based design and optimization of rectangular micro-cantilever-based aerosols mass sensor, Sensors, 20(3) (2020) 626.
C. Li, B. Yang, X. Guo and X. Chen, Design, analysis and simulation of a MEMS-based gyroscope with differential tunneling magnetoresistance sensing structure, Sensors, 20(17) (2020) 4919.
C. Ai, X. Zhao and D. Wen, Characteristics research of a high sensitivity piezoelectric MOSFET acceleration sensor, Sensors, 20(17) (2020) 4988.
D. Zhang, A. Cai, Y. Zhao and T. Hu, Macro modeling of V-shaped electro-thermal MEMS actuator with human error factor, Micromachines, 12(6) (2021) 622.
H. H. Hillmer, M. S. Q. Iskhandar, M. K. Hasan, S. Akhundzada, B. Al-Qargholi and A. Tatzel, MOEMS micromirror arrays in smart windows for daylight steering, J. Optical Microsystems, 1(1) (2021) 014502.
S. Finny and R. Resmi, Analysis of squeeze film damping in piston mode micromirrors, 2016 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT) (2016) 1–5.
G. S. Wood, A. Torin, A. K. Al-Mashaal, L. Smith, E. Mastropaolo, M. J. Newton and R. Cheung, Design and characterization of a micro-fabricated graphene-based MEMS microphone, IEEE Sens. J., 19 (2019) 7234–7242.
S. A. Zawawi, A. A. Hamzah, B. Y. Majlis and F. Mohd-Yasin, A review of MEMS capacitive microphones, Micromachines, 11(5) (2020) 484.
L. Herzog and K. Augsburg, Study on friction in automotive shock absorbers, part 2: validation of friction simulations via novel single friction point test rigs, Vehicles, 3(2) (2021) 197–211.
B.-H. Kang, J.-H. Hwang and S.-B. Choi, A new design model of an MR shock absorber for aircraft landing gear systems considering major and minor pressure losses: experimental validation, Applied Sciences, 11(17) (2021) 7895.
E. Amer, M. Wozniak, G. Jönsson and F. Arrhén, Evaluation of shock tube retrofitted with fast-opening valve for dynamic pressure calibration, Sensors, 21(13) (2021) 4470.
Z. Dou, J. Tang, Z. Liu, Q. Sun, Y. Wang, Y. Li, M. Yuan, H. Wu, Y. Wang, W. Pei and H. Chen, Wearable contact lens sensor for non-invasive continuous monitoring of intraocular pressure, Micromachines, 12(2) (2021) 108.
A. Henriksson, L. Kasper, M. Jäger, P. Neubauer and M. Birkholz, An approach to ring resonator biosensing assisted by dielectrophoresis: design, simulation and fabrication, Micromachines, 11(11) (2020) 954.
Ö. E. Aşırım, A. Yolalmaz and M. Kuzuoğlu, High-fidelity harmonic generation in optical micro-resonators using BFGS algorithm, Micromachines, 11(7) (2020) 686.
J.-L. Zhang, S. Liao, C. Chen, X.-T. Yang, S.-A. Lin, F. Tan, B. Li, W.-W. Wang, Z.-X. Zhong and G.-G. Zeng, Research on trimming frequency-increasing technology for quartz crystal resonator using laser etching, Micromachines, 12(8) (2021) 894.
A. Tsitlakidis, A. S. Tsingotjidou, A. Kritis, A. Cheva, P. Selviaridis, E. C. Aifantis and N. Foroglou, Atomic force microscope nanoindentation analysis of diffuse astrocytic tumor elasticity: relation with tumor histopathology, Cancers, 13(18) (2021) 4539.
E. H. C. P. Sinnecker, J. M. García-Martín, D. Altbir, E. C. J. D’Albuquerque and J. P. Sinnecker, A magnetic force microscopy study of patterned T-shaped structures, Materials, 14(6) (2021) 1567.
J. Fei, Y. Fang and Z. Yuan, Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for a micro gyroscope with backstepping controller, Micromachines, 11(11) (2020) 968.
