Abstract
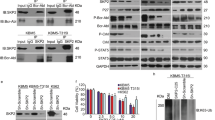
In the present study, we studied downstream signals of BCR-ABL with regard to Src family kinases and YAP, a transcription cofactor and an effector of the Hippo pathway. We first checked the phosphorylation status of YAP and found that it was constitutively phosphorylated at tyrosine 357 in CML-derived cell lines (TCC-S and K562) but not in AML-derived cell lines (HL-60 and KG-1a). Treatment with imatinib or RK-20449 inhibited cell growth and decreased tyrosine phosphorylation of YAP in both CML lines. Expression of Survivin or Cyclin D1 was decreased in TCC-S, but not in either HL-60 or KG-1a. Furthermore, we established BCR-ABL stable transfectant and control empty vector transfectant from TF-1, a factor-dependent human erythroleukemia cell line, to verify our results obtained with CML cell lines. YAP was phosphorylated at Y357 constitutively in BCR-ABL stable transfectant but not in control transfectant, and treatment with imatinib or RK-20449, a Src family kinase-specific inhibitor, inhibited cell growth, YAP tyrosine phosphorylation, and expression of Cyclin D1 in BCR-ABL stable transfectant. These results suggest that BCR-ABL induces tyrosine phosphorylation of YAP presumably through Src family kinases, which results in expression of Survivin and Cyclin D leading to leukemogenesis in CML cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue A, Kobayashi CI, Shinohara H, Miyamoto K, Yamauchi N, Yuda J, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells and molecular target therapies for overcoming resistance and disease persistence. Int J Hematol. 2018;108:365–70.
Chereda B, Melo JV. Natural course and biology of CML. Ann Hematol. 2015;94:107–21.
Hoelbl A, Schuster C, Kovacic B, Zhu B, Wickre M, Hoelzl MA, et al. Stat5 is indispensable for the maintenance of bcr/abl -positive leukaemia: stat5 in leukaemia maintenance. EMBO Mol Med. 2010;2:98–110.
Klejman A, Rushen L, Morrione A, Slupianek A, Skorski T. Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase inhibitors enhance the anti-leukemia effect of STI571. Oncogene. 2002;21:5868–76.
Sattler M, Mohi MG, Pride YB, Quinnan LR, Malouf NA, Podar K, et al. Critical role for Gab2 in transformation by BCR/ABL. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:479–92.
Wilson MB, Schreiner SJ, Choi H-J, Kamens J, Smithgall TE. Selective pyrrolo-pyrimidine inhibitors reveal a necessary role for Src family kinases in Bcr-Abl signal transduction and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2002;21:8075–88.
Rubbi L, Titz B, Brown L, Galvan E, Komisopoulou E, Chen SS, et al. Global phosphoproteomics reveals crosstalk between Bcr-Abl and negative feedback mechanisms controlling src signaling. Sci Signal. 2011;4:ra18.
Zhao B, Tumaneng K, Guan K-L. The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:877–83.
Taniguchi K, Wu L-W, Grivennikov SI, de Jong PR, Lian I, Yu F-X, et al. A gp130–Src–YAP module links inflammation to epithelial regeneration. Nature. 2015;519:57–62.
Li P, Silvis MR, Honaker Y, Lien W-H, Arron ST, Vasioukhin V. αE-catenin inhibits a Src–YAP1 oncogenic module that couples tyrosine kinases and the effector of Hippo signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 2016;30:798–811.
Taniguchi K, Moroishi T, de Jong PR, Krawczyk M, Grebbin BM, Luo H, et al. YAP–IL-6ST autoregulatory loop activated on APC loss controls colonic tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017;114:1643–8.
Sugihara T, Werneburg NW, Hernandez MC, Yang L, Kabashima A, Hirsova P, et al. YAP tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear localization in cholangiocarcinoma cells are regulated by LCK and independent of LATS activity. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16:1556–67.
Afar DE, McLaughlin J, Sherr CJ, Witte ON, Roussel MF. Signaling by ABL oncogenes through cyclin D1. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1995;92:9540–4.
Wang Z, Sampath J, Fukuda S, Pelus LM. Disruption of the Inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin sensitizes Bcr-abl–Positive cells to STI571-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8224–32.
Rangatia J, Bonnet D. Transient or long-term silencing of BCR-ABL alone induces cell cycle and proliferation arrest, apoptosis and differentiation. Leukemia. 2006;20:68–76.
Saito Y, Yuki H, Kuratani M, Hashizume Y, Takagi S, Honma T, et al. A pyrrolo-pyrimidine derivative targets human primary aml stem cells in vivo. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:181ra52.
Kano Y. In vitro cytotoxic effects of a tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 in combination with commonly used antileukemic agents. Blood. 2001;97:1999–2007.
Kitamura T, Tange T, Terasawa T, Chiba S, Kuwaki T, Miyagawa K, et al. Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates dependently on GM-CSF, IL-3, or erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol. 1989;140:323–34.
Gu L, Chiang K-Y, Zhu N, Findley HW, Zhou M. Contribution of STAT3 to the activation of survivin by GM-CSF in CD34 + cell lines. Exp Hematol. 2007;35:957–66.
Muramatsu T, Imoto I, Matsui T, Kozaki K, Haruki S, Sudol M, et al. YAP is a candidate oncogene for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:389–98.
Zhang W, Gao Y, Li F, Tong X, Ren Y, Han X, et al. YAP promotes malignant progression of Lkb1 -deficient lung adenocarcinoma through downstream regulation of survivin. Cancer Res. 2015;75:4450–7.
Mizuno T, Murakami H, Fujii M, Ishiguro F, Tanaka I, Kondo Y, et al. YAP induces malignant mesothelioma cell proliferation by upregulating transcription of cell cycle-promoting genes. Oncogene. 2012;31:5117–22.
Vlahov N, Scrace S, Soto MS, Grawenda AM, Bradley L, Pankova D, et al. Alternate RASSF1 transcripts control src activity, E-cadherin contacts, and YAP-mediated invasion. Curr Biol. 2015;25:3019–34.
Levy D, Adamovich Y, Reuven N, Shaul Y. Yap1 phosphorylation by c-Abl Is a critical step in selective activation of proapoptotic genes in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell. 2008;29:350–61.
Hu Y, Liu Y, Pelletier S, Buchdunger E, Warmuth M, Fabbro D, et al. Requirement of Src kinases Lyn, Hck and Fgr for BCR-ABL1-induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2004;36:453–61.
Donato E, Biagioni F, Bisso A, Caganova M, Amati B, Campaner S. YAP and TAZ are dispensable for physiological and malignant haematopoiesis. Leukemia. 2018;32:2037–40.
Li H, Huang Z, Gao M, Huang N, Luo Z, Shen H, et al. Inhibition of YAP suppresses CML cell proliferation and enhances efficacy of imatinib in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0414-z.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Xiaoyan Jiang (BC Cancer Agency—Terry Fox Laboratory) for MSCV-BCR-ABL-IRES-GFP, Dr. Yusuke Furukawa (Jichi University) for TCC-S, and Dr. Toshio Kitamura (University of Tokyo) for TF-1. We also thank our laboratory members, M.Sc. Konomi Maeda, M.Sc. Haruka Oshima, and Dr. Ryotaro Nishi for their collaborations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no competing interests in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Moriyama, K., Hori, T. BCR-ABL induces tyrosine phosphorylation of YAP leading to expression of Survivin and Cyclin D1 in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Int J Hematol 110, 591–598 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-019-02726-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-019-02726-7