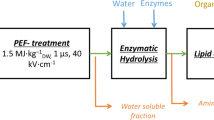
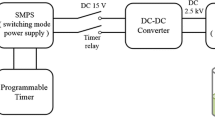
Abstract
Developing effective, energy-efficient methods to extract lipids from microalgae remains a challenge in bioenergy. This study assesses electric pulse (EP) pretreatments to enhance lipid extraction from Chlorella protothecoides. In tandem with solvent extraction, we applied 10, 50, 100, 200, and 300 60 kV/cm, 60 ns duration EPs or 3, 17, 33, 67, and 100 60 kV/cm, 300 ns duration EPs to match the energy density u applied to the sample for each EP duration. Lipid recovery increased with increasing u for each EP duration until reaching a maximum for 17 300 ns EPs (the second lowest u) and 100 60 ns EPs (the third lowest u) to achieve a 13.3% and 16.1% increase in lipid extraction, respectively. Lipid extraction declined at higher u due to increased cell lysis. The largest net energy released calculated from the difference between the energy available from the extracted lipids and the applied energy of the EPs occurred at the lowest u for each EP duration. Applying trains of 100 μs EPs induced qualitatively similar behavior. These results suggest that a more detailed parametric study may optimize EP parameters for net energy release for specific microalgae and solvents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goettel M, Eing C, Gusbeth C, Straessner R, Frey W (2013) Pulsed electric field assisted extraction of intracellular valuables from microalgae. Algal Res 2:401–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.07.004
Garner AL (2019) Pulsed electric field inactivation of microorganisms: from fundamental biophysics to synergistic treatments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:2917–2929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10067-y
Breton M, Mir LM (2012) Microsecond and nanosecond electric pulses in cancer treatments. Bioelectromagnetics 33:106–123. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20692
Frey W, Gusbeth C, Schwartz T (2013) Inactivation of Pseudomonas putida by pulsed electric field treatment: a study on the correlation of treatment parameters and inactivation efficiency in the short-pulse range. J Membr Biol 246:769–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9547-6
Lambricht L, Lopes A, Kos S, Sersa G, Préat V, Vandermeulen G (2016) Clinical potential of electroporation for gene therapy and DNA vaccine delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 13:295–310. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2016.1121990
Schoenbach KH, Beebe SJ, Buescher ES (2001) Intracellular effect of ultrashort electrical pulses. Bioelectromagnetics 22:440–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.71
Schoenbach KH, Joshi RP, Kolb JF, Chen N, Stacey M, Blackmore PF, Buescher ES, Beebe SJ (2004) Ultrashort electrical pulses open a new gateway into biological cells. Proc IEEE 92:1122–1137. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2004.829009
Napotnik TB, Reberšek M, Vernier PT, Mali B, Miklavčič D (2016) Effects of high voltage nanosecond electric pulses on eukaryotic cells (in vitro): a systematic review. Bioelectrochemistry 110:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2016.02.011
Vernier PT, Levine ZA, Gundersen MA (2013) Water bridges in electropermeabilized phospholipid bilayers. Proc IEEE 101:494–504. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2012.2222011
Napotnik TB, Wu YH, Gundersen MA, Miklavčič D, Vernier PT (2012) Nanosecond electric pulses cause mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in Jurkat cells. Bioelectromagnetics 33:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20707
Beebe SJ, Fox PM, Rec LJ, Willis ELK, Schoenbach KH (2003) Nanosecond, high-intensity pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis in human cells. FASEB J 17:1493–1495. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-0859fje
Zhang J, Blackmore PF, Hargrave BY, Xiao S, Beebe SJ, Schoenbach KH (2008) Nanosecond pulse electric field (nanopulse): a novel non-ligand agonist for platelet activation. Arch Biochem Biophys 471:240–248
Garner AL, Frelinger AL III, Gerrits AJ, Gremmel T, Forde EE, Carmichael SL, Michelson AD, Neculaes VB (2019) Using extracellular calcium concentration and electric pulse conditions to tune platelet-rich plasma growth factor release and clotting. Med Hypotheses 125:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2019.02.036
