Abstract
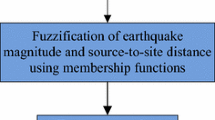
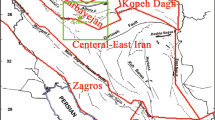
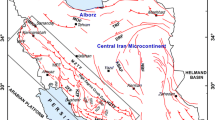
The land of Iran due to being located on the orogenic belt Alpine-Himalayas, one of the seismic regions of the world, it has always suffered heavy damage from earthquakes. Seismic hazard analysis is the determination of the potential level of ground motion parameters that might be generated by future earthquakes. Due to the diversity of parameters which might influence the occurrence of earthquakes, seismic hazard analysis like many other issues in seismology is a complicated problem, hence, it creates inevitable uncertainties in consequences. Therefore, Fuzzy logic is a suitable tool which is used as a decision-making method to solve problems and to model uncertainties and ambiguities. In this study, seismic hazard analysis is performed based on fuzzy logic technique and deterministic method (FDSHA). Also, the three input parameters, the earthquake maximum magnitude (Mmax), source-to-site distance (R), and fault type (F) and peak ground acceleration (PGA) as the output parameter are defined as fuzzy sets. Membership functions for input and output parameters are determined based on the judgment of the expert and fuzzy rules for peak ground acceleration according to the input parameters and the judgment of the expert is defined. The study area is Anzali Port, which is located in the Alborz orogenic belt in northern Iran. The results of estimating deterministic seismic hazard using fuzzy system show that the peak ground acceleration in Anzali Port is 0.55 g which is obtained from seismic source with a maximum magnitude of 8 with a faulting mechanism oblique at a distance of 72 km from it. Also, the results obtained from seismic hazard analysis by a deterministic method based on fuzzy logic, are in good agreement with the results obtained from other methods for Anzali Port.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambraseys NN, Melville CP (1982) A history of Persian earthquakes. Cambridge University Press
Andric JM, Lu DG (2016) Risk assessment of bridges under multiple hazards in operation period. Saf Sci 83:80–92
Andric JM, Lu DG (2017) Fuzzy methods for prediction of seismic resilience of bridges. Int J Dis Risk Reduct 22:458–468
Berberian M (1977) Contribution to the seismotectonics of Iran (Pare III). Geological Survey of Iran No. 40
Boostan E, Tahernia N, Shafiee A (2015) Fuzzy-probabilistic seismic hazard assessment, case study: Tehran region, Iran. Nat Hazards 77:525–541
Building and Housing Research Center (BHRC) (2008) Regulations designed buildings against standard earthquake
Chen D, Dong W, Shah HC (1988) Earthquake recurrence relationships from fuzzy earthquake magnitudes. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 7:136–142
Chongfu H (1996) Fuzzy risk assessment of urban natural hazards. Fuzzy Sets Syst 83:271–282
Cornell A (1968) Engineering seismic risk analysis. Bull Seismol Soc Am 58(5):1583–1606
Frangopol Μ, Ikejima K, Hong K (1988) Seismic hazard prediction using a probabilistic-fuzzy approach. Struct Saf 5(2):109–117
Ghafari M, Taghizadeh-Farahmand F, Jamail T (2019) Evaluation of Deterministic seismic hazard in Bardsir city in Kerman province by using fuzzy system. J Emerg Manage 8:21–32 (in Persion)
Giovinazzi S, Lagomarsino S (2004) Amacroseismic method for the vulnerability assessment of buildings. In: Proceedings of the 13th world conference on earthquake engineering, Vancouver
Hamzehloo H, Alikhanzadeh A, Rahmani M, Ansari A (2012) Seismic hazard maps of Iran. In: Proceedings of the 15th world conference on earthquake engineering, Lisbon
Hessami K, Jamali F, Tabasi H (2003) Major active faults map of Iran. 1:2,500,000, Tehran, Iran. International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology
Juang CH, Elton DJ (1986) Fuzzy logic for estimation of earthquake intensity based on building damage records. Civ Eng Environ Syst 3(4):187–191
Karimiparidari S, Zare M, Memarian H, Kijko A (2013) Iranian earthquakes; a uniformed catalog with moment magnitude. J Seismol 17:897–911
Kim Y, Hurlebus S, Langari R (2010) Model-based multi-input, multi-output supervisory semiactive nonlinear fuzzy controller. Aided Civil Infrastruct Eng 25(5):387–393
Kosko B (1994) Fuzzy system as universal approximators. IEEE Trans Comp 43(11):1329–1333
Laasri EL, Akhouayri ES, Agliz D, Atmani A (2012) Seismic signal discrimination between earthquakes and quarry blasts using fuzzy logic approach. In: Proceedings of the 5th International conference image and signal processing, Agadir, pp 166–174
Lamarre M, Dong W (1986) Evaluation of seismic hazard with fuzzy algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 3rd, U.S. National conference on earthquake engineering, vol 1, Charleston, pp 221–231
Mamdani EH, Assilian S (1975) An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. Int J Man–Machine Stud 7(1):1–13
Mirzaei N, Mengtan G, Yuntai CH (1998) Seismic source regionalization for seismic zoning of Iran: major seismotectonic provinces. J Earthq Predict Res 7:465–495
Mirzaei N, Gao MT, Chenx YT (1997) A uniform catalog of earthquakes for hazard assessment in Iran. Acta Seismol Sin 10(6):713–726
Mirzaei N, Gao M, Chen YT (1999) Delineation of potential seismic sources for seismic zoning of Iran. J Seismol 3:17–30
Mousavi-Bafrouei SH, Mirzaei N, Shabani E, Eskandari-Ghadi M (2015) Seismic hazard zoning in Iran and estimating peak ground acceleration in provincial capitals. J Earth Space Phys 4:15–38 (in Persion)
Ross JT (1995) Fuzzy logic with engineering applications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sadrykia M, Delavar MR, Zare M (2017) A GIS-based fuzzy decision making model for seismic vulnerability assessment in areas with incomplete data. Int J Geo-Inform 6(4):119
Sánchez-Silva M, Garcia L (2001) Earthquake damage assessment based on fuzzy logic and neural networks. Earthquake Spectra 17(1):89–112
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst SMC 15(1):116–132
Tavakoli B, Ghafory-Ashtiany M (1999) Seismic hazard assessment of Iran. Annali Di Geofisica 42(6):1013–1022
Wadia-Fascetti S, Gunes B (2000) Earthquake response spectra models incorporating fuzzy logic with statistics. Comput Aided Civ Inf Eng 15:134–146
Wang YM, Elhang TM (2008) An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for bridge risk assessment. Expert Syst Appl 34(4):3099–3106
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zadeh LA (1973) Outline of a new approach to the analysis of complex systems and decision processes. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet 3:28–44
Zare M (2012) Development of seismic hazard zoning map for Iran, based on new seismic source determination. In: Proceedings of the 15th world conference on earthquake engineering, Lisbon
Acknowledgement
We would like to show our gratitude to Nourbaksh Mirzaei and S. H. Moosavi-Bafroei, for providing us with the coordinates of seismic sources. We used the software packages Mathlab (STAMMLER 2015) for data processing and plotting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afsari, N., Abdipour, M.S. & Taghizadeh-Farahmand, F. Seismic Hazard Analysis from Deterministic Method Using Fuzzy Logic in Anzali Port. Earth Sci Inform 15, 563–572 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00742-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00742-y