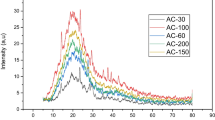
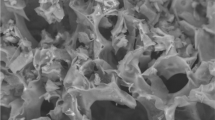
Abstract
Activated Carbon (AC) is an adsorbent having high surface area which makes the process of removing heavy metals from wastewater (such as landfill leachate) very effective. This study explored the utilization of three methods of modification of AC produced from coconut shell by treating it with nitric acid (HNO3), potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and heating at 600°C to improve the adsorption capacity. The AC can remove multi-pollutants in the filtration process which was used to treat landfill leachate. The water quality parameters such as pH, TSS, Ammonia-Nitrogen and a few heavy metals were considered in the present study. Results showed that the removal of these parameters was proportional with the increase of contact time and the bed depth of AC. The isotherm analysis of the adsorption of modified AC showed the best Removal Efficiency (RE) can be achieved when AC treated with KMnO4 for NH3-N, zinc, TSS and sulphide. The morphology of the AC was studied through Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) pattern analysis and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) analysis. It was found that various types of oxygen functional groups were introduced onto the surface of coconut shell derived AC through oxidation using HNO3. FTIR was used to characterize the surface oxygen functional groups. The surface functional groups such as N-H and C-H stretching played a significant role in heavy metals adsorption. Hence, it can be concluded that the hybrid technique by using electrolysis process with AC adsorption be an effective way to remove the suspended solids and heavy metals from landfill leachate and thus able to reduce environmental pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, C. K., Park, D., Woo, S. H., and Park, J. M. (2009). “Removal of cationic heavy metal from aqueous solution by activated carbon impregnated with anionic surfactants.” J. Hazard. Mater, Vol. 164, pp. 1130–1136, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.036.
Ahsan, A., Kamaludin, M., Rahman, M. M., Anwar, A. H. M. F., Bek, M. A., and Idrus, S. (2014). “Removal of various pollutants from leachate using a low cost technique.” Water, Air, and Soil Pollution Vol. 225, No. 12, 2163:1–9, DOI: 10.1007/s11270-014-2163-y.
Ahsan, A., Ismail, N., Rahman, M. M., Imteaz, M., Rahman, A., Mohammad, N., and Salleh, M. A. M. (2013). “Municipal solid waste recycling in Malaysia: present scenario and future prospects.” Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, Vol. 22, No. 12a, pp. 3654–3664.
Aksu, Z. and Kutsal, T. A. (1991). “Bisepartion process for removing lead (II) ions from waste water by using C. vulgaris.” Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, Vol. 52, pp. 109–118.
Alkalay, D., Guerrero, L., Lema, J. M., Mendez, R., and Chamy, R. (1998). “Review: Anaerobic treatment of municipal sanitary landfill leachates: The problem of refactory and toxic components.” World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol. 14, pp. 309–320, DOI: 10.1023/A:1008876107787.
Babel, S. and Kurniawan, T. A. (2004). “Cr (VI) removal from synthetic wastewater using coconut shell charcoal and commercial activated carbon modified with oxidizing agents and/or chitosan.” Chemosphere, Vol. 54, pp. 951–967, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.001.
Canizares, P., M. Carmona, J. Lobato, Martinez, F., and Rodrigo, M. (2005). “Electrodissolution of aluminium electrodes in electrocoagulation processes.” Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, Vol. 44, No. 12, pp. 4178–4185, DOI: 10.1021/ie048858a.
Chiang, H. L., Huang, C. P., and Chiang, P. C. (2002). “The surface characteristics of activated carbon as affected by ozone and alkaline treatment.” Chemosphere, Vol. 47, No. 3, pp. 257–265, DOI: 10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00215-6.
Cossu, R, Polcaro, A. M., Lavagnolo, M. C., Mascia, M., Palmas, S., and Renoldi, F. (1998). “Electrochemical treatment of landfill leachate: Oxidation at Ti/PbO2 and Ti/SnO2 anodes.” Environ. Sci. Technol., Vol. 32, 22, pp.3570–3573, DOI: 10.1021/es971094o.
