Abstract
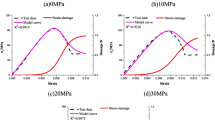
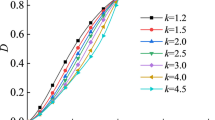
The integrity coefficient Kv of bed rock is one of the important approaches to evaluate the stability of engineering rock mass, but this parameter is difficult in frequent field tests. The integrity coefficient is the quantitative index for evaluating the complete deformation of rock mass, while the damage variable represents the level of damage of the jointed rock mass, and both have similar physical meanings and represent the degree of deterioration of surrounding rock. Damage variables and damage constitutive models were constructed based on Weibull distribution damage model and Synthetic Rock Mass (SRM) model. The relationship between damage variables and numerical calculation and damage constitutive curves of different weathered granite rocks in Hongtuzhang tunnel was calculated. A new method for evaluating integrity coefficient of rock mass is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BQ:
-
Basic quality of rock mass
- [BQ]:
-
Modified basic quality of rock mass
- D :
-
Two damage coupled states damage variable
- D 0 :
-
Initial damage variable
- D mx :
-
Ball maximum diameter, mm
- D min :
-
Ball minimum diameter, mm
- D s :
-
Load damage variable
- E 0 :
-
Elastic modulus of intact rock, GPa
- E*:
-
Elastic modulus of rock mass, GPa
- E c :
-
Elastic modulus of ball, GPa
- \({\bar E_c}\) :
-
Elastic modulus of bond, GPa
- K 1 :
-
Correction coefficient of groundwater state influence
- K 2 :
-
Correction coefficient of occurrence influence of main weak structural plane
- K 3 :
-
Correction coefficient of initial stress state influence
- k n :
-
Normal stiffness of ball, GPa
- \({\bar k_n}\) :
-
Bond normal stiffness, GPa
- k nj :
-
Joint normal stiffness, GPa
- k s :
-
Shear stiffness of ball, GPa
- \({\bar k_s}\) :
-
Bond shear stiffness, GPa
- k sj :
-
Joint shear stiffness, GPa
- Kv :
-
Integrity coefficient
- m :
-
Shape Parameter of Weibull Distribution
- n :
-
Number of microcracks
- P 10 :
-
Linear density of structural plane, item/m
- R c :
-
Uniaxial saturation ultimate compressive strength, MPa
- V pm :
-
P wave velocity of bed rock in testing area, km/s
- V pr :
-
P wave velocity of intact rock in testing area, km/s
- ε :
-
Strain, %
- ε 0 :
-
Reference strain of Weibull Distribution
- ε f :
-
Strain at peak stress, %
- φ :
-
Joint dilation angle, °
- \(\bar \lambda \) :
-
Radius multiplier of bond
- μ :
-
Friction coefficient
- ν :
-
Poisson’s ratio
- σ :
-
Stress, MPa
- \({\bar \sigma _c}\) :
-
Bond normal strength, MPa
- σ f :
-
Strength of surrounding rock reaches peak stress, MPa
- σ j :
-
Joint normal stress, MPa
- \({\bar \tau _c}\) :
-
Bond shear strength, MPa
- τ j :
-
Joint shear stress, MPa
References
An Y H, Wang Q (2012) Analysis ofrepresentative element volume size based on 3D fracture network. Rock and Soil Mechanics 33(12):3775–3780
Bahaaddini M, Sharrock G, Hebblewhite BK (2013) Numerical investigation of the effect of joint geometrical parameters on the mechanical properties of a non-persistent jointed rock mass under uniaxial compression. Computers and Geotechnics 49:206–225, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.10.012
Chao Z, Yun B (2020) Research on the establishment and application of parameter oriented geometric damage model for rocks. Rock and Soil Mechanics 41(12):3899–3909, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0474
Chen PY (2018) Loading rate effect analysis on rock particle flow model under uniaxial compression. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering 14(3):635–642
Deisman N, Ivars DM, Pierce M (2008) PFC2D Smooth joint contact model numerical experiments. GeoEdmonton 08. Organizing Committee, 83–87
Duan SW, Xu XE (2013) Discussion of problems in calculation and application of rock mass integrity coefficient. Jounrnal of Engineering Geology 21(4):548–553, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/014572170202800512
Esmaieli K, Hadjigeorgiou J, Grenon M (2010) Estimating geometrical and mechanical REV based on synthetic rock mass models at Brunswick Mine. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 47(6):915–926, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.05.010
Hazzard JF, Young RP, Maxwell SC (2000) Micromechanical modeling of cracking and failure in brittle rocks. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 105(B7): 16683–16697, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JB900085
Huang D, Li XQ, Song WC (2022) Precise grading of surrounding rock based on the numerical calculation of the jointed rock mass. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers — Geotechnical Engineering 174(6):1–12