W. Zhao, Y. Cheng, S. Zhao, X. Hu, Y. Rong, J. Duan and J. Chen, Navigation grade MEMS IMU for a satellite, Micromachines, 12(2) (2021) 151.
X. Li, B. Bhushan, K. Takashima, C.-W. Baek and Y.-K. Kim, Mechanical characterization of micro/nanoscale structures for MEMS/NEMS applications using nanoindentation techniques, Ultramicroscopy, 97(1) (2003) 481–494.
J. Yao, W. Qiang, X. Guo, H. Fan, Y. Zheng, Y. Xu and X. Yang, Defect filling method of sensor encapsulation based on micro-nano composite structure with parylene coating, Sensors, 21(4) (2021) 1107.
R. Filters-Syms and A. Bouchaala, Mechanical synchronization of MEMS electrostatically driven coupled beam filters, Micromachines, 12(10) (2021) 1191.
C. Tu, J.-Y. Lee and X.-S. Zhang, Dissipation analysis methods and Q-enhancement strategies in piezoelectric MEMS laterally vibrating resonators: a review, Sensors, 20(17) (2020) 4978.
J. E. Lee, Engineering high Q-factor MEMS resonators and probing losses, 2017 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), (2017) 439–443.
Z. Chen, T. Wang, Q. Jia, J. Yang, Q. Yuan, Y. Zhu and F. Yang, A novel Lamé mode RF-MEMS resonator with high quality factor, International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 204 (2021) 106484.
M. I. Younis and A. H. Nayfeh, Simulation of squeeze-film damping of microplates actuated by large electrostatic load, J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn., 2(3) (2007) 232–242.
S. Finny and R. Resmi, Material and geometry optimization for squeeze film damping in a micromirror, 2016 International Conference on Emerging Technological Trends (ICETT) (2016) 1–5.
Y. Zhang, L. He, J. Yang, G. Zhu, X. Jia and W. Yan, Multi-objective optimization design of a novel integral squeeze film bearing damper, Machines, 9(10) (2021) 206.
A. Albukhari and U. Mescheder, Investigation of the dynamics of a 2-DoF actuation unit cell for a cooperative electrostatic actuation system, Actuators, 10(10) (2021) 276.
P. Xu, C. Si, Y. He, Z. Wei, L. Jia, G. Han, J. Ning and F. Yang, A novel high-Q dual-mass MEMS tuning fork gyroscope based on 3D wafer-level packaging, Sensors, 21(19) (2021) 6428.
R. Resmi, M. R. Baiju and V. S. Babu, Material dependent thermoelastic damping limited quality factor analysis of disc resonators, 2017 International Conference of Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA) (2017) 675–680.
G. D. Vukasin et al., Effect of substrate thickness on anchor damping in MEMS devices, 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII (2019) 1843–1845.
S. Mol and R. Resmi, Anchor loss limited Q factor analysis of disk resonator for varying disk geometry, 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT) (2017) 1033–1037.
Y. Tong and T. Han, Anchor loss reduction of lamb wave resonator by pillar-based phononic crystal, Micromachines, 12(1) (2021) 62.
H. A. Alharthi, Characterization of the vibration and strain energy density of a nanobeam under two-temperature generalized thermoelasticity with fractional-order strain theory, Mathematical and Computational Applications, 26(4) (2021) 78.
F. Serdean, M. Pustan, C. Dudescu, C. Birleanu and M. Serdean, Analysis of the thermoelastic damping effect in electrostatically actuated MEMS resonators, Mathematics, 8(7) (2020) 1124.
Y. Tai, P. Li, Y. Zheng and J. Tian, Entropy generation and thermoelastic damping in the in-plane vibration of microring resonators, Entropy, 21(7) (2019) 631.
C. K. Thein and F. M. Foong, Material damping analysis of triangular cantilever beam for electromagnetic vibration energy harvesting applications, Engineering Proceedings, 10(1) (2021) 1.
H. M. Youssef, A. A. El-Bary and E. A. N. Al-Lehaibi, Characterization of the quality factor due to the static prestress in classical Caputo and Caputo-Fabrizio fractional thermoelastic silicon microbeam, Polymers, 13(1) (2021) 27.
