Abstract
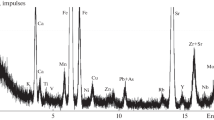
In this study, the environmental safety and geochemical properties of Coal Combustion Products (CCPs) produced coal-fired power plants were investigated. Samples of CCPs were taken from all of the coal-fired power plants of Korea. Heavy metal concentration, Electrical Conductivity (EC), and pH measurements were conducted to evaluate the environmental stability and geochemical properties of the CCPs. X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction analyses were performed and enrichment factors and an index of geo-accumulation were calculated to evaluate the levels of contamination in the CCPs. The pH value of the CCPs ranged from 7.6 to 9.3, slightly alkaline, and the EC ranged between 110 and 4,940 μS/cm. CCPs from anthracite coal had a lower silica-alumina ratio and lower proportions of CaO and MgO, and greater proportions of K2O, than CCPs from bituminous coal. The EF value of Fe, Ti, and P in some CCP samples classified moderate enrichment category, all other elements in the samples were classified in the deficiency to minimal enrichment category. Also, the heavy metal concentrations in all CCP samples were lower than the environmental standards, indicating that the CCPs satisfied environmental regulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba, A., Gurdal, G., Sengunalp, F., and Ozay, O. (2008). “Effects of leachant temperature and pH on leachability of metals from fly ash. A case study: Can thermal power plant, province of Canakkale, Turkey.” Environ Monit Assess, Vol. 139, No. 1, pp. 287–298, DOI: 10.1007/s10661-007-9834-8.
Baba, A. and Kaya, A. (2004). “Leaching characteristics of solid wastes from thermal power plants of western Turkey and comparison of toxicity methodologies.” J Environ Manage, Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 199–207, DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2004.06.005.
Bhangare, R. C., Ajmal, P. Y., Sahu, S. K., Pandit, G. G., and Puranik, V. D. (2011). “Distribution of trace elements in coal and combustion residues from five thermal power plants in India.” International Journal of Coal Geology, Vol. 86, No. 4, pp. 349–356, DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2011.03.008.
Brigden, K., Santillo, D., and Stringer, R. (2002). “Hazardous emissions from Thai coal-fired power plants: Toxic and potentially toxic elementsin fly ashes collected from the Mae Moh and Thai Petrochemical Industry coal-fired power plants in Thailand.” Greenpeace Research Laboratories, Department of Biological Sciences, University of Exeter, Exeter, 1–26.
Carpenter, A. C., Gardner, K. H., Fopiano, J., Benson, C. H., and Edil, T. B. (2007). “Life cycle based risk assessment of recycled materials in roadway construction.” Waste Manag, Vol. 27, No. 10, pp. 1458–1464, DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2007.03.007.
CFR (2004). Code of Federal Regulations, Title 40: Protection of Environment, Part 261: Identification and Listing of Hazardous Waste Support C: Characteristics of Hazardous Waste, 261.22: Characteristics of Corrosivity. USEPA.
Choi, S. K., Lee, S., Song, Y. K., and Moon, H. S. (2002). “Leaching characteristics of selected Korean fly ashes and its implications for the groundwater composition near the ash disposal mound.” Fuel, Vol. 81, No. 8, pp. 1083–1090, DOI: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00006-6.
Edil, T., Benson, C., Bin-Shafique, M., Tanyu, B., Kim, W. H., and Senol, A. (2002). “Field evaluation of construction alternatives for roadways over soft subgrade.” Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 36–48, DOI: 10.3141/1786-05.
Font, O., Moreno, N., Querol, X., Izquierdo, M., Alvarez, E., Diez, S., Elvira, J., Antenucci, D., Nugteren, H., Plana, F., López, A., Coca, P., and Peña, F. G. (2010). “X-ray powder diffraction-based method for the determination of the glass content and mineralogy of coal (co)-combustion fly ashes.” Fuel, Vol. 89, No. 10, pp. 2971–2976, DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.11.024.
Goodarzi, F. (2006). “Characteristics and composition of fly ash from Canadian coal-fired power plants.” Fuel, Vol. 85, No. 10, pp. 1418–1427, DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2005.11.022.
IEA (2009). International Energy Agency, World energy outlook 2009-Executive summary, OECD/IEA Electricity Information.
Jaturapitakkul, C. and Cheerarot, R. (2003). “Development of bottom ash as pozzolanic material.” Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 48–53, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2003) 15:1(48).