Huang D, Wang JF, Liu S (2015) Comprehensive study on the smooth joint model in DEM simulation of jointed rock masses. Granular Matter 17:775–791, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-015-0594-9
Hudson, John A (1997) Engineering rock mechanics 207–221, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-008043864-1/50014-8
Itasca Consulting Group Inc. (2016) PFC manual, version 5.0. Minneapolis
Ji M, Chen K, Guo HJ (2018) Constitutive model of rock uniaxial damage based on rock strength statistics. Advances in Civil Engineering 2018:1–8, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5047834
Kawamoto T, Ichikawa Y, Kyoya T (2010) Deformation and fracturing behaviour of discontinuous rock mass and damage mechanics theory. International Journal for Numerical & Analytical Methods in Geomechanics 12(1):1–30, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.1610120102
Li X, Cao WG, Su YH (2012) A statistical damage constitutive model for softening behavior of rocks. Engineering Geology 143–144:1–17, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.05.005
Li X, Li D, Xu Y, Feng X (2020) A DFN based 3D numerical approach for modeling coupled groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock mass. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 149:119179, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.119179
Lin H, Feng JJ, Cao RH, Xie XJ (2022) Comparative analysis of rock damage models based on different distribution functions. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 40:301–310
Lisjak A, Grasselli G (2014) A review of discrete modeling techniques for fracturing processes in discontinuous rock masses. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 6(4):301–314, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2013.12.007
Liu HY, Lv SR, Zhang LM, Yuan XP (2015a) A dynamic damage constitutive model for a rock mass with persistent joints. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 75(4):132–139, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.01.013
Liu HY, Yuan XP (2015) A damage constitutive model for rock mass with persistent joints considering joint shear strength. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 52(8):3107–3117, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0252
Liu T, Lin BQ, Zou QL, Zhu CJ, Guo C, Li J (2015b) Investigation on mechanical properties and damage evolution of coal after hydraulic slotting. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 24(5): 489–499, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.04.016
Lu Bo, Ge XR, Zhu DL, Chen JP (2005) Fractal study on the representative element volume of jointed rock masses. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 24(8):1355–1361, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.03.016
Mas Ivars D, Pierce M, Darcel C, Reyes-Montes J, Potyondy DO, Young RP, Cundall PA (2011) The synthetic rock mass approach for jointed rock mass modeling. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 48(2):219–244, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.11.014
Miyoshi T, Elmo D, Rogers S (2018) Influence of data analysis when exploiting DFN model representation in the application of rock mass classification systems. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.08.003
Oda M (1988) A method for evaluating the representative elementary volume based on joint survey of rockmass. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 25(3):281–287, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/t88-049
Pang ZH (1988) Numerical estimation of rock mass Rev based on joint network model and element free Galerkin method (EFGM). Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of geotechnical mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Park JW, Song JJ (2009) Numerical simulation of a direct shear test on a rock joint using a bonded-particle model. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 46(8):1315–1328, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.03.007
Potyondy DO, Cundall PA (2004) A bonded-particle model for rock. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 41(8):1329–64, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJRMMS.2004.09.011
PRC NSWG (Peoples Republic of China National Standards Writing Group) (2004) JTJ D70-2004 Code for design of road tunnel. China Communications Press, Beijing, China
PRC NSWG (Peoples Republic of China National Standards Writing Group) (2010) JTJ/T D70-2010 Guidelines for design of highway tunnel. China Communications Press, Beijing, China
Wang TT, Huang TW (2009) A constitutive model for the deformation of a rock mass containing sets of ubiquitous joints. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 46(3):521–530, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.09.011