Daifullah, A. A. M., Yakout, S. M., and Elreefy, S. A. (2007). “Adsorption of fluoride in aqueous solutions using KMnO4-modified activated carbon derived from steam pyrolysis of rice straw.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 147, pp. 633–643, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.062.
Deng, Y. and Englehardt, J. D. (2007). “Electrochemical oxidation for landfill leachate treatment.” Waste Management, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 380–388, DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.02.004.
El-Hendawy, A. A. (2003). “Influence of HNO3 oxidation on the structure and adsorptive properties of corncob-based activated carbon.” Carbon, Vol. 41, pp. 713–722, DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00029-0.
Fang, B., Wei, Y. Z., Suzuki, K., and Kumagai, M. (2005). “Surface modification of car-bonaceous materials for EDLCs application.” Electrochim. Acta, Vol. 50, No. 18, pp. 3616–3621, DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2004.12.032.
Faulwetter, J. L., Gagnon, V., Sundberg, C., Chazarenc, F., Burr, M. D., Brisson, J., Camper, A. K., and Stein, O. R. (2009). “Microbial processes influencing performance of treatment wetlands: A review.” Ecological Engineering, Vol. 35, No. 6, pp. 987–1004.
Farinella, N. V., Matos, G. D., and Arruda, M. A. Z. (2007). “Grape bagasse as a potential bio sorbent of metals in effluent treatments.” Bioresource Technology, Vol. 98, No. 10, pp. 1940–1946, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.07.043.
Figueiredo, J. L., Pereira, M. F., R., Freitas, M. M. A., and Orfao, J. J. M. (1999). “Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons.” Carbon, Vol. 37, pp. 1379–1389, DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00333-9.
Freundlich, H. (1906). “Over the adsorption in solution.” J. Phys. Chem., Vol. 57, No. 385471, pp. 1100–1107.
Graber, A., Skvarc, R., and Junge-Berberovi, R. (2009). “Elimination of phenols, ammonia and cyanide in wash water from biomass gasification, and nitrogen recycling using planted trickling filters.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 60, No. 12, pp. 3253–3259, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2009.728.
Hameed, B., Salman, J., and Ahmed, A. (2009). “Adsorption isotherm and kinetic modelling of 2, 4-D pesticide on activated carbon derived from date stones.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 163, No. 1, pp. 121–126, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.069.
Hejazifar, M., Azizian, S., Sarikhani, H., Zhao, Q., and Li, D. (2011). “Microwave assisted preparation of efficient activated carbon from grapevine hytidome for the removal of methyl violet from aqueous solution.” Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, Vol. 92, pp. 258–266, DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2011.06.007.
Huang, G., Shi, J. X., and Langrish, T. A. G. (2009). “Removal of Cr (V) from aqueous solution using activated carbon modified with nitric acid.” Chemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 152, pp. 434–439, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.05.003.
Jiang, Z. X., Liu, Y., Sun, X. P., Tian, F. P., Sun, F. X., Liang, C. H., You, W. S., Han, C. R., and Li, C. (2003). “Activated carbons chemically modified by concentrated H2SO4 for the adsorption of the pollutants from waste water and the dibenzothiophene from fuel oils.” Langmuir, Vol. 19, pp. 731–736, DOI: 10.1021/la020670d.
Li, W., Peng, J., Zhang, L., Yang, K., Xia, H., Zhang, S., and Guo, S. H. (2009). “Preparation of activated carbon from coconut shell chars in pilot-scale microwave heating equipment at 60kW.” Waste Management, Vol. 29, No. 2, pp. 756–760, DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2008.03.004.
Justin, M. Z. and Zupancic, M. (2009). “Combined purification and reuse of landfill leachate by constructed wetland and irrigation of grass and willows.” Desalination, Vol. 246, Nos. 1-3, pp. 157–168, DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2008.03.049.
Kadlec, R. H. and Knight, R. L. (1996). Treatment Wetlands, CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton, Florida.
