Abstract
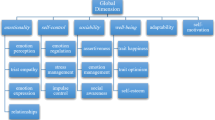
The present study focused on the translation of the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (TEIQue) to the Turkish speaking people. The TEIQue was completed by 500 undergraduate students created from two different sample. Study followed two step as linguistic equivalence and validity-reliability analyses. Psychometric analysis provided evidence in support of the reliability of the TEIQue (at the facet, factor, and global levels) and the confirmed four-factor structure (Well-Being, Sociability, Self-Control, and Emotionality). This solution accounted for 66.3% of the total variance, and factor loading was .493–816. With regard to CFA and internal consistency of four factors and Global TEIQue, the Turkish version showed acceptable psychometrics and was in concordance with the original version. This study also found significant sex differences among factors and Global TEI. Female participants had higher scores on Wellbeing, Emotionality, and Global TEI. TEIQue would contribute as the base for further studies, and literature by adding data from Turkey.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-On, R. (1997). EQ–I Bar-On Emotional Quotient Inventory: Technical manual. Toronto: Multi-Health Systems.
Bar-On, R. (2006). The Bar-On model of emotional-social intelligence (ESI). Psicothema, 18, 13–25.
Bartlett, M. S. (1954). A note on the multiplying factors for various chi square approximations. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 16, 296–298.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238–246.
Bernstein, I. H., & Teng, G. (1989). Factoring items and factoring scales are different: Spurious evidence for multidimensionality due to item categorization. Psychological Bulletin, 105, 467–477.
Boyatzis, R. E. (2006). Using tipping points of emotional intelligence and cognitive competencies to predict financial performance of leaders. Psicothema, 18, 124–131.
Brouzos, A., Misailidi, P., & Hadjimattheou, A. (2014). Associations between emotional intelligence, socio-emotional adjustment, and academic achievement in childhood: The influence of age. Canadian Journal of School Psychology, 29(2), 83–99.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1989). Single sample cross validation indices for covariance structures. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 24, 445–155.
Cooper, A., & Petrides, K. V. (2010). A psychometric analysis of the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire – Short Form (TEIQue – SF) using item response theory. Journal of Personality Assessment, 92, 449–457.
Freudenthaler, H. H., Neubauer, A. C., Gabler, P., Scherl, W. G., & Rindermann, H. (2008). Testing and validating the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (TEIQue) in a German-speaking sample. Personality and Individual Differences, 45, 673–678.
Gardner, J. K., & Qualter, P. (2010). Concurrent and incremental validity of three trait emotional intelligence measures. Australian Journal of Psychology, 62, 5–13.
Gudmundsson, E. (2009). Guidelines for translating and adapting psychological instruments. Nordic Psychology, 61(2), 29–45.
Hambleton, R. K. (2001). The next generation of the ITC Test translation and adaptation guidelines. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 17, 164–172.
Hoyle, R. H. (1995). The structural equation modeling approach: Basic concepts and fundamental issues. In R. H. Hoyle (Ed.), Structural equation modeling, concepts, issues, and applications (pp. 1–15). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Joreskog, K. G., & Sorbom, D. (1984). LISREL VI user's guide (3rd ed.). Mooresville: Scientific Software.
Kaiser, H. (1974). An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika, 39, 31–36.
Marjanović, Z. J., & Dimitrijević, A. A. (2014). Reliability, construct and criterion-related validity of the Serbian adaptation of the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (TEIQue). Psihologija, 47(2), 249–262.
Martins, A., Ramalho, N., & Morin, E. (2010). A comprehensive meta - analysis of the relationship between emotional intelligence and health. Personality and Individual Differences, 49, 554–564.
Martskvishvili, K., Arutinov, L., & Mestvirishvili, M. (2013). A psychometric investigation of the Georgian version of the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 29(2), 84–88.
Mavroveli, S., Petrides, K. V., Rieffe, C., & Bakker, F. (2007). Trait emotional intelligence, psychological well-being and peer-rated social competence in adolescence. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 25, 263–275.
Mayer, J. D., & Salovey, P. (1997). What is emotional intelligence? In P. Salovey & D. Sluyter (Eds.), Emotional development and emotional intelligence: Educational implications (pp. 3–31). New York: Basic Books.
Mikolajczak, M., & Luminet, O. (2008). Trait emotional intelligence and the cognitive appraisal of stressful events: An exploratory study. Personality and Individual Differences, 44, 1445–1453.
Mikolajczak, M., Luminet, O., Leroy, C., & Roy, E. (2007). Psychometric properties of the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire: Factor structure, reliability, construct, and incremental validity in a French-speaking population. Journal of Personality Assessment, 88, 338–353.
Pérez-González, J. C., & Sánchez-Ruiz, M. J. (2014). Trait emotional intelligence anchored within the Big Five, Big Two and Big One frameworks. Personality and Individual Differences, 65, 53–58.
Peterson, R. A. (1994). A meta-analysis of Cronbach's coefficient alpha. Journal of Consumer Research, 21(2), 381.
Petrides, K. V. (2001). A psychometric investigation into the construct of emotional intelligence. Doctoral dissertation. University College, London.
Petrides, K. V. (2009). Psychometric properties of the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (TEIQue). In C. Stough et al. (Eds.), Assessing Emotional Intelligence. The Springer Series on Human Exceptionality. doi 10.1007/978-0-387-88370-0_5.
Petrides, K. V., & Furnham, A. (2000). On the dimensional structure of emotional intelligence. Personality and Individual Differences, 29, 313–320.
Petrides, K. V., & Furnham, A. (2001). Trait emotional intelligence: Psychometric investigation with reference to established trait taxonomies. European Journal of Personality, 15, 425–448.
Petrides, K. V., Niven, L., & Mouskounti, T. (2006). The trait emotional intelligence of ballet dancers and musicians. Psicothema, 18, 101–107.
Petrides, K. V., Pita, R., & Kokkinaki, F. (2007). The location of trait emotional intelligence in personality factor space. British Journal of Psychology, 98, 273–289.
Petrides, K. V., Vernon, P. A., Schermer, J. A., Ligthart, L., Boomsma, D. I., & Veselka, L. (2010). Relationships between trait emotional intelligence and the Big Five in the Netherlands. Personality and Individual Differences, 48, 906–910.
Salovey, P., & Mayer, J. D. (1990). Emotional intelligence. Imaginition, Cognition and Personality, 9, 185–211.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Professor Konstantinos Petrides for Turkish translation and modification procedure of TEIQue.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Funding Sources
This reasearch was supported by TUBITAK (THE SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNOLOGICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF TURKEY 2219-International Research Program).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulutas, I. Psicometric Properties of the Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (TEIQe) in Turkish. Curr Psychol 38, 775–781 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-017-9647-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-017-9647-z