Abstract
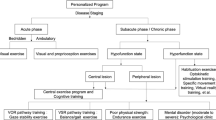
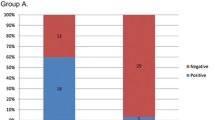
Aim: The aim of the study is to compare the effects of vestibular rehabilitation and pharmacological treatment in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Materials and methods: Thirty patients (40.93 ± 8.66 years old) diagnosed with BPPV were recruited. Patients were equally divided into pharmacological control group and vestibular rehabilitation group. The pharmacological control group was further divided into Group A (n = 8, 2 doses/day, 24 mg betahistine) and Group B (n = 7, 1 dose/day, 50 mg dimenhydrinate in addition to betahistine). Patients in the rehabilitation group underwent repeated head and eye movements, and Epley or Barbecue Roll Maneuvers were applied for 4 weeks. Subjective assessment of vertigo was measured with the visual analog scale. Static balance parameters were measured with the tandem, one-legged stance, and Romberg tests. Dynamic visual acuity was measured with a Snellen chart, and vestibular dysfunction was measured with the Unterberger (Fukuda stepping) test. All parameters were evaluated before and after treatment. Results: Vestibular rehabilitation resulted in greater improvement in severity of vertigo, balance parameters except Romberg test, and vestibular dysfunction than pharmacological therapy (p < 0,001). There was no significant difference in dynamic visual acuity between groups (p = 0,24). The effects of medication with the active ingredients betahistine and dimenhydrinate were similar (p > 0,05). Conclusion: The vestibular rehabilitation method can positively change the severity of vertigo, balance ability, and vestibular dysfunction compared to pharmacological therapy. Dimenhydrinate administered in combination with betahistine was not superior to betahistine alone but can be recommended for its antiemetic effect.

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Kaur J, Shamanna K (2017) Management of Benign Paroxysmal positional Vertigo: a comparative study between Epleys Manouvre and Betahistine. Int Tinnitus J 21:30–34. https://doi.org/10.5935/0946-5448.20170007
Maslovara S, Soldo SB, Puksec M et al (2012) Benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo (BPPV): influence of pharmacotherapy and rehabilitation therapy on patients’ recovery rate and life quality. NeuroRehabilitation 31:435–441. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-2012-00814
Ogun OA, Janky KL, Cohn ES et al (2014) Gender-based comorbidity in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. PLoS ONE 9:e105546. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105546
Sharma K, Ojha T, Dabaria R et al (2022) Relation between posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo and vitamin D Deficiency. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-03070-1
Celis-Aguilar E, Mayoral-Flores HO, Torrontegui-Zazueta LA et al (2021) Effectiveness of Brandt Daroff, Semont and Epley maneuvers in the treatment of Benign Paroxysmal positional Vertigo: a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02516-w
Nuti D, Zee DS, Mandalà M (2020) Benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo: what we do and do not know. Semin Neurol 40:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-3402733
Herdman S, Clendaniel R (2014) Vestibular Rehabilitation. In: Vestibular Rehabilitation 4th Edition, 4th ed. p 50
Hain TC, Uddin M (2003) Pharmacological treatment of vertigo. CNS Drugs 17:85–100. https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-200317020-00002
Wu P, Cao W, Hu Y, Li H (2019) Effects of vestibular rehabilitation, with or without betahistine, on managing residual dizziness after successful repositioning manoeuvres in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026711
Yetiser S, Salturk Z (2021) A review of the quality of life after therapeutic maneuvers in patients with benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 33:339–346. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJORL.2021.55574.2912
Sacco RR, Burmeister DB, Rupp VA, Greenberg MR (2014) Management of Benign Paroxysmal positional Vertigo: a Randomized Controlled Trial. J Emerg Med 46:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.08.116
Rodrigues DL, Ledesma ALL, de Oliveira CAP, Bahmad F (2019) Effect of vestibular exercises associated with repositioning maneuvers in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Otology and Neurotology 40:E824–E829. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002324
Lee JD, Shim DB, Park HJ et al (2014) A Multicenter Randomized double-blind study: comparison of the Epley, Semont, and Sham Maneuvers for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo. Audiol Neurotology 19:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1159/000365438
Gold DR, Morris L, Kheradmand A, Schubert MC (2014) Repositioning maneuvers for Benign Paroxysmal positional Vertigo. Curr Treat Options Neurol 16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-014-0307-4
Balıkçı HH, Özbay İ (2014) Effects of postural restriction after modified Epley maneuver on recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 41:428–431
Stambolieva K, Angov G (2010) Effect of treatment with betahistine dihydrochloride on the postural stability in patients with different duration of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Int Tinnitus J 16:32–36
Akula S, Reddy LS, Kiran AS, suresh AM (2022) Clinical study of BPPV and the effectiveness of Canalolith Repositioning Manoeuvre in subjects of BPPV. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02779-3
Carnevale C, Arancibia-Tagle DJ, Rizzo-Riera E et al (2018) Efficacy of particle repositioning Manoeuvres in Benign positional paroxysmal Vertigo: a revision of 176 cases treated in a Tertiary Care Centre. Acta Otorrinolaringologica (English Edition) 69:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otoeng.2017.06.014