Kalmykova, Y., Strömvall, A., Rauch, S., and Morrison, G. (2009). “Peat filter performance under changing environmental conditions.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 166, No. 1, pp. 389–393, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.062.
Khaleel, M. R., Ahsan, A., Imteaz, M., El-Sergany, M. M., Daud, N. N. N., Mohamed, T. A., and Ibrahim, B. A. (2015). “Performance of GACC and GACP to treat institutional wastewater: A sustainable technique.” Membrane Water Treatment, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 339–349, DOI: 10.12989/mwt.2015.6.4.339.
Kim, D.-W., Kim, M.-T., Rhee, K. Y., Kim, S., and Park, S.-J. (2014). “Influence of KMnO4 oxidation on the electrochemical performance of pitch-based activated carbons.” Res. Chem. Intermed, Vol. 40, pp. 2527–2534, DOI 10.1007/s11164-014-1664-z.
Langmuir, I. (1916). “The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids.” Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 38, No. 11, pp. 2221–2295, DOI: 10.1021/ja02268a002.
Langergrabert, G., Rousseau, D. P. L., Garcia, J., and Mena, J. (2009). CWM1: A general model to describe biokinetic processes in subsurface flow constructed wetlands.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 59, No. 9, pp.1687–1697, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2009.131.
Liu, Q. S., Zheng, T., Wang, N. Li, P., and Abulikemu, G. (2010). “Modification of bamboo-based activated carbon using microwave radiation and its effects on the adsorption on methylene blue.” Appl. Surf. Sci., Vol. 256, pp. 3309–3315, DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.12.025.
Liu, S. X., Chen, X., Chen, X. Y., Liu, Z. F., and Wang, H. L. (2007). “Activated carbon with excellent Chromium (VI) adsorption performance prepared by acid-base surface modification.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 141, pp. 315–319, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.006.
Marselli, B., Garcia-Gomez, J., Michaud, P. A., Rodrigo, M. A., and Comninellis, Ch. (2003). “Electrogeneration of Hydroxyl radicals on Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes.” J. Electrochem. Soc., Vol. 150, pp. 79–83, DOI: 10.1149/1.1553790.
McEnaney, B. (1987). “Estimation of the dimensions of micropores in active carbons using the Dubinin-Radushkevich equation.” Carbon, Vol. 25, No. 1, pp. 69–75, DOI: 10.1016/0008-6223(87)90041-8.
Menendez, J. A., Menendez, E. M., Iglesias, M. J., Garcia, A., Pis, J. J. (1999). “Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons by means of microwave-induced treatments.” Carbon, Vol. 37, pp. 1115–1121, DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00302-9.
Moreno-Pirajan, J. C. (2011). “The removal and kinetic study of Mn, Fe, Ni and Cu ions from wastewater onto activated carbon from coconut shells.” Adsorption, Vol. 17, pp. 505–514, DOI: 10.1007/s10450-010-9311-5.
Nabais, J. M. V., Carrott, P. J. M., Riberiro Carrott, M. M. L., and Menendez, J. A. (2004). “Preparation and modification of activated carbon fibres by microwave heating.” Carbon, Vol. 42, pp. 1315–1320, DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.01.033.
Pereira, L., Pereira, R., Pereira, M. F. R., Van der Zee, F. P., Cervantes, F. J., and Alves, M. M. (2010). “Thermal modification of activated carbon surface chemistry improves its capacity as redox mediator for azo dye reduction.” J. Hazard. Mater, Vol. 183, pp. 931–939, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.005.
Rahman, M. M., Bari, Q. H., Mohammad, N., Ahsan, A., Sobuz, H. R., and Uddin, M. A. (2013). “Characterization of rice husk carbon produced through simple technology.” Advances in Materials Science and Application, Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 25–30.
Renou, S., Givaudan, J., Poulain, S., and Dirassouyan, Moulin, P. (2008). “Landfill leachate treatment: review and opportunity.” J. Hazard Mater, Vol. 150, pp. 468–493, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.077.