Jayaranjan, M. L. D., van Hullebusch, E. D., and Annachhatre, A. P. (2014). “Reuse options for coal fired power plant bottom ash and fly ash.” Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 467–486, DOI: 10.1007/s11157-014-9336-4.
Kayabal, K. and Buluş, G. (2000). “The usability of bottom ash as an engineering material when amended with different matrices.” Engineering Geology, Vol. 56, No. 3, pp. 293–303, DOI: 10.1016/S0013-7952(99)00097-6.
Ke, T. and Lovell, C. (1992). Corrosivity of Indiana bottom ash, Transportation Research Record.
KEPCO (2015). Korea Electric Power Co., Statistics of electric power in Korea.
Kim, B., Prezzi, M., and Salgado, R. (2005). “Geotechnical properties of fly and bottom ash mixtures for use in highway embankments.” Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, Vol. 131, No. 7, pp. 914–924, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:7(914).
Kim, H. K. and Lee, H. K. (2015). “Coal bottom ash in field of civil engineering: A review of advanced applications and environmental considerations.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 1802–1818, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-015-0282-7.
Kim, Y. T. and Do, T. H. (2012). “Effect of bottom ash particle size on strength development in composite geomaterial.” Engineering Geology, Vol. 139-140, pp. 85–91, DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.04.012.
Kim, Y. T., Lee, C., and Park, H. I. (2011). “Experimental study on engineering characteristics of composite geomaterial for recycling dredged soil and bottom ash.” Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 1–15, DOI: 10.1080/1064119x.2010.514237.
Kopsick, D. A. and Angino, E. E. (1981). “Effect of leachate solutions from fly and bottom ash on groundwater quality.” Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 54, Nos. 1–3, pp. 341–356, DOI: 10.1016/0022-1694 (81)90167-0.
Kumar, S. and Stewart, J. (2003). “Evaluation of Illinois pulverized coal combustion dry bottom ash for use in geotechnical engineering applications.” Journal of Energy Engineering, Vol. 129, No. 2, pp. 42–55, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9402(2003)129:2(42).
Lee, T. (2011). “Leaching characteristics of bottom ash from coal fired electric generating plants, and waste tire; Individually and mixtures when used as construction site fill materials.” Waste Manag, Vol. 31, pp. 246–252, DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.10.010.
Levandowski, J. and Kalkreuth, W. (2009). “Chemical and petrographicalcharacterization of feed coal, fly ash and bottom ash from the Figueira Power Plant, Paraná, Brazil.” International Journal of Coal Geology, Vol. 77, No. 3, pp. 269–281, DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2008.05. 005.
Loska, K., Wiechuła, D., and Korus, I. (2004). “Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry.” Environment International, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 159–165, DOI: 10.1016/s0160-4120(03)00157-0.
Medeiros, M. H. F., Gobbi, A., Réus, G. C., and Helene, P. (2013). “Reinforced concrete in marine environment: Effect of wetting and drying cycles, height and positioning in relation to the sea shore.” Construction and Building Materials, Vol. 44, pp. 452–457, DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.02.078.
Muller, G. (1969). “Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River.” Geojournal, Vol. 2, pp. 108–118.
Muller, G. (1981). “Die Schwermetallbelastung der Sedimenten des Neckars und Seiner Nebenflüsse.” Chemiker-Zeitung, Vol. 6, pp. 157–164.
Naveedullah, Hashmi, M. Z., Yu, C., Shen, H., Duan, D., Shen, C., Lou, L., and Chen, Y. (2013). “Risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in agricultural soils of siling reservoir watershed in Zhejiang Province, China.” Biomed Res Int., 2013, 590306, DOI: 10.1155/2013/590306.
Ozkan, O., Yuksel, I., and Muratoglu, O. (2007). “Strength properties of concrete incorporating coal bottom ash and granulated blast furnace slag.” Waste Manag, Vol. 27, No. 2, pp. 161–167, DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.01.006.
Park, J., Choi, W., Kim, T., and Son, Y. (2013). Evaluation of Heavy Metal Contamination and Geochemical Characteristics of CCPs in Korea, World of coal ash conference, Lexington, KY.
Park, J., Son, Y., Noh, S., and Bong, T. (2016). “The suitability evaluation of dredged soil from reservoirs as embankment material.” Journal of Environmental Management, Vol. 183, pp. 443–452, DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.063.