Torres AS, Caiafa A, Garner AL, Klopman S, LaPlante N, Morton C, Conway K, Michelson AD, Frelinger AL III, Neculaes VB (2014) Platelet activation using electric pulse stimulation: growth factor profile and clinical implications. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 77:S94–S100. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000000322
Vasilkoski Z, Esser AT, Gowrishankar TR, Weaver JC (2006) Membrane electroporation: the absolute rate equation and nanosecond time scale pore creation. Phys Rev E 74:021904. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.74.021904
Garner AL, Chen G, Chen N, Sridhara V, Kolb JF, Swanson RJ, Beebe SJ, Joshi RP, Schoenbach KH (2007) Ultrashort electric pulse induced changes in cellular dielectric properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.159
Pakhomov AG, Kolb JF, White JA, Joshi RP, Xiao S, Schoenbach KH (2007) Long-lasting plasma membrane permeabilization in mammalian cells by nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF). Bioelectromagnetics 28:655–663. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20354
Vernier PT, Sun Y, Gundersen MA (2006) Nanoelectropulse-driven membrane perturbation and small molecule permeabilization. BMC Cell Biol 7:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2121-7-37
Eing C, Goettel M, Straessner R, Gusbeth C, Frey W (2013) Pulsed electric field treatment of microalgae - benefits for microalgae biomass processing. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 41:2901–2907. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2013.2274805
Silve A, Papachristou I, Wüstner R, Sträßner R, Schirmer M, Leber K, Guo B, Interrante L, Posten C, Frey W (2018) Extraction of lipids from wet microalga Auxenochlorella protothecoides using pulsed electric field treatment and ethanol-hexane blends. Algal Res 29:212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.11.016
Xu H, Miao X, Wu Q (2006) High quality biodiesel production from a microalga Chlorella protothecoides by heterotrophic growth in fermenters. J Biotechnol 126:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.05.002
He X, Dai J, Wu Q (2016) Identification of sporopollenin as the outer layer of cell wall in microalga Chlorella protothecoides. Front Microbiol 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01047
Xiong W, Li X, Xiang J, Wu Q (2008) High-density fermentation of microalga Chlorella protothecoides in bioreactor for microbio-diesel production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1285-1
Grady J, Morgan JA (2011) Heterotrophic growth and lipid production of Chlorella protothecoides on glycerol. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34:121–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-010-0474-y
Kolb JF, Kono S, Schoenbach KH (2006) Nanosecond pulsed electric field generators for the study of subcellular effects. Bioelectromagnetics. 27:172–187
Garner AL, Chen N, Yang J, Kolb J, Swanson RJ, Loftin KC, Beebe SJ, Joshi RP, Schoenbach KH (2004) Time domain dielectric spectroscopy measurements of HL-60 cell suspensions after microsecond and nanosecond electrical pulses. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 32:2073–2084. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2004.835973
Lai YS, Parameswaran P, Li A, Baez M, Ritmann BE (2014) Effect of pulsed electric field treatment on enhancing lipid recovery from the microalga, Scenedesmus. Bioresour Technol 173:457–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.124
Lepage G, Roy CC (1984) Improved recovery of fatty acid through direct transesterification without prior extraction or purification. J Lipid Res 25:1391–1396 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6530596
Joannes C, Sipaut CS, Dayou J, Yasir SM, Mansa RF (2015) Review paper on cell membrane electroporation of microalgae using electric field treatment method for microalgae lipid extraction. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 78:012034. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/78/1/012034
Pakhomov AG, Gianulis E, Vernier PT, Semenov I, Xiao S, Pakhomova ON, Bodenes P (2015) Multiple nanosecond electric pulses increase the number but not the size of long-lived nanopores in the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1848:958–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.12.026
Yanfeng G, Shenghua L, Hejun G, Tiegang H, Longbao Z (2007) A new diesel oxygenate additive and its effects on engine combustion and emissions. Appl Thermal Eng 27:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.04.0217