Shafeeyan, M. S., Daud, W. M. A. W., Houshmand, A., and Shamiri, A. (2010). “A review on surface modification of activated varbon for carbon dioxide adsorption.” Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, Vol. 89, No. 2, pp. 143–151, DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2010.07.006.
Shaheed, R., Azhari, C. H., Ahsan, A., and Mohtar, W. H. M. W. (2015). “Production and characterisation of low-tech activated carbon from coconut shell.” Journal of Hydrology and Environment Research, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 6–14.
Shen, W., Li, Z., and Liu, Y. (2008). “Surface chemical functional groups modification of porous carbon.” Recent Patents on Chemical Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 27–40.
Sonavane, P. G. and Munavalli, G. R. (2009). “Modeling nitrogen removal in a constructed wetland treatment system.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 60, No. 2, pp. 301–309, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2009.319.
Sun, G. and Austin, D. (2007). “A mass balance study on nitrification and deammonification in vertical flow constructed wetlands treating landfill leachate.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 56, No. 3, pp. 117–123, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2007.503.
Tadda, M. A., Ahsan, A., Shitu, A., ElSergany, M, Arunkumar, T., Jose, B., Razzaque, M. A., and Daud, N. N. N. (2016). “A review on activated carbon: process, application and prospects.” Journal of Advanced Civil Engineering Practice and Research, Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 7–13.
Tangjuank, S., Insuk, N., Udee, V., and Tonrakoon, J. (2009). “Chromium (III) sorption from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared from cashew nut shells.” International Journal of Physical Sciences, Vol. 4, No. 8, pp. 412–417.
Timur, S., Kantarli, I. C., Onenc, S., and Yanik, J. (2010). “Characterization and application of activated carbon produced from oak cups pulp.” Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, Vol. 89, pp. 129–136, DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2010.07.002.
Valdes, H., Sanchez-Polo, M., Rivera-Utrilla, J., and Zaror, C. A. (2002). “Effect of ozone treatment on surface properties of activated carbon.” Langmuir, Vol. 18, No. 6, pp. 2111–2116, DOI: 10.1021/la010920a.
Vilar, A., Eiroa, M., Kennes, C., and Veiga, M. C. (2010). “The SHARON process in the treatment of landfill leachate.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 61, No. 1, pp. 47–52, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2010.786.
Welander, U. (1998). Characterization and treatment of Municipal landfill leachate, Published Thesis, Department of Biotechnology, Lund University, Sweden.
Wibowo, N., Setyadhi, L., Wibowo, D., Setiawan, J., and Ismadji, S. (2007). “Adsorption of benzene and toluene from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon and its acid and heat treated forms: Influence of surface chemistry on adsorption.” Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 146, pp. 237–242, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.011.
Wiszniowski, J., Robert, D., Surmacz-Gorska, J., Miksch, K., and Weber, J. (2006). “Landfill leachate treatment methods: A review”. Environmental Chemistry Letters, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 51–61, DOI: 10.1007/s10311-005-0016-z.
Yin, C. Y., Aroua, M. K., and Daud, W. M. A.W. (2007). “Review of modifications of activated carbon for enhancing contaminant uptakes from aqueous solutions.” Sep. Purif Technol., Vol. 52, pp. 403–415, DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.009.
Yuen, F. K. and Hameed, B. H. (2009). “Recent developments in preparation and regeneration of activated carbons by microwaves.” Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, Vol. 149, pp. 19–27, DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2008.12.005.
Zhang, J. and Yang, L.-J. (2011). “Notice of reaction study on adsorption of chromium (VI) by modified activated carbon with potassium permanganate.” Paper presented at the Bionformatics and Biomedical Engineering (iCBBE), 5th International Conference, DOI: 10.1109/icbbe.2011.5781100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erabee, I.K., Ahsan, A., Jose, B. et al. Adsorptive Treatment of Landfill Leachate using Activated Carbon Modified with Three Different Methods. KSCE J Civ Eng 22, 1083–1095 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1430-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1430-z