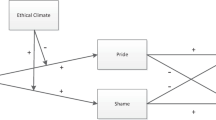
Abstract
The majority of research on the antecedents of unethical pro-organizational behavior (UPB) has mainly focused on negative ethics-related variables, while ignoring positive factors that may not be related to ethics but might affect employee UPB. In this research, based on social exchange theory, we hypothesized that empowering leadership would prompt employee UPB. We argue that, driven by self-interest and positive reciprocity, empowered employees may be more willing to engage in UPB when organizations encourage self-interest for more positive treatment. Study 1 supported these hypotheses, which implied that instrumental ethical climate strengthened the link between empowering leadership and UPB. Meanwhile, role theory notes that role factors are strongly correlated with employees role stress. Thus, based on the theoretical framework of Study 1, we introduced the mediator variable — role stress and examined whether role stress was the bridge between empowering leadership and employee UPB using Study 2. The results from Study 2 showed that empowering leadership could prompt employee UPB and that the relationship was mediated by role stress. In addition, the relationship between empowering leadership and UPB was moderated by instrumental ethical climate. Furthermore, we tested the moderated mediation model, yet it was not verified. Finally, we discussed both theoretical and practical implications.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
All authors make sure that all data and materials as well as software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Aguinis, H., & Bradley, K. J. (2014). Best practice recommendations for designing and implementing experimental vignette methodology studies. Organizational Research Methods, 17(4), 351–371. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428114547952
Ahearne, M., Mathieu, J., & Rapp, A. (2005). To empower or not to empower your sales force? An empirical examination of the influence of leadership empowerment behavior on customer satisfaction and performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(5), 945–955. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.90.5.945
Blau, P. M. (2017). Exchange and power in social life. Routledge.
Castilla, E. J., & Benard, S. (2010). The paradox of meritocracy in organizations. Administrative Science Quarterly, 55, 543–576. https://doi.org/10.2189/asqu.2010.55.4.543
Chen, X., Yuan, Y., Liu, J., Zhu, L., & Zhu, Z. (2020). Social bonding or depleting? A team-level investigation of leader self-sacrifice on team and leader work engagement. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 93, 912–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/joop.12315
Cheng, K., Wei, F., & Lin, Y. H. (2019). The trickle-down effect of responsible leadership on unethical pro-organizational behavior: The moderating role of leader-follower value congruence. Journal of Business Research, 102, 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.04.044
Cheong, M., Spain, S. M., Yammarino, F. J., & Yun, S. (2016). Two faces of empowering leadership: Enabling and burdening. Leadership Quarterly, 27, 602–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2016.01.006
Cheong, M., Yammarino, F. J., Dionne, S. D., Spain, S. M., & Tsai, C. Y. (2019). A review of the effectiveness of empowering leadership. Leadership Quarterly, 30(1), 34–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2018.08.005
Chui, C., Kouchaki, M., & Gino, F. (2021). “Many others are doing it, so why shouldn’t I?”: How being in larger competitions leads to more cheating. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 164, 102–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2021.01.004
Cordery, J. L., Morrison, D., Wright, B. M., & Wall, T. D. (2010). The impact of autonomy and task uncertainty on team performance: A longitudinal field study. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 31(2–3), 240–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.657
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1985). Intrinsic motivation and selfdetermination in human behavior. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-2271-7_2
Dennerlein, T., & Kirkman, B. L. (2022). The hidden dark side of empowering leadership: The Moderating role of hindrance stressors in explaining when empowering employees can promote moral disengagement and unethical pro-organizational behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0001013
Edwards, J. R., & Lambert, L. S. (2007). Methodsfor integrating moderation and mediation: A general analytical framework using moderated path analysis. Psychological Methods, 12(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989x.12.1.1
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39, 175–191. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03193146
Foulk, T. A., Lanaj, K., Tu, M. H., Erez, A., & Archambeau, L. (2018). Heavy is the head that wears the crown: An actor-centric approach to daily psychological power, abusive leader behavior, and perceived incivility. Academy of Management Journal, 61(2), 661–684. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2015.1061
Goldberg, L., & Greenberg, M. (1994). A survey of ethical conduct in risk management: Environmental economists. Ethics & Behavior, 4(04), 331–343. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327019eb0404_2
Graham, K. A., Resick, C. J., Margolis, J. A., Shao, P., Hargis, M. B., & Kiker, J. D. (2019). Egoistic norms, organizational identification, and the perceived ethicality of unethical pro-organizational behavior: Amoral maturation perspective. Human Relations, 73(9), 1199–1225. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018726719862851
Hao, P., He, W., & Long, L. R. (2018). Why and when empowering leadership has different effects on employee work performance: The pivotal roles of passion for work and role breadth self-efficacy. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 25(1), 85–100. https://doi.org/10.1177/1548051817707517
Harris, T. B., Li, N., Boswell, W. R., Zhang, X.-A., & Xie, Z. (2014). Getting what’s new from newcomers: Empowering leadership, creativity, and adjustment in the socialization context. Personnel Psychology, 67(3), 567–604.