S. D. Senturia, Thermoelastic damping in fine grained polysilicon flexural beam resonators, J. Microelectromech. Syst., 11(5) (2002) 499–504.
D. V. Parayil, S. S. Kulkarni and D. N. Pawaskar, Analytical and numerical solutions for thick beams with thermoelastic damping, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 94 (2015) 10–19.
S. Vengallatore, Analysis of thermoelastic damping in laminated composite micromechanical beam resonators, J. Micromech. Microengg. (2005) 2398–2404.
X. Li, L. Li, Y. Hu, Z. Ding and W. Deng, Bending, buckling and vibration of axially functionally graded beams based on nonlocal strain gradient theory, Composite Structures, 165 (2017) 250–265.
I. Pradiptya and H. M. Ouakad, Size-dependent behavior of slacked carbon nanotube actuator based on the higher-order strain gradient theory, Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des., 14(3) (2018) 393–415.
R. Resmi, V. S. Babu and M. R. Baiju, Impact of dimensionless length scale parameter on material dependent thermoelastic attenuation and study of frequency shifts of rectangular microplate resonators, 2021 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. (2021) 1091012067.
Y. Fang, P. Li, H. Zhou and W. Zuo, Thermoelastic damping in rectangular microplate resonators with three-dimensional heat conduction, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 133 (2017) 578–589.
R. Resmi, V. S. Babu and M. R. Baiju, Analysis of thermoelastic damping limited quality factor and critical dimensions of circular plate resonators based on axisymmetric and non-axisymmetric vibrations, AIP Advances, 11 (2021) 035108.
P. Li, Y. Fang and R. Hu, Thermoelastic damping in rectangular and circular microplate resonators, J. Sound Vib., 331(3) (2012) 721–733.
W. Zuo, P. Li, J. Zhang and Y. Fang, Analytical modeling of thermoelastic damping in bilayered microplate resonators, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 106 (2016) 128–137.
S. Liu, Y. Sun, J. Ma and J. Yang, Theoretical analysis of thermoelastic damping in bilayered circular plate resonators with two-dimensional heat conduction, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 135 (2018) 114–123.
J. Kim and J. Reddy, A general third-order theory of functionally graded plates with modified couple stress effect and the von Kármán nonlinearity: theory and finite element analysis, Acta. Mech., 226(9) (2015) 2973.
Y. C. Pei, Thermoelastic damping in rotating flexible microdisk, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 61(1) (2012) 52–64.
S. T. Hossain, S. McWilliam and A. A. Popov, An investigation on thermoelastic damping of high-Q ring resonators, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 106 (2016) 209–219.
C. Zener, Internal friction in solids, I. theory of internal friction in reeds, Phys. Rev., 52(3) (1937) 230–235.
C. Zener, Internal friction in solids, II. general theory of thermoelastic internal friction, Phys. Rev., 53(1) (1938) 90–99.
T. V. Roszhart, The effect of thermoelastic internal friction on the Q of micromachined silicon resonators, IEEE Solid-State Sensor and Actuator Workshop (1990) 13–16.
R. Lifshitz and M. L. Roukes, Thermoelastic damping in micro-and nanomechanical systems, Phys. Rev. B., 61(8) (2000) 5600–5609.
S. Evoy, A. Olkhovets, D. W. Carr, J. M. Parpia and H. G. Craighead, Temperature-dependent internal friction in silicon nanoelectromechanical systems, Appl. Phys. Lett., 77 (2000) 2397.
A. Duwel, R. N. Candler, T. W. Kenny and M. Varghese, Engineering MEMS resonators with low thermoelastic damping, J. Microelectromech. Syst., 15(6) (2006) 1437–1445.
J. Yang, T. Ono and M. Esashi, Energy dissipation in submicrometer thick single-crystal silicon cantilevers, J. Microelectromech. Syst., 11(6) (2002) 775–783.
G. Rezazadeh, A. Tahmasebi and M. Zubstov, Application of piezoelectric layers in electrostatic MEM actuators: controlling of pull-in voltage, Microsyst.Technol., 12 (2006) 1163–1170.