Si L, Shen B, Li Y et al (2021) Clinical characteristics of patients with persistent apogeotropic and persistent geotropic direction-changing positional Nystagmus. J Clin Neurol (Korea) 17:443–454. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2021.17.3.443
Zuma e Maia F, Ramos BF, Cal R et al (2020) Management of lateral semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo.Front Neurol11
Martins e Silva DC, Bastos VH, de Oliveira Sanchez M et al (2015) Effects of vestibular rehabilitation in the elderly: a systematic review. Aging Clin Exp Res 28:599–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-015-0479-0
Strupp M, Zwergal A, Feil K et al (2015) Pharmacotherapy of vestibular and cerebellar disorders and downbeat nystagmus: translational and back-translational research. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1343:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12774
Scholtz AW, Ilgner J, Loader B et al (2016) Cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate in the treatment of vertigo in medical practice. Wien Klin Wochenschr 128:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-015-0905-5
Hahn A, Novotny M, Shotekov PM et al (2011) Comparison of cinnarizine / dimenhydrinate fixed combination with the Respective Monotherapies for Vertigo of various Origins. Clin Drug Investig 31:371–383
Wipperman J (2014) Dizziness and vertigo. Prim Care - Clin Office Pract 41:115–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2013.10.004
Fujino A, Tokumasu K, Yosio S et al (1994) Vestibular training for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Its efficacy in comparison with antivertigo drugs. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Sur 120:497–504
Ribeiro KMOB, de Freitas F, de Ferreira RV BM, et al (2016) Effects of balance vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy in elderly with benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo: a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil 39:1198–1206. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2016.1190870
Martellucci S, Pagliuca G, de Vincentiis M et al (2016) Features of residual dizziness after Canalith Repositioning Procedures for Benign Paroxysmal positional Vertigo. Otolaryngol - Head Neck Surgery: official J Am Acad Otolaryngology-Head Neck Surg 154:693–701. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599815627624
Moreno JLB, Matos YR, Perez ER et al (2019) Effectiveness of the Epley manoeuvre in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a randomised clinical trial in primary care. Br J Gen Pract 69:E52–E60. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp18X700253
Çelebisoy N, Bayam E, Güleç F et al (2009) Balance in posterior and horizontal canal type benign paroxysmal positional vertigo before and after canalith repositioning maneuvers. Gait Posture 29:520–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2008.12.002
Ribeiro KMOB, de Freitas F, de Ferreira RV BM, et al (2017) Effects of balance vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy in elderly with benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo: a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil 39:1198–1206. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2016.1190870
Yetiser S, Ince D (2018) Dynamic visual acuity in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol 138:987–992. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2018.1498595
Herdman S, Schubert M, Das V, Tusa R (2003) Recovery of dynamic visual acuity in unilateral vestibular hypofunction. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:810–824. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.129.8.819
Honaker JA, Boismier TE, Shepard NP, Shepard NT (2009) Fukuda stepping test: sensitivity and specificity. J Am Acad Audiol 20:311–314. https://doi.org/10.3766/jaaa.20.5.4
Taylan Cebi I, Karatas A (2021) The assessment of fukuda stepping test results in prognosis of benign paroxysmal postural vertigo. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2021.05.005
Scholtz AW, Hahn A, Stefflova B et al (2019) Efficacy and safety of a fixed combination of Cinnarizine 20 mg and Dimenhydrinate 40 mg vs Betahistine Dihydrochloride 16 mg in patients with peripheral vestibular Vertigo: a prospective, multinational, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized, non-inferior. Clin Drug Investig 39:1045–1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-019-00858-6
Inan HC, Kirac M (2019) An evaluation of the Effects of Betahistine and Dimenhydrinate on posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 57:191–196. https://doi.org/10.5152/tao.2019.4185
Jalali MM, Gerami H, Saberi A, Razaghi S (2020) The impact of Betahistine versus Dimenhydrinate in the resolution of residual dizziness in patients with benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo: a Randomized Clinical Trial. Annals of Otology. Rhinology and Laryngology 129(5):434–440. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003489419892285
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Prof. Dr. Z. Candan ALGUN for her guidance on the study design.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interests.
Consent for Publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Ethics Approval
This study was performed in line with the princi-ples of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics approval was obtained from the Istanbul Medipol University Non-Interventional Clinical Research Ethics Committee. (E-19383).
Clinical Trials Number
NCT05127694.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
ATA, G., ŞAKUL, A.A., Kılıç, G. et al. Comparison of the Efficacy of Vestibular Rehabilitation and Pharmacological Treatment in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75 (Suppl 1), 483–490 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03598-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03598-4