Abstract
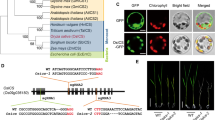
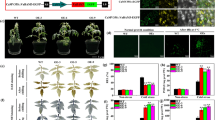
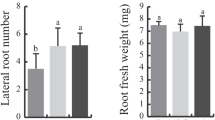
Hpa1 is a harpin protein produced by Xanthomonas oryzae, an important bacterial pathogen of rice, and has the growth-promoting activity in plants. To understand the molecular basis for the function of Hpa1, we generated an inactive variant protein, Hpa1ΔNT, by deleting the nitroxyl-terminal region of the Hpa1 sequence and compared Hpa1ΔNT with the full-length protein in terms of the effects on vegetative growth and related physiological responses in Arabidopsis. When Hpa1 was applied to plants, it acted to enhance the vegetative growth but did not affect the floral development. Enhanced plant growth was accompanied by induced expression of growth-promoting genes in plant leaves. The growth-promoting activity of Hpa1 was further correlated with a physiological consequence shown as promoted leaf photosynthesis as a result of facilitated CO2 conduction through leaf stomata and mesophyll cells. On the contrary, plant growth, growth-promoting gene expression, and the physiological consequence changed little in response to the Hpa1ΔNT treatment. These analyses suggest that Hpa1 requires the nitroxyl-terminus to facilitate CO2 transport inside leaf cells and promote leaf photosynthesis and vegetative growth of the plant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfano JR and Collmer A 1997 The type III (Hrp) secretion pathway of plant pathogenic bacteria: trafficking harpins, Avr proteins, and death. J. Bacteriol. 179 5655–5662
Ausubel FM 2005 Are innate immune signaling pathways in plants and animals conserved. Nat. Immunol. 6 973–979
Ayadi M, Cavez D, Miled N, Chaumont F and Masmoudi K 2011 Identification and characterization of two plasma membrane aquaporins in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. subsp. durum) and their role in abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 49 1029–1039
Bae EK, Lee H, Lee JS and Noh EW 2011 Drought, salt and wounding stress induce the expression of the plasma membrane intrinsic protein 1 gene in poplar (Populus alba×P. tremula var. glandulosa). Gene 483 43–48
Chen L, Qian J, Qu S, Long J, Yin Q, Zhang C, Wu X, Sun F, Wu T, Hayes M, Beer SV and Dong H 2008a Identification of specific fragments of HpaGXooc, a harpin from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola that induce disease resistance and enhance growth in plants. Phytopathology 98 781–791
Chen L, Zhang SS, Qu SP, Long JY, Yin Q, Qian J, Sun F, Zhang SJ, et al. 2008b A selected fragment of HpaGXooc, a harpin protein from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola, affects disease reduction and grain yield of rice in extensive grower plantings. Phytopathology 98 792–802
Cox MC, Benschop JJ, Vreeburg RA, Wagemaker CA, Moritz T, Peeters AJ and Voesenek LA 2004 The roles of ethylene, auxin, abscisic acid, and gibberellin in the hyponastic growth of submerged Rumex palustris petioles. Plant Physiol. 136 2948–2960
de Groot BL and Hub JS 2011 A decade of debate: significance of CO2 permeation through membrane channels still controversial. ChemPhysChem 12 1021–1022
Deng BL, Deng S, Sun F, Zhang S and Dong H 2011 Down-regulation of free riboflavin content induces hydrogen peroxide and a pathogen defense in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 77 185–201
Dong H, Delaney TP, Bauer DW and Beer SV 1999 Harpin induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis through the systemic acquired resistance pathway mediated by salicylic acid and the NIM1 gene. Plant J. 20 207–215
Dong HP, Peng J, Bao Z, Meng X, Bonasera JM, Chen G, Beer SV and Dong H 2004 Downstream divergence of the ethylene signaling pathway for harpin-stimulated Arabidopsis growth and insect defense. Plant Physiol. 136 3628–3638
Dong HP, Yu H, Bao Z, Guo X, Peng J, Yao Z, Chen G and Dong H 2005 The ABI2-dependent abscisic acid signalling controls HrpN-induced drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Planta 221 313–327
Evans JR, Kaldenhoff R, Genty B and Terashima I 2009 Resistances along the CO2 diffusion pathway inside leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 60 2235–2248
Flexas J, Barbour MM, Brendel O, Cabrera HM, Carriquí M, Díaz-Espejo A, Douthe C, Dreyer E, et al. 2012 Mesophyll diffusion conductance to CO2: an unappreciated central player in photosynthesis. Plant Sci. 193–194 70–84
Flexas J, Ortuño MF, Ribas-Carbo M, Diaz-Espejo A, Flórez-Sarasa ID and Medrano H 2007 Mesophyll conductance to CO2 in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 175 501–511
Gomes D, Agasse A, Thiébaud P, Delrot S, Gerós H and Chaumont F 2009 Aquaporins are multifunctional water and solute transporters highly divergent in living organisms. Bioch. Biophy. Acta 1788 1213–1228