Hassan, S., DeHart-Davis, L., & Jiang, Z. (2019). How empowering leadership reduces employee silence in public organizations. Public Administration, 97(1), 116–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/padm.12571
Kahn, D. M., L., R, Wolfe, R. P., Quinn, J., Snoek, D., & Rosenthal, R. A. (1964). Organizational stress: Studies in role conflict and ambiguity. https://doi.org/10.2307/2391654
Kish-Gephart, J. J., Harrison, D. A., & Treviño, L. K. (2010). Bad apples, bad cases, and bad barrels: Meta-analytic evidence about sources of unethical decisions at work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017103
Langfred, C. W., & Moye, N. A. (2004). Effects of task autonomy on performance: An extended model considering motivational, informational, and structural mechanisms. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89, 934–945. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.89.6.934
Lapidus, R. S., Roberts, J. A., & Chonko, L. B. (1997). Stressors, leadership substitutes, and relations with supervision among industrial salespeople. Industrial Marketing Management, 26(3), 255–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/0019-8501(96)00045-4
Lazarus, R. S., Deese, J., & Osier, J. F. (1952). The effects of psychological stress upon performance. Psychological Bulletin, 49, 293–316. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0061145
Li, N., Chiaburu, D. S., & Kirkman, B. L. (2017). Cross-level influences of empowering leadership on citizenship behavior: Organizational support climate as a double-edged sword. Journal of Management, 43(4), 1076–1102. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206314546193
Lu, J. G., Brockner, J., Vardi, Y., & Weitz, E. (2017). The dark side of experiencing job autonomy: Unethical behavior. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 73, 222–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2017.05.007
Luan, Y., Zhao, K., Wang, Z., & Hu, F. (2023). Exploring the antecedents of unethical pro-organizational behavior (UPB): A meta-analysis. Journal of Business Ethics, 187, 119–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-022-05269-w
Martin, K. D., & Cullen, J. B. (2006). Continuities and extensions of ethical climate theory-A meta-analytic review. Journal of Business Ethics, 69, 175–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-006-9084-7
Pennino, C. M. (2002). Does tenure impact upon the principled reasoning of managers? Journal of Business Ethics, 40, 219–226.
Peterson, M. F., Peter, B. S., Adebowale, A., et al. (1995). Role conflict, ambiguity, and overload: A 21-nation study. Academy of Management Journal, 38(2), 429–452.
Reynolds, W. (1982). Development of reliable and valid short forms of the Marlowe-Crowne social desirability scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38, 119–125. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4679(198201)38:1%3c119::aid-jclp2270380118%3e3.0.co;2-i
Schilpzand, P., Houston, L., & Cho, J. (2018). Not too tired to be proactive: Daily empowering leadership spurs next-morning employee proactivity as moderated by nightly sleep quality. Academy of Management Journal, 61(6), 2367–2387. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2016.0936
Shore, L. M., Etrick, L. E. T., Lynch, P., & Barksdale, K. (2006). Social and economic exchange: Construct development and validation. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 36(4), 837–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0021-9029.2006.00046.x
Simha, A., & Cullen, J. B. (2012). Ethical climates and their effects on organizational outcomes: Implications from the past and prophecies for the future. The Academy of Management Perspectives, 26(4), 20–34. https://doi.org/10.5465/amp.2011.0156
Spreitzer, G. M., Kizilos, M. A., & Nason, S. W. (1997). A dimensional analysis of the relationship between psychological empowerment and effectiveness, satisfaction, and strain. Journal of Management, 23(5), 679–704. https://doi.org/10.1177/014920639702300504
Summers, T. P., DeCotiis, T. A., & DeNisi, A. S. (1995). A field study of some antecedents and consequences of felt job stress. In R. Crandall,P. L. Perrewe (Eds.), Occupational stress: A handbook (pp. 113–128). https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003072430-11
Thau, S., Derfler-Rozin, R., Pitesa, M., Mitchell, M. S., & Pillutla, M. M. (2015). Unethical for the sake of the group: Risk of social exclusion and pro-group unethicalbehavior. Journalof Applied Psychology, 100(1), 98–113. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036708
Tobias, D., & Kirkman, B. L. (2022). The hidden dark side of empowering leadership: The moderating role of hindrance stressors in explaining when empowering employees can promote moral disengagement and unethical pro-organizational behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0001013
Umphress, E. E., & Bingham, J. B. (2011). When employees do bad things for good reasons: Examining unethical pro-organizational behaviors. Organization Science, 22(3), 621–640. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.1100.0559
Umphress, E. E., Bingham, J. B., & Mitchell, M. S. (2010). Unethical behavior in the name of the company: The moderating effect of organizational identification and positive reciprocity beliefs on unethical pro-organizational behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95(4), 769–780. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019214
Victor, B., & Cullen, J. B. (1987). A theory and measure of ethical climate in organizations. Research in Corporate Social Performance and Polic, y, 9(1), 51–71.
Victor, B., & Cullen, J. B. (1988). The organizational bases of ethical work climates. Administrative Science Quarterly, 33(1), 101–125.
Wang, T., Long, L., Zhang, Y., & He, W. (2019). A social exchange perspective of employee-organization relationships and employee unethical pro-organizational behavior: The moderating role of individual moral identity. Journal of Business Ethics, 159(2), 473–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-018-3782-9
Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Li, P., & Henry, S. E. (2022). You raise me up and I reciprocate: Linking empowering leadership to organizational citizenship behavior and unethical pro-organizational behavior. Applied Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1111/apps.12398
Wimbush, J. C., & Shepard, J. M. (1994). Toward an understanding of ethical climate: Its relationship to ethical behavior and supervisory influence. Journal of Business Ethics, 13(8), 637–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00871811
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 72071124.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers [72071124]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Zhang Suchuan and He Huiying. The first draft of the manuscript was written by He Huiying and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial interests
Suchuan Zhang and Huiying He declare that they have no financial interests.
Non-financial interests
None.
Ethical approval statement
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any any of the authors.
Competing interest
Suchuan Zhang and Huiying He declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., He, H. Examining the link between empowering leadership and unethical pro-organizational behavior: the mediating role of role stress and the moderating role of instrumental ethical climate. Curr Psychol 43, 16554–16571 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05610-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05610-0