P. Sairam and V. Srikar, Thermoelastic damping in bilayered micromechanical beam resonator, J. Micromechanics and Microengineering, 17(3) (2007) 532–538.
S. Prabhakar and S. Vengallatore, Theory of thermoelastic damping in micromechanical resonators with two-dimensional heat conduction, J. Microelectromech. Syst., 17(2) (2008) 494–502.
K. Tunvir, C. Q. Ru and A. Mioduchowski, Thermoelastic dissipation of hollow micromechanical resonators, Physica E-low-dimensional Systems & Nanostructures — PHYSICA E, 42 (2010) 2341–2352.
K. Tunvir, Thermoelastic dissipation in stepped-beam resonators, Microsystem Technologies, 19 (2012) 721–731.
K. Tunvir, C. Q. Ru and A. Mioduchowski, Effect of cross-sectional shape on thermoelastic dissipation of micro/nano elastic beams, International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 62 (2012) 77–88.
K. Tunvir, C. Q. Ru and A. Mioduchowski, Large-deflection effect on thermoelastic dissipation of microbeam resonators, Journal of Thermal Stresses, 35 (2012) 1076–1094.
Z. Nourmohammadi, S. Prabhakar and S. Vengallatore, Thermoelastic damping in layered microresonators: critical frequencies, peak values, and rule of mixture, Microelectromechanical Systems, 22 (2013) 747–754.
J. N. Sharma and R. Kaur, Transverse vibrations in thermoelastic-diffusive thin microbeam resonators, J. Thermal Stresses, 37 (2014) 1265–1285.
Z. Y. Zhong, J. P. Zhou and H. L. Zhang, Thermoelastic damping in functionally graded microbeam resonators, IEEE Sensors J., 17(11) (2017) 3381–3390.
E. Taati, On buckling and post-buckling behavior of functionally graded micro-beams in thermal environment, International Journal of Engineering Science, 128 (2018) 63–78.
Y. Fu, L. Li and Y. Hu, Enlarging quality factor in microbeam resonators by topology optimization, J. Thermal Stress., 42(3) (2019) 341–360.
A. Seyfi, M. Nouraei and P. Haghi, Influence of Magnetic Field on The Wave Propagation Response of Functionally Graded (FG) Beam Lying on Elastic Foundation in Thermal Environment, Waves in Random and Complex Media (2021).
I. Kaur, P. Lata and K. Singh, Study of frequency shift and thermoelastic damping in transversely isotropic nano-beam with GN III theory and two temperature, Archive of Applied Mechanics, 91 (2021) 1–15.
S. Guha and A. K. Singh, Frequency shifts and thermoelastic damping in different types of nano-/micro-scale beams with sandiness and voids under three thermoelasticity theories, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 510 (2021) 116301.
N. Fleck, G. Muller, M. Ashby and J. Hutchinson, Strain gradient plasticity: theory and experiment, Acta Metall. Mater., 42(2) (1994) 475–487.
K. W. McElhaney, J. J. Vlassak and W. D. Nix, Determination of indenter tip geometry and indentation contact area for depth-sensing indentation experiments, J. Mater. Res., 13 (1998) 1300–1306.
I. Chasiotis and W. G. Knauss, A new microtensile tester for the study of MEMS materials with the aid of atomic force microscopy, Exp. Mech., 42 (2002) 51–57.
T. P. Weihs, S. Hong, J. C. Bravman and W. D. Nix, Mechanical deflection of cantilever microbeams: a new technique for testing the mechanical properties of thin films, J. Mater. Res., 3 (1988) 931–942.
A. Cauchy, Mémoiresur les systèmesisotropes de points matériels, Oeuvres Complètes, 1re Série — Tome II (1850a) 351–386.
A. Cauchy, Mémoiresur les vibrations d’un double système de molécules et de l’éthercontinudans un corps cristallisé, 1re Série — Tome II (1850) 338–350.
