Abstract
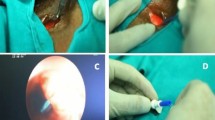
Alaryngeal speech in laryngectomees has revolutionized the patient outlook toward the morbid procedure and the concept of permanent stoma unlike olden era when stigma of stoma with loss of voice was rampant. To analyse acceptance of voice rehabilitation options and their success and management of complications in a tertiary care centre. All patients who underwent laryngectomy from August 2014 to 2018 June at our institution were included in the study. The voice rehabilitation options like oesophageal speech, tracheao-oesophageal puncture and voice prosthesis insertion (TEP), and electrolarynx were explained to the patients. The options put forward to the patients, the importance of Taub test, Interval between treatment and secondary TEP insertion, life span of the prosthesis, Patients acceptance and success rates and the troubleshooting were noted. A total of 96 patients underwent total laryngectomy, 72 patients were willing for rehabilitation. 15% (11) patients had primary TEP, 22% (16) had secondary TEP insertion, esophageal speech in 36% (26) patients and 27% (19) patients opted for the electrolarynx. The rest 24 patients were not keen on any further interventions after laryngectomy. Speech rehabilitation is an integral part in surgical management of carcinoma of the larynx. Alaryngeal speech in laryngectomees have revolutionized the patient outlook towards the morbid procedure. Esophageal speech is the least successful method of rehabilitation but still the cheapest method and requires a lot of motivation. Primary and Secondary TEP insertions have similar success rates. Successful treatment for cancer of larynx ends with successful voice rehabilitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bien S, Rinaldo A, Silver CE et al (2008) History of voice rehabilitation following laryn-gectomy. Laryngoscope 118(3):4538
Weir N (1990) Otolaryngology. An illustrated history. Butterworths, London
Gussenbauer C (1874) Ueber die erste durch Th. Billroth am Menschen ausgeführte Kehlkopf-Exstirpation und die Anwendung eines künstlichen Kehlkopfes. Arch Klin Chir 17:34356
Singer MI, Blom ED (1980) An endoscopic technique for restoration of voice after laryngectomy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 89:529–533
Babin E, Beynier D, Le Gall D et al (2009) Psychosocial quality of life in patients after total laryngectomy. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord) 130(1):29–34
Singer S, Danker H, Dietz A et al (2008) Sexual problems after total or partial laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 118(12):2218–2224
Blom ED (2000) Current status of voice restoration following total laryngectomy. Oncology (Williston Park) 14(6):915–922 (discussion: 927–8, 931)
Pawar PV, Sayed SI, Kazi R, Jagade MV (2008) Current status and future prospects in prosthetic voice rehabilitation following laryngectomy. J Cancer Res Ther 4:186–191
Finizia C, Bergman B (2001) Health-related quality of life in patients with laryngeal cancer: a post-treatment comparison of different modes of communication. Laryngoscope 111(5):918–923
Eadie TL, Doyle PC (2005) Quality of life in male TE speakers. J Rehabil Res Dev 42:115–124
Varghese BT, Mathew A, Sebastian P et al (2011) Comparison of quality of life between voice rehabilitated and nonrehabilitated laryngectomies in a developing world community. Acta Otolaryngol 131(3):310–315
Singer S, Merbach M, Dietz A, Schwarz R (2007) Psychosocial determinants of successful voice rehabilitation after laryngectomy. J Chin Med Assoc 70:407–423
Jassar P, England RJ, Stafford ND (1999) Restoration of voice after laryngectomy. J R Soc Med 92:299–302
De Raucourt D, Rame JP, Daliphard F, Le Pennec D, Béquignon A, Luquet A (1998) Voice rehabilitation with a voice prosthesis. Study of 62 patients with 5 years follow-up. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord) 119:297–300
Van den Hoogen FJ, Van den Berg RJ, Oudes MJ, Manni JJ (1998) A prospective study of speech and voice rehabilitation after total laryngectomy with the low-resistance Groningen, Nijdam and Provox voice prostheses. Clin Otolaryngol 23:425–431
Labruna A, Klatsky I, Huo J, Weiss MH (1995) Tracheoesophageal puncture in irradiated patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 104:279–281
Trudeau MD, Schuller DE, Hall DA (1989) The effects of radiation on tracheoesophageal puncture. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 115:1116–1117
Blom ED (2000) Tracheoesophageal voice restoration: origin – evolution – state-of-the-art. Folia Phoniatr Logop 52:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1159/000021508
Myers EN, Suen JY (eds) (1996) Cancer of the head and neck, 3rd edn. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, pp 839–852
Quer M, Burgués-Vila J, Garcia-Crespillo P (1992) Primary tracheoesophageal puncture vs esophageal speech. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:188–190
Blom ED, Singer MI, Hamaker RC (1986) A prospective study of tracheoesophageal speech. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112:440–447
McIvor J, Evans PF, Perry A, Cheesman AD (1990) Radiological assessment of post laryngectomy speech. Clin Radiol 41:312–316