Pires, M. and Querol, X. (2004). “Characterization of Candiota (South Brazil) coal and combustion by-product.” International Journal of Coal Geology, Vol. 60, No. 1, pp. 57–72, DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2004.04.003.
Reimann, C. and de Caritat, P. (2005). “Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors.” Sci Total Environ, Vol. 337, No. 1, pp. 91–107, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.06.011.
RMRC (2008). Recycled Material Resource Center, User guideline for byproducts and secondary use materials in pavement construction: Coal bottom ash/boiler slag.
Rudnick, R. and Gao, S. (2003). “Composition of the continental crust.” Treatise on Geochemistry, Vol. 3, pp. 1–64.
Sauer, J. J., Benson, C. H., and Edil, T. B. (2005). “Metals leaching from highway test sections constructed with industrial byproducts.” Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 05-21.
Sharma, S., Fulekar, M. H., Jayalakshmi, C. P., and Straub, C. P. (1989). “Fly ash dynamics in soil-water systems.” Critical Reviews in Environmental Control, Vol. 19, No. 3, pp. 251–275, DOI: 10.1080/10643388909388367.
Shin, S. K., Kim, W. I., Jeon, T. W., Kang, Y. Y., Jeong, S. K., Yeon, J. M., and Somasundaram, S. (2013). “Hazardous waste characterizationamong various thermal processes in South Korea: A comparative analysis.” J. Hazard Mater, Vol. 260, pp. 157–166, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.022.
Singh, G., Kumar, S., Singh, M. K., and Mohapatra, S. K. (2016). “Environmental impact assessment of ash disposal system of a thermal power plant.” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.171.
Singh, G. and Paul, B. C. (2001). “Assessment of groundwater quality impacts due to use of coal combustion byproducts to control subsidence from underground mines.” Environment International, Vol. 26, No. 7, pp. 567–571, DOI: 10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00042-3.
Singh, R. K., Gupta, N. C., and Guha, B. K. (2012). “The leaching characteristics of trace elements in coal fly ash and an ash disposal system of thermal power plants.” Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, Vol. 34, No. 7, pp. 602–608, DOI: 10.1080/15567036.2011.621928.
Son, Y., Bong, T., and Noh, S. (2015). “Alternative methods for assessing particle breakage in weathered soil.” Soils and Foundations, Vol. 55, No. 1, pp. 192–200, DOI: 10.1016/j.sandf.2014.12.015.
Son, Y., Oh, M., and Lee, S. (2009). “Estimation of soil weathering degree using electrical resistivity.” Environmental Earth Sciences, Vol. 59, No. 6, pp. 1319–1326, DOI: 10.1007/s12665-009-0119-0.
Sutherland, R. (2000). “Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii.” Environmental Geology, Vol. 39, No. 6, pp. 611–627, DOI: 10.1007/s002540050473.
Suwanvitaya, P. and Wattanachai, P. (2006). Comparison of metals leaching from Mortar with Mae Moh and Calaca bottom ashes as sand replacement.
Targan, Ş., Olgun, A., Erdogan, Y., and Sevinc, V. (2003). “Influence of natural pozzolan, colemanite ore waste, bottom ash, and fly ash on the properties of Portland cement.” Cement and Concrete Research, Vol. 33, No. 8, pp. 1175–1182, DOI: 10.1016/s0008-8846(03)00025-5.
Taylor, S. R. and McLennan, S. M. (1995). “The geochemical evolution of the continental crust.” Reviews of Geophysics, Vol. 33, No. 2, pp. 241–265, DOI: 10.1029/95RG00262.
Vassilev, S. V., Vassileva, C. G., Karayigit, A. I., Bulut, Y., Alastuey, A., and Querol, X. (2005). “Phase-mineral and chemical composition of composite samples from feed coals, bottom ashes and fly ashes at the Soma power station, Turkey.” International Journal of Coal Geology, Vol. 61, No. 1, pp. 35–63, DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2004.06.004.
Yan, M., Sun, C., Xu, J., Dong, J., and Ke, W. (2014). “Role of Fe oxides in corrosion of pipeline steel in a red clay soil.” Corrosion Science, Vol. 80, pp. 309–317, DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Son, Y., Noh, S. et al. An Evaluation of the Environmental Safety and Geochemical Characteristics of Coal Combustion Products. KSCE J Civ Eng 22, 1700–1708 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1806-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1806-0