Abstract
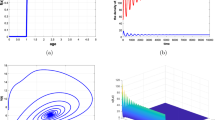
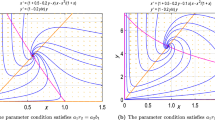
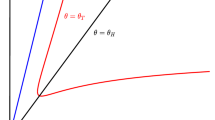
The main objective of this thesis is to learn about the dynamics of a diffusive Leslie–Gower predator–prey system with functional response and time delay under homogeneous Neumann boundary conditions. By in-depth analyzing eigenvalues distribution, it proves that there are (diffusion-induced, delay-induced) Turing–Hopf bifurcations around positive equilibrium state. More than this, base on the foundation of the regular modality and the center manifold theory, It is responsible for establishing a precise formula, which is to determine the Turing–Hopf bifurcation property of a diffusive Leslie–Gower predator–prey system with functional response. After that, we applied the formula to a diffusive Leslie–Gower predator–prey system with Beddington–DeAngelis functional response and time delay integrally. Finally, the results have been verified and replenished by numerical simulation adequately.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berryman, A.A.: The origins and evolution of predator-prey theory. Ecology 73, 1530–1535 (1992)
Wollkind, J.D., Logan, J.A.: Temperature-dependent predator-prey mite ecosystem on apple tree foliage. J. Math. Biol. 6, 265–283 (1978)
Wollkind, J.D., Collings, J.B., Logan, J.A.: Metastability in a temperature-dependent model system for predator-prey mite outbreak interactions on fruit trees. Bull. Math. Biol. 50, 379–409 (1988)
May, R.M.: Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystems. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (1978)
Leslie, P.H., Gower, J.C.: The properties of a stochastic model for the predator-prey type of interaction between two species. Biometrika 47, 219–234 (1960)
Li, Y., Xiao, D.: Bifurcations of a predator-prey system of Holling and Leslie types. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34, 606–620 (2007)
Artidi, R., Ginzburg, L.R.: Coupling in predator-prey dynamics: ratio-dependence. J. Theor. Biol. 139, 311–326 (1989)
Song, Y., Zou, X.: Bifurcation analysis of a diffusive ratio-dependent predator-prey model. Nonlinear Dyn. 78, 49–70 (2014)
Song, Y., Peng, Y., Zou, X.: Persistence, stability and Hopf bifurcation in a diffusive ratio-dependent predator-prey model with delay. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24, 1450093 (2014)
Shi, H., Li, Y.: Global asymptotic stability of a diffusive predator-prey model with ratio-dependent functional response. Appl. Math. Comput. 250, 71–77 (2015)
Zhou, J.: Bifurcation analysis of a diffusive predator-prey model with ratio-dependent Holling type III functional response. Nonlinear Dyn. 81, 1535–1552 (2015)
Yang, W., Li, X.: Global asymptotical stability for a diffusive predator-prey model with ratio-dependent Holling type III functional response. Differ. Equ. Dyn. Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12591-017-0370-x
Banerjee, M., Banerjee, S.: Turing instabilities and spatio-temporal chaos in ratio-dependent Holling-Tanner model. Math. Biosci. 236, 64–76 (2012)
Arditi, R., Saiah, H.: Empirical evidence of the role of heterogeneity in ratio-dependent consumption. Ecology 73, 1544–1551 (1992)
Kuang, Y., Beretta, E.: Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J. Math. Biol. 36, 389–406 (1998)
Li, B., Kuang, Y.: Heteroclinic bifurcation in the Michaelis-Menten-type ratio-dependent predator-prey system. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 67, 1453–1464 (2007)
Ruan, S., Tang, Y., Zhang, W.: Versal unfoldings of predator-prey systems with ratio-dependent functional response. J. Differ. Equ. 249, 1410–1435 (2010)
Beddington, J.R.: Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J. Anim. Ecol. 44, 331–340 (1975)
DeAngelis, D.L., Goldstein, R.A., O’Neill, R.V.: A model for trophic interaction. Ecology 56, 881–892 (1975)
Han, R., Dai, B., Wang, L.: Delay induced spatiotempopal patterns in a diffusive intraguild predation model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. Math. Biosci. Eng. 15(3), 595–627 (2018)
Du, P., Duan, C., Liao, X.: Dynamics behaviors of a reaction-diffusion predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and delay. Appl. Math. 5, 843–851 (2014)
Hu, G., Li, X., Wang, Y.: Pattern formation and spatiotemporal chaos in a reaction-diffusion predator-prey system. Nonlinear Dyn. 81, 265–275 (2015)
Fan, M., Kuang, Y.: Dynamics of a nonautonomous predator-prey system with the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 295, 15–39 (2004)
Crowley, P.H., Martin, E.K.: Functional responses and interference within and between year classes of a dragonfly population. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 8, 211–221 (1989)
Li, H.: Asymptotic behavior and multiplicity for a diffusive Leslie-Gower predator-prey system with Crowley-Martin functional response. Comput. Math. Appl. 68, 693–705 (2014)
Ali, N., Jazar, M.: Global dynamics of a modified Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with Crowley-Martin functional responses. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 43, 271–293 (2013)