Izdebsky K, Reed CG, Ross JC, Hilsinger RL (1994) Problems with tracheoesophageal fistula voice restoration in totally laryngectomized patients. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:840–845
Willians SE, Watson JB (1987) Speaking proficiency variation according to method of alaryngeal voicing. Laryngoscope 97:737–739
Cornu AS, Vlantis AC, Elliott H, Gregor RT (2003) Voice rehabilitation after laryngectomy with the Provox voice prosthesis in South Africa. J Laryngol Otol 117:56–59
Hilgers FJ, Schouwenburg PF (1990) A new low-resistance, self- retaining prosthesis (Provox) for voice rehabilitation after total laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 100:1202–1207
de Carpentier JP, Ryder WD, Saeed SR, Woolford TJ (1996) Survival times of Provox valves. J Laryngol Otol 110:37–42
Laccourreye O, Ménard M, Crevier-Buchman L, Couloigner V, Brasnu D (1997) In situ lifetime, causes for replacement, and complications of the Provox voice prosthesis. Laryngoscope 107:527–530
Heaton JM, Parker AJ (1994) Indwelling tracheo-oesophageal voice prostheses post-laryngectomy in Sheffield, UK: a 6-year review. Acta Otolaryngol 114:675–678
Ackerstaff AH, Hilgers FJ, Meeuwis CA et al (1999) Multi-institutional assessment of the Provox 2 voice prosthesis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:167–173
Graville D, Gross N, Andersen P, Everts E, Cohen J (1999) The long-term indwelling tracheoesophageal prosthesis for alaryngeal voice rehabilitation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:288–292
Op de Coul BM, Hilgers FJ, Balm AJ, Tan IB, van den Hoogen FJ, van Tinteren H (2000) A decade of postlaryngectomy vocal rehabilitation in 318 patients: a single institution’s experience with consistent application of provox indwelling voice prostheses. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:1320–1328
Schafer P, Klutzke N, Schwedtfeger FP (2001) Voice restoration with voice prosthesis after total laryngectomy. Assessment of survival time of 378 Provox-1, Provox-2 and Blom-Singer voice prosthesis. Laryngorhinootologie 80:667–681
Free RH, Busscher HJ, Elving GJ, van der Mei HC, van Weissenbruch R, Albers FW (2001) Biofilm formation on voice prostheses: in vitro influence of probiotics. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:946–951
Lequeux T, Badreldin A, Saussez S, Thill MP, Oujjan L, Chantrain G (2003) A comparison of survival lifetime of the Provox and the Provox2 voice prosthesis. J Laryngol Otol 117:875–878
Ramalingam W, Chikara D, Rajagopal G, Mehta AR, Sarkar S (2007) Tracheo-esophageal puncture (TEP) for voice rehabilitation in laryngectomised patients Blom-singer® vs Provox® prosthesis: our experience. Med J Armed Forces India 63:15–18
Yenigun A, Eren SB, Ozkul MH, Tugrul S, Meric A (2015) Factors influencing the longevity and replacement frequency of Provox voice prostheses. Singap Med J 56:632–636
Krishnamurthy A, Khwajamohiuddin S (2018) Analysis of factors affecting the longevity of voice prosthesis following total laryngectomy with a review of literature. Indian J Surg Oncol 9(1):39–45
Simpson CB, Postma GN, Stone REJ, Ossoff RH (1997) Speech outcomes after laryngeal cancer management. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 30(2):189–205
Moukarbel RV, Doyle PC, Yoo JH, Franklin JH, Day AMB, Fung K (2011) Voice-related quality of life (V-RQOL) outcomes in laryngectomees. Head Neck 33:31–36
Ptok M (1990) Objektive Meßverfahren zur Bewertung der postoperativen Stimmqualität nach Kehlkopfoperationen bei Malignompatienten. Sprache-Stimme-Gehör 14:11–17
Makitie AA, Niemensivu R, Juvas A et al (2003) Post laryngectomy voice restoration using a voice prosthesis: a single institution’s ten-year experience. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 112:1007–1010
Chone CT, Gripp FM, Spina AL et al (2005) Primary versus secondary tracheoesophageal puncture for speech rehabilitation in total laryngectomy: long-term results with indwelling voice prosthesis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:89–93
Maniglia AJ, Lundy DS, Casiano RC, Swim SC (1989) Speech restoration and complications of primary versus secondary tracheoesophageal puncture following total laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 99:489–491
Trudeau MD, Hirsch SM, Schuller DE (1986) Vocal restorative surgery: why wait? Laryngoscope 96:975–977
Aust MR, McCaffrey TV (1997) Early speech results with the Provox prosthesis after laryngectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123:966–968
Akbas Y, Dursun G (2003) Voice restoration with low pressure blom singer voice prosthesis after total laryngectomy. Yonsei Med J 44:615–618
Fagan JJ, Lentin R, Oyarzabal MF, Isaacs S, Sellars SL (2002) Tracheoesophageal speech in a developing world community. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:50–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iype, E.M., Janardhanan, D., Patil, S. et al. Voice Rehabilitation After Laryngectomy: A Regional Cancer Centre Experience and Review of Literature. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 72, 518–523 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01707-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01707-w