Wang XM, Xia L, Zheng YH, Yu QC (2013) Study of representative elementary volume for fractured rock mass based on three-dimensional fracture connectivity. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 32(S2):3297–3302
Wang XM, Zheng YH (2015) Review of advances in investigation of representative elementary volume and scale effect of fractured rock masses. Rock and Soil Mechanics 36(12):3456–3464, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2015.12.016
Wang YQ, Li JQ, Wang ZF, Chang HT (2022) Structural failures and geohazards caused by mountain tunnel construction in fault zone and its treatment measures: A case study in Shaanxi. Engineering Failure Analysis 138(8):106386, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106386
Wong TF, Wong RHC, Chau KT, Tang CA (2006) Microcrack statistics, weibull distribution and micromechanical modeling of compressive failure in rock. Mechanics of Materials 38(7):664–681, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2005.12.002
Wu AQ, Liu FZ (2012) Advancement and application of the standard for engineering classification of rock masses. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 31(8):5–15, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.08.003
Wu N, Liang ZZ, Li YC, Li H, Li WR, Zhang ML (2019) Stress-dependent anisotropy index of strength and deformability of jointed rock mass: Insights from a numerical study. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 78(8):5905–5917, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01483-5
Wu SC, Gao YH, Gao YT, Li YB, Cheng AP (2014) Research on representative elemental volume of equivalent joint rock mass. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology 43(6):1120–1126, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000244
Yang JH, Dai JH, Chi Y, Jiang SH (2020) Estimation of rock mass properties in excavation damage zones of rock slopes based on the Hoek-Brown criterion and acoustic testing. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 126(2):104192, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104192
Yang SQ, Huang YH (2017) An experimental study on deformation and failure mechanical behavior of granite containing a single fissure under different confining pressures. Environmental Earth Sciences 76(10):364, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6696-4
Yin XY, Zhang AM, Li C (2021) A modified engineering classification method for schistose surrounding rocks of tunnel. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 39(4):377–395, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01498-w
Zhang QS, Yang GS, Ren JX (2003) New study of damage variable and constitutive equation of rock. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering (1):30–34
Zhang XP, Wong LNY (2012) cracking processes in rock-like material containing a single flaw under uniaxial compression: A numerical study based on parallel bonded-particle model approach. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 45(5):711–737, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0176-z
Zhao H, Shi C, Zhao M, Li X (2017) Statistical damage constitutive model for rocks considering residual strength. International Journal of Geomechanics 17(1):04016033.1–04016033.9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000680
Zhao Y, Yang TH, Zhang PH, Xu HY, Zhou JR, Yu QL (2019) Method for generating a discrete fracture network from microseismic data and its application in analyzing the permeability of rock masses: A case study. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 52:3133–3155, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1712-x
Zhao ZL, Wang X, Wen ZJ (2018) Analysis of rock damage characteristics based on particle discrete element model. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 36:897–904, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0363-0
Zhou J, Wei J, Yang T, Zhu W, Li L, Zhang P (2018) Damage analysis of rock mass coupling joints, water and microseismicity. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 71:366–381, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.09.006
Zhou Y, Wu SC, Jiao JJ, Zhang XP (2011) Research on mesomechanical parameters of rock and soil mass based on BP neural network. Rock and Soil Mechanics 32(12):3821–3826, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181f49ac7
Zhu DL (2003) REV and numerical estimation of deformation and strength of jointed rock mass. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of geotechnical mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, D., Li, Xq. & Song, Wc. Damage Evolution and Integrity Assessment of Jointed Rock Mass Based on Synthetic Rock Mass Approach. KSCE J Civ Eng 27, 2235–2247 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-023-1553-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-023-1553-3