Ibey BL, Ullery JC, Pakhomova ON, Roth CC, Semenov I, Beier HT, Tarango M, Xiao S, Schoenbach KH, Pakhomov AG (2014) Bipolar nanosecond electric pulses are less efficient at electropermeabilization and killing cells than monopolar pulses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443:568–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.004
Garner AL, Caiafa A, Jiang Y, Klopman S, Morton C, Torres AS, Loveless AM, Neculaes VB (2017) Design, characterization and experimental validation of a compact, flexible pulsed power architecture for ex vivo platelet activation. PLoS One 12:e0181214. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181214
Beveridge JR, Wall K, MacGregor SJ, Anderson JG, Rowan NJ (2004) Pulsed electric field inactivation of spoilage microorganisms in alcoholic beverages. Proc IEEE 92:1138–1143. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2005.852345
Coustets M, Ganeva V, Galutzov B, Teissie J (2015) Millisecond duration pulses for flow-through electro-induced protein extraction from E. coli and associated eradication. Bioelectrochemistry 103:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2014.08.008
Garner AL, Deminsky M, Neculaes VB, Chashihin V, Knizhnik A, Potapkin B (2013) Cell membrane thermal gradients induced by electromagnetic fields. J Appl Phys 113:214701. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4809642
Song J, Joshi RP, Schoenbach KH (2011) Synergistic effects of local temperature enhancements on cellular responses in the context of high-intensity, ultrashort electric pulses. Med Biol Eng Comput 49:713–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-011-0745-z
Song J, Garner AL, Joshi RP (2017) Effect of thermal gradients created by electromagnetic fields on cell-membrane electroporation probed by molecular-dynamics simulations. Phys Rev Appl 7:024003. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.7.024003
Dong T, Knoshaug EP, Pienkos PT, Laurens LML (2016) Lipid recovery from wet oleaginous microbial biomass for biofuel production: a critical review. Appl Energy 177:879–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.002
Azencott HR, Peter GF, Prausnitz MR (2007) Influence of the cell wall on intracellular delivery to algal cells by electroporation and sonication. Ultrasound Med Biol 33:1805–1817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2007.05.008
Ly HV, Longo ML (2004) The influence of short-chain alcohols on interfacial tension, mechanical properties, area/molecule, and permeability of fluid lipid bilayers. Biophys J 87:1013–1033. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.103.034280
Cooney M, Young G, Nagle N Extraction of bio-oils from microalgae. Sep Purif Rev 38:291–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/15422110903327919
Ivorra A, Villemejane J, Mir LM (2010) Electrical modeling of the influence of medium conductivity on electroporation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:10055–10064. https://doi.org/10.1039/C004419A
Kotnik T, Miklavčič D (2006) Theoretical evaluation of voltage inducement on internal membranes of biological cells exposed to electric fields. Biophys J 90:480–491. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.105.070771
Acknowledgments
We thank Anand Vadlamani and Andrew Fairbanks for helping to set up the NSEP generator and Lakshya Mittal and Raji Sundararajan for assisting with the electroporator.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CG, MLM, SR, JAM, and ALG conceived and designed the experiment; CG, MLM, and ZEZ collected and assembled the data; CG, MLM, and ALG analyzed and interpreted the data; and CG and MLM drafted the article. All authors critically contributed to the reading, commenting, and writing of the manuscript. All authors certify that they have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content, including participation in the concept, design, analysis, writing, or revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of Informed Consent
No conflicts, informed consent, human or animal rights applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geissler, C.H., Mulligan, M.L., Zmola, Z.E. et al. Electric Pulse Pretreatment for Enhanced Lipid Recovery from Chlorella protothecoides. Bioenerg. Res. 13, 499–506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-019-10064-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-019-10064-z