Abstract
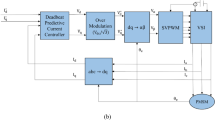
This paper presents a method for compensating the force ripple in permanent magnet linear synchronous motors (PMLSMs) by adopting a composite feedforward compensation scheme. Firstly, the vector control system of PMLSMs is described, and various force disturbances influencing the electromagnetic thrust are analyzed. As a result, the mathematical model of the whole system considering the force ripple is established. Then, a novel composite feedforward compensation scheme is proposed, which consists of a recursive least squares (RLS) parameter identification component and two feedforward compensation loops corresponding to the reference position trajectory and the force ripple, respectively. Finally, the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed composite feedforward compensation are demonstrated by simulation. The main incentive of this paper is the combination with the composite feedforward compensation loop corresponding to the reference position trajectory to improve the compensation effect of force ripple in PMLSMs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
YUAN F, WANG X Y, TAO J F, et al. Research on vane end face of cam-rotor vane servo motor based on disturbing torque [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Science), 2016, 21(6): 641–647.
PEI R L, ZENG L B, CHEN X, et al. Studies of high-efficiency electrical steels used in electric vehicle motors [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Science), 2012, 17(3): 319–322.
CHEN S Y, LIU T S. Intelligent tracking control of a PMLSM using self-evolving probabilistic fuzzy neural network [J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2017, 11(6): 1043–1054.
YANG C Y, MA T T, CHE Z Y, et al. An adaptivegain sliding mode observer for sensorless control of permanent magnet linear synchronous motors [J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 3469–3478.
HOBURG J F. Modeling maglev passenger compartment static magnetic fields from linear Halbach permanent-magnet arrays [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2004, 40(1): 59–64.
RONG Z L, HUANG Q. A new PMSM speed modulation system with sliding mode based on active disturbance-rejection control [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(6): 1406–1415.
XUE Y B, YAO Z Q, CHENG D, et al. Coast-down modeling of canned motor based on torque behavior study [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Science), 2015, 20(4): 420–426.
ZHANG Z J, ZHOU H B, DUAN J A, et al. Design and analysis of a new ring winding structure for permanent magnet linear synchronous motors [J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2016, 44(12): 3311–3321.
WANG M Y, LI L Y, PAN D H. Detent force compensation for PMLSM systems based on structural design and control method combination [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(11): 6845–6854.
CHUNG S U, KIM J M, WOO B C, et al. Development of doubly salient permanent magnet linear synchronous motor for general-purpose automation applications [J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2013, 14(12): 2075–2080.
BARCARO M, BIANCHI N, MAGNUSSEN F. Remarks on torque estimation accuracy in fractional-slot permanent-magnet motors [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(6): 2565–2572.
CHUNG S U, KIM J M. Double-sided iron-core PMLSM mover teeth arrangement design for reduction of detent force and speed ripple [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(5): 3000–3008.
BANG D J, HWANG S H. Wide air-gap control for multi-module permanent magnet linear synchronous motors without magnetic levitation windings [J]. Journal of Power Electronics, 2016, 16(5): 1773–1780.
CHO K, NAM K. Periodic learning disturbance observer based precision motion control in PMLSM motion systems considering long-term instability problem [J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2016, 17(9): 1101–1112.
TAN K K, LEE T H, DOU H F, et al. Precision motion control with disturbance observer for pulsewidth-modulated-driven permanent-magnet linear motors [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2003, 39(3): 1813–1818.
CHEN S L, TAN K K, HUANG S N. Modeling and compensation of ripples and friction in permanentmagnet linear motor using a hysteretic relay [J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2010, 15(4): 586–594.
TAN K K, HUANG S N, LEE T H. Robust adaptive numerical compensation for friction and force ripple in permanent-magnet linear motors [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2002, 38(1): 221–228.
TAN K K, LEE T H, DOU H, et al. Force ripple suppression in iron-core permanent magnet linear motors using an adaptive dither [J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2004, 341(4): 375–390.
BARATAM A, KARLAPUDY A M, MUNAGALA S. Implementation of thrust ripple reduction for a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor using an adaptive feed forward controller [J]. Journal of Power Electronics, 2014, 14(4): 687–694.
ZHANG D L, CHEN Y P, AI W, et al. Force ripple suppression technology for linear motors based on back propagation neural network [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 21(2): 13–16.
LU S W, TANG X Q, SONG B, et al. Identification and compensation of force ripple in PMSLM using a JITL technique [J]. Asian Journal of Control, 2015, 17(5): 1559–1568.
CHE Z Y, CHEN J Q, YANG C Y, et al. Permanent magnet linear synchronous motor control system based on sliding mode variable structure [J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2017, 44(10): 8–12 (in Chinese).
BASCETTA L, ROCCO P, MAGNANI G. Force ripple compensation in linear motors based on closed-loop position-dependent identification [J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2010, 15(3): 349–359.
ZHANG D L, CHEN Y P, AI W, et al. Precision motion control of permanent magnet linear motors [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2007, 35(3/4): 301–308.
ZHAO S, TAN K K. Adaptive feedforward compensation of force ripples in linear motors [J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2005, 13(9): 1081–1092.
CHEN P, ZHENG J. PMLSM servo system design and implement base on DSP28335 [J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2013(1): 80–83 (in Chinese).
SON Y I, KIM I H, CHOI D S, et al. Robust cascade control of electric motor drives using dual reducedorder PI observer [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3672–3682.
TAN K K, HUANG S N, DOU H F, et al. Adaptive robust motion control for precise trajectory tracking applications [J]. ISA Transactions, 2001, 40(1): 57–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61374043 and 61603392), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (Nos. 2013M530278 and 2014T70558)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Che, Z. & Zhou, L. Composite Feedforward Compensation for Force Ripple in Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motors. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 24, 782–788 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-019-2111-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-019-2111-5
Key words
- permanent magnet linear synchronous motor (PMLSM)
- force ripple
- composite feedforward compensation
- recursive least squares (RLS)