W. Voigt, Theoretischestudienüber die elasticitätsverhältnisse der krystalle. i. ableitung der grundgleichungenaus der annahmemitpolaritätbegabtermoleküle, Abhandlungen der Mathematischen Classe der Königlichen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaftenzu Göttingen, 24 (1887) 3–52.
R. D. Mindlin and H. F. Tiersten, Effects of couple-stresses in linear elasticity, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 11(1) (1962) 415–448.
R. D. Mindlin, Influence of couple-stresses on stress concentrations, Experimental Mechanics, 3(1) (1963) 1–7.
R. D. Mindlin, Micro-structure in linear elasticity, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 16(1) (1964) 51–78.
R. A. Toupin, Elastic materials with couple-stresses, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 11(1) (1962) 385–414.
R. A. Toupin, Theories of elasticity with couple-stress, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 17(2) (1964) 85–112, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253050.
W. T. Koiter, Couple-stresses in the theory of elasticity, I and II, Proceedings Series B, Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, 67 (1964) 17–47.
E. Cosserat and F. Cosserat, Theory of Deformable Bodies, Hermann et Fils, Paris (1909).
A. C. Eringen, Theory of micropolar elasticity, Microcontinuum Field Theories, Springer, New York (1999) 101–248.
A. C. Eringen and D. G. B. Edelen, On nonlocal elasticity, International Journal of Engineering Science, 10(3) (1972) 233–248.
A. C. Eringen, Linear theory of nonlocal elasticity and dispersion of plane waves, International Journal of Engineering Science, 10(5) (1972) 425–435.
F. Yang, A. C. M. Chong, D. C. C. Lam and P. Tong, Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity, International Journal of Solids and Structures, 39(10) (2002) 2731–2743.
M. Fathalilou and G. Rezazadeh, Effects of the length scale parameter on the thermoelastic damping of a micro-beam considering the couple stress theory, International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 8(6) (2016) 1650083.
B. A. Hamidi, S. A. Hosseini, R. Hassannejad and F. Khosravi, An exact solution on gold microbeam with thermoelastic damping via generalized Green-Naghdi and modified couple stress theories, Journal of Thermal Stress, 43(2) (2020) 157–174.
A. Rahmani, S. Faroughi, M. I. Friswell and A. Babaei, Eringen’s nonlocal and modified couple stress theories applied to vibrating rotating nanobeams with temperature effects, Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures (2021).
D. C. C. Lam, F. Yang, A. C. M. Chong, J. Wang and P. Tong, Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 51(8) (2003) 1477–1508.
S. Kong, S. Zhou, Z. Nie and K. Wang, Static and dynamic analysis of micro beams based on strain gradient elasticity theory, Int. J. Eng. Sci., 47(4) (2009) 487–498.
F. Allahkarami, M. Nikkhah-bahrami and M. G. Saryazdi, Magneto-thermo-mechanical dynamic buckling analysis of a FGCNTs-reinforced curved microbeam with different boundary conditions using strain gradient theory, Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des., 14 (2018) 243–261.
I. Pradiptya and H. M. Ouakad, Size-dependent behavior of slacked carbon nanotube actuator based on the higher-order strain gradient theory, Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des., 14(3) (2018) 393–415.
J. Y. Yu, X. G. Tian and J. Liu, Size-dependent damping of a nanobeam using nonlocal thermoelasticity: extension of Zener, Lifshitz, and Roukes’ damping model, Acta. Mech., 228 (2017) 1287–1302.
S. Rashahmadi and S. A. Meguid, Modeling size-dependent thermoelastic energy dissipation of graphene nanoresonators using nonlocal elasticity theory, Acta. Mech., 230(3) (2019) 771–785.
V. Borjalilou, M. Asghari and E. Taati, Thermoelastic damping in nonlocal nanobeams considering dual-phase-lagging effect, Journal of Vibration and Control, 26(11–12) (2020) 1042–1053.
X. Li, L. Li, Y. Hu, Z. Ding and W. Deng, Bending, buckling and vibration of axially functionally graded beams based on nonlocal strain gradient theory, Composite Structures, 165 (2017) 250–265.