Harley PC, Loreto F, Di Marco G and Sharkey TD 1992 Theoretical considerations when estimating the mesophyll conductance to CO2 flux by analysis of the response of photosynthesis to CO2. Plant Physiol. 98 1429–1436
He SY 1998 Type III protein secretion systems in plant and animal pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 36 363–392
Heckwolf M, Pater D, Hanson DT and Kaldenhoff R 2011 The Arabidopsis thaliana aquaporin AtPIP1;2 is a physiologically relevant CO2 transport facilitator. Plant J. 67 795–804
Jacobi V, Dufour J, Bouvet GF, Aoun M and Bernier L 2010 Identification of transcripts up-regulated in asexual and sexual fruiting bodies of the Dutch elm disease pathogen Ophiostoma novo-ulmi. Can. J. Microbiol. 56 697–705
Kaldenhoff R 2012 Mechanisms underlying CO2 diffusion in leaves. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15 276–281
Kim JF and Beer SV 2000 hrp genes and harpins of Erwinia amylovora: A decade of discovery; in Fire blight and its causative agent, Erwinia amylovora (ed) JL Vanneste (Wallingford, UK: CAB International) pp 141–162
Kwack MS, Kim EN, Lee H, Kim J-W, Chun S-C and Kim KD 2005 Digital image analysis to measure lesion area of cucumber anthracnose by Colletotrichum orbiculare. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 71 418–421
Lee SH, Chung GC, Jang JY, Ahn SJ and Zwiazek JJ 2012 Overexpression of PIP2;5 aquaporin alleviates effects of low root temperature on cell hydraulic conductivity and growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 159 479–488
Liu F, Liu H, Jia Q, Wu X, Guo X, Zhang S, Song F and Dong H 2006 The internal glycine-rich motif and cysteine suppress several effects of the HpaGXooc protein in plants. Phytopathology 96 1052–1059
Maurel C 2007 Plant aquaporins: Novel functions and regulation properties. FEBS Lett. 581 2227–2236
Miao W, Wang X, Li M, Song C, Wang Y, Hu D and Wang J 2010a Genetic transformation of cotton with a harpin-encoding gene hpa Xoo confers an enhanced defense response against different pathogens through a priming mechanism. BMC Plant Biol. 10 67
Miao W, Wang X, Song C, Wang Y, Ren Y and Wang J 2010b Transcriptome analysis of Hpa1 Xoo transformed cotton revealed constitutive expression of genes in multiple signalling pathways related to disease resistance. J. Exp. Bot. 61 4263–4275
Oh CS and Beer SV 2007 AtHIPM, an ortholog of the apple HrpN-interacting protein, is a negative regulator of plant growth and mediates the growth-enhancing effect of HrpN in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 145 426–436
Peng J, Bao Z, Ren H, Wang J and Dong H 2004 Expression of harpinXoo in transgenic tobacco induces pathogen defense in the absence of hypersensitive cell death. Phytopathology 94 1048–1055
Peng JL, Dong H, Dong HP, Delaney TP, Bonasera BM and Beer SV 2003 Harpin-elicited hypersensitive cell death and pathogen resistance requires the NDR1 and EDS1 genes. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 62 317–326
Pons TL, Flexas J, von Caemmerer S, Evans JR, Genty B, Ribas-Carbo M and Brugnoli E 2009 Estimating mesophyll conductance to CO2: methodology, potential errors, and recommendations. J. Exp. Bot. 60 2217–2234
Postaire O, Tournaire-Roux C, Grondin A, Boursiac Y, Morillon R, Schäffner AR and Maurel C 2010 A PIP1 aquaporin contributes to hydrostatic pressure-induced water transport in both the root and rosette of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 152 1418–1430
Ren H, Gu G, Long J, Qian J, Wu T, Song T, Zhang S, Chen Z and Dong H 2006a Combinative effects of a bacterial type-III effector and a biocontrol bacterium on rice growth and disease resistance. J. Biosci. 31 617–627
Ren H, Song T, Wu T, Sun L, Liu Y, Yang F, Chen Z and Dong H 2006b Effects of a biocontrol bacterium on growth and defence of transgenic rice plants expressing a bacterial type-III effector. Ann. Microbiol. 56 281–287
Ren X, Zhang C, Bao Z, Chen L, Wu X and Dong H 2008 Root growth of Arabidopsis thaliana is regulated by ethylene and abscisic acid signaling interaction in response to HrpNEa, a bacterial protein of harpin group. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 31 617–627
Rivers RL, Dean RM, Chandy G, Hall JE, Roberts DM and Zeidel ML 1997 Functional analysis of nodulin 26, an aquaporin in soybean root nodule symbiosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 272 16256–16261
Ruiz-Lozano JM, del Mar Alguacil M, Bárzana G, Vernieri P and Aroca R 2009. Exogenous ABA accentuates the differences in root hydraulic properties between mycorrhizal and non mycorrhizal maize plants through regulation of PIP aquaporins. Plant Mol. Biol. 70 565–579
Sang S, Li X, Gao R, You Z, Lü B, Liu P, Ma Q and Dong H 2012 Apoplastic and cytoplasmic location of harpin protein Hpa1Xoo plays different roles in H2O2 generation and pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 79 375–391
Shao M, Wang J, Dean RA, Lin Y, Gao X and Hu