Zhou, J.: Positive solutions for a modified Leslie-Gower prey-predator model with Crowley-Martin functional responses. Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 21, 621–661 (2014)
Chen, S., Shi, J.: Global attractivity of equilibrium in Gierer-Meinhardt system with activator production saturation and gene expression time delays. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 14, 1871–1886 (2013)
Cao, X., Jiang, W.: Turing-Hopf bifurcation and spatiotemporal patterns in a diffusive predator-prey system with Crowley-Martin functional response. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 43, 428–450 (2018)
Klausmeier, C.A.: Regular and irregular patterns in semiarid vegetation. Science 285, 838–838 (1999)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology II. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg (2002)
Wu, J.: Theory and Applications of Partial Functional Differential Equations. Springer-Verlag, New York (1996)
Hsu, S.B., Huang, T.W.: Global stability for a class of predator-prey systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 55, 763–783 (1995)
Yi, F., Wei, J., Shi, J.: Bifurcation and spatio-temporal patterns in a homogeneous diffusive predator-prey system. J. Differ. Equ. 246, 1944–1977 (2009)
Shi, H., Li, W., Lin, G.: Positive steady states of a diffusive predator-prey system with modified Holling-Tanner functional response. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 11, 3711–3721 (2010)
Yang, W.: Global asymptotical stability and persistent property for a diffusive predator-prey system with modified Leslie-Gower functional response. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 14, 1323–1330 (2013)
Zhang, C., Ke, A., Zheng, B.: Patterns of interaction of coupled reaction-diffusion systems of the FitzHugh-Nagumo type. Nonlinear Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05065-8
Liu, B., Wu, R., Chen, L.: Turing-Hopf bifurcation analysis in a superdiffusive predator-prey model. Chaos 28, 113118 (2018)
Xu, X., Wei, J.: Turing-Hopf bifurcation of a class of modified Leslie-Gower model with diffusion. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 23(2), 765–783 (2018)
Chen, X., Jiang, W.: Turing-Hopf bifurcation and multi-stable spatio-temporal patterns in the Lengyel-Epstein system. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 49, 386–404 (2019)
Song, Y., Zhang, T., Peng, Y.: Turing-Hopf bifurcation in the reaction-diffusion equations and its applications. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 33, 229–258 (2016)
Song, Y., Jiang, H., Liu, Q., Yuan, Y.: Spatiotemporal dynamics of the diffusive Mussel-Algae model near Turing-Hopf bifurcation. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 16(4), 2030–2062 (2017)
Ruan, S.: On nonlinear dynamics of predator-prey models with discrete delay. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 4(2), 140–188 (2009)
Faria, T.: Normal forms and Hopf bifurcation for partial differential equations with delay. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 352, 2217–2238 (2000)
Faria, T.: Stability and bifurcation for a delayed predator-prey model and the effect of diffusion. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 254, 433–463 (2001)
Chen, S., Shi, J., Wei, J.: Global stability and Hopf bifurcation in a delayed diffusive Leslie-Gower predator-prey system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 22, 1250061 (2012)
Lu, Z., Liu, X.: Analysis of a predator-prey model with modified Holling-Tanner functional response and time delay. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 9, 641–650 (2008)
Zhang, J.: Bifurcation analysis of a modified Holling-Tanner predator-prey model with time delay. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 1219–1231 (2012)
Yang, R., Zhang, C.: Dynamics in a diffusive predator-prey system with a constant prey refuge and delay. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 31, 1–22 (2016)
Jiang, W., Wang, H., Cao, X.: Turing Instability and Turing-Hopf Bifurcation in Diffusive Schnakenberg Systems with Gene Expression Time Delay. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10884-018-9702-y
Song, Y., Jiang, H., Yuan, Y.: Turing-Hopf bifurcation in the reaction-diffusion system with delay and application to a diffusive predator-prey model. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.11948/2156-907X.20190015
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.11701208), the key Projects of Natural Science Research in Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province (No.2022AH051948, No.2023AH051363), the young Backbone Teachers Overseas Study and Research Funding Project in Department of Education in Anhui Province(No.JWFX2023035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors are seriously and solemnly declaring that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H. Stable spatially inhomogeneous periodic solutions for a diffusive Leslie–Gower predator–prey model. J. Appl. Math. Comput. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-024-02018-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-024-02018-2