L. Lu, X. Guo and J. Zhao, A unified nonlocal strain gradient model for nanobeams and the importance of higher order terms, International Journal of Engineering Science, 119(Supplement C) (2017) 265–277.
B. A. Hamidi, S. A. Hosseini and H. Hayati, Forced torsional vibration of nanobeam via nonlocal strain gradient theory and surface energy effects under moving harmonic torque, Waves in Random and Complex Media, 32(1) (2020) 318–333.
M. Fathalilou, M. Sadeghi, G. Rezazadeh, M. Jalilpour, A. Naghiloo and S. Ahouighazvin, Study on the pull-in instability of gold micro-switches using variable length scale parameter, Journal of Solid Mechanics, 3 (2011) 114–123.
M. Rahaeifard, M. Kahrobaiyan, M. Asghari and M. Ahmadian, Static pull-in analysis of microcantilevers based on the modified couple stress theory, Sens. Actuat. A, 171(2) (2011) 370–374.
M. Asghari, M. H. Kahrobaiyan, M. Nikfar and M. T. Ahmadian, A sizedependent nonlinear Timoshenko micro-beam model based on the strain gradient theory, Acta Mechanica., 223(6) (2012) 1233–1249.
G. Rezazadeh, A. S. Vahdat, S. Tayefehrezaei and C. Cetinkaya, Thermoelastic damping in a micro-beam resonator using modified couple stress theory, Acta. Mechanica., 223(6) (2012) 1137–1152.
A. S. Vahdat, G. Rezazadeh and G. Ahmadi, Thermoelastic damping in a micro-beam resonator tunable with piezoelectric layers, Acta Mech. Solida. Sin., 25 (2012) 73–81.
M. Shaat and S. Mohamed, Nonlinear-electrostatic analysis of micro-actuated beams based on couple stress and surface elasticity theories, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 84 (2014) 208–217.
B. Akgöz and Ö. Civalek, A new trigonometric beam model for buckling of strain gradient microbeams, International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 81 (2014) 88–94.
E. Taati, M. M. Najafabadi and H. B. Tabrizi, Size-dependent generalized thermoelasticity model for Timoshenko microbeams, Acta Mech., 225(7) (2014) 1823–1842.
A. A. Emami and A. Alibeigloo, Exact solution for thermal damping of functionally graded Timoshenko microbeams, J. Thermal Stress, 39(2) (2016) 231–243.
H. Zhang, T. Kim, G. Choi and H. H. Cho, Thermoelastic damping in micro-and nanomechanical beam resonators considering size effects, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 103 (2016) 783–790.
H. Zhou and P. Li, Thermoelastic damping in micro- and nanobeam resonators with non-Fourier heat conduction, IEEE Sensors J., 17(21) (2017) 6966–6977.
J. Lei, Y. He, S. Guo, Z. Li and D. Liu, Thermal buckling and vibration of functionally graded sinusoidal microbeams incorporating nonlinear temperature distribution using DQM, Journal of Thermal Stresses, 40(6) (2017) 665–689.
X. Li and Y. Luo, Size-dependent postbuckling of piezoelectric microbeams based on a modified couple stress theory, International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 9(4) (2017) 1750053.
M. Bostani and A. K. Mohammadi, Thermoelastic damping in microbeam resonators based on modified strain gradient elasticity and generalized thermoelasticity theories, Acta. Mech., 229 (2018) 173–192.
M. Kandaz and H. Dal, A comparative study of modified strain gradient theory and modified couple stress theory for gold microbeams, Archive of Applied Mechanics, 88 (2018) 2051–2070.
M. Al-shujairi and Ç. Mollamahmutoğlu, Buckling and free vibration analysis of functionally graded sandwich micro-beams resting on elastic foundation by using nonlocal strain gradient theory in conjunction with higher order shear theories under thermal effect, Composites Part B: Engineering, 154 (2018) 292–312.
V. Borjalilou and M. Asghari, Small-scale analysis of plates with thermoelastic damping based on the modified couple stress theory and the dualphase-lag heat conduction model, Acta Mechanica., 229(9) (2018) 3869–3884.
