Abstract
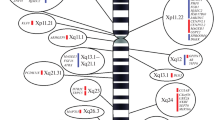
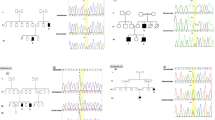
Microduplications of the X chromosome are a rare cause of X-linked intellectual disability (XLID), a clinically and genetically heterogeneous spectrum of disorders. In the present study, a 950-kb Xp22.12 microduplication including the RPS6KA3 gene was detected in affected members of a family, including the proband (male), his mother and one maternal uncle. Four female carriers had major depression and one of them also had mild intellectual disability. The present and previous cases with overlapping microduplications suggest that Xp22.12 microduplications can be included in the neuropsychiatric copy number variations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertini V., Cambi F., Bruno R., Toschi B., Forli F., Berrettini S. et al. 2015 625 kb microduplication at Xp22.12 including RPS6KA3 in a child with mild intellectual disability. J. Hum. Genet. 60, 777–780.
Field M., Tarpey P., Boyle J., Edkins S., Goodship J., Luo Y. et al. 2006 Mutations in the RSK2(RPS6KA3) gene cause Coffin-Lowry syndrome and nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Clin. Genet. 70, 509–515.
Gécz J., Shoubridge C. and Corbett M. 2009 The genetic landscape of intellectual disability arising from chromosome X. Trends Genet. 25, 308--316.
Hauge C. and Frödin M. 2006 RSK and MSK in MAP kinase signalling. J. Cell Sci. 119, 3021–3023.
Jacquot S., Zeniou M., Touraine R. and Hanauer A. 2002 X-linked Coffin-Lowry syndrome (CLS, MIM 303600, RPS6KA3 gene, protein product known under various names: pp90(rsk2), RSK2, ISPK, MAPKAP1). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 10, 2–5.
Koolen D. A., Kramer J. M., Neveling K., Nillesen W. M., Moore-Barton H. L., Elmslie F. V. et al. 2012 Mutations in the chromatin modifier gene KANSL1 cause the 17q21.31 microdeletion syndrome. Nat. Genet. 44, 639–641.
Madrigal I., Rodríguez-Revenga L., Armengol L., González E., Rodriguez B., Badenas C. et al. 2007 X-chromosome tiling path array detection of copy number variants in patients with chromosome X-linked mental retardation. BMC Genomics 8, 443.
Manouvrier-Hanu S., Amiel J., Jacquot S., Merienne K., Moerman A., Coëslier A. et al. 1999 Unreported RSK2 missense mutation in two male sibs with an unusually mild form of Coffin-Lowry syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 36, 775–778.
Matsumoto A., Kuwajima M., Miyake K., Kojima K., Nakashima N., Jimbo E. F. et al. 2013 An Xp22.12 microduplication including RPS6KA3 identified in a family with variably affected intellectual and behavioral disabilities. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 755–757.
Merienne K., Jacquot S., Pannetier S., Zeniou M., Bankier A., Gecz J. et al. 1999 A missense mutation in RPS6KA3 (RSK2) responsible for non-specific mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 22, 13–14.
Pereira M. P., Heron D. and Hanauer A. 2007 The first large duplication of the RSK2 gene identified in a Coffin-Lowry syndrome patient. Hum. Genet. 122, 541--543.
Pereira P. M., Schneider A., Pannetier S., Heron D. and Hanauer A. 2010 Coffin-Lowry syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18, 627--633.
Potocki L., Bi W., Treadwell-Deering D., Carvalho C. M., Eifert A., Friedman E. M. et al. 2007 Characterization of Potocki-Lupski syndrome (dup(17)(p11.2p11.2)) and delineation of a dosage- sensitive critical interval that can convey an autism phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 633–649.
Stefansson H., Meyer-Lindenberg A., Steinberg S., Magnusdottir B., Morgen K., Arnarsdottir S. et al. 2014 CNVs conferring risk of autism or schizophrenia affect cognition in controls. Nature 505, 361–366.
Tejada M. I., Martínez-Bouzas C., García-Ribes A., Larrucea S., Acquadro F., Cigudosa J. C. et al. 2011 A child with mild X-linked intellectual disability and a microduplication at Xp22.12 including RPS6KA3. Pediatrics 128, e1029–1033.
Tzschach A., Chen W., Erdogan F., Hoeller A., Ropers H. H., Castellan C. et al. 2008 Characterization of interstitial Xp duplications in two families by tiling path array CGH. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 46, 197–203.
Uliana V. and Percesepe A. 2016 Reverse phenotyping comes of age. Mol. Genet. Metab. 118, 230–231.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the ‘Fondazione Emma ed Ernesto Rulfo per la Genetica Medica’ (Italy). This study makes used of data generated by the DECIPHER Consortium. We are indebted to the family members for their collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: S. Ganesh
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uliana, V., Bonatti, F., Zanatta, V. et al. Spectrum of X-linked intellectual disabilities and psychiatric symptoms in a family harbouring a Xp22.12 microduplication encompassing the RPS6KA3 gene. J Genet 98, 10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1055-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1055-8