F. Allahkarami, M. Nikkhah-bahrami and M. G. Saryazdi, Magneto-thermomechanical dynamic buckling analysis of a FGCNTs-reinforlifshiced curved microbeam with different boundary conditions using strain gradient theory, International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design, 14(2) (2018) 243–261.
S. Rashahmadi and S. A. Meguid, Modeling size-dependent thermoelastic energy dissipation of graphene nanoresonators using nonlocal elasticity theory, Acta Mech., 230(3) (2019) 771–785.
R. Resmi, M. R. Baiju and V. S. Babu, Thermoelastic damping dependent quality factor analysis of rectangular plates applying modified coupled stress theory, AIP Conference Proceedings, 2166 (2019) 020029.
V. Borjalilou, M. Asghari and E. Bagheri, Small-scale thermoelastic damping in micro-beams utilizing the modified couple stress theory and the dual-phase-lag heat conduction model, J. Thermal Stress., 42 (2019) 801–814.
V. Borjalilou, M. Asghari and E. Taati, Thermoelastic damping in nonlocal nanobeams considering dual-phase-lagging effect, J. Vib. Control, 26(11–12) (2020) 1042–1053.
Z. Yang, D. Cheng, G. Cong, D. Jin and V. Borjalilou, Dual-phase-lag Thermoelastic Damping in Nonlocal Rectangular Nanoplates, Waves in Random and Complex Media (2021).
S. Shuanhu, T. He and F. Jin, Thermoelastic damping analysis of size-dependent nano-resonators considering dual-phase-lag heat conduction model and surface effect, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 170 (2021) 120977.
F. Ebrahimi, A. Seyfi, M. Nouraei and P. Haghi, Influence of Magnetic Field on the Wave Propagation Response of Functionally Graded (FG) Beam Lying on Elastic Foundation in Thermal Environment, Waves in Random and Complex Media (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
R. Resmi obtained her B.Tech. in Electronics Engineering from Cochin University of Science and Technology, India in 2000 and her M.Tech. from the College of Engineering Trivandrum, University of Kerala. She is currently working as an Assistant Professor at the LBS Institute of Technology for Women, Kerala, India. Her research interests include RF MEMS resonators and sensors design, energy dissipation analysis in MEMS/NEMS structures, biomedical signal processing and instrumentation, image processing, and VLSI systems design. She is currently completing her Ph.D. in the Department of Electronics and Communication, College of Engineering Trivandrum, under the University of Kerala. Orcid Id: http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0849-5509.
V. Suresh Babu obtained his B.Tech. from the Electronics and Communication Engineering Department of Kerala University, Trivandrum, India in 1989, his M.Tech. in Integrated Electronic Devices and Circuits from IIT Madras in 1996, and his Ph.D. in Electronics and Communication in 2013 from Kerala University. Form 1990 to 1991, he was with the Kerala State Electronics Development Corporation Ltd., Trivandrum, India. Since 1991, he has been a Member of the Faculty of the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering in Government Engineering Colleges in Kerala. He is currently a Professor at the Electronics and Communications Engineering Department, College of Engineering Trivandrum, Kerala, India. His areas of interest are solar photovoltaics and nano-electronic devices. Orcid Id: http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8024-2621.
M. R. Baiju obtained his B.Tech. in Electronics and Communication Engineering from the College of Engineering, Trivandrum, India, in 1988, M.Tech. in Electronics Design and Technology, and Ph.D. in Power Electronics from the Center for Electronics Design and Technology, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India, in 1997 and 2004, respectively. From 1988 to 1991, he was with the National Thermal Power Corporation Ltd., New Delhi, India. Since 1991, he has been a Member of the Faculty of the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, College of Engineering Trivandrum, Kerala. His areas of interest include multilevel inverter control strategies, MEMS, and VLSI systems.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resmi, R., Babu, V.S. & Baiju, M.R. Material-dependent thermoelastic damping limited quality factor and critical length analysis with size effects of micro/nanobeams. J Mech Sci Technol 36, 3017–3038 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-022-0533-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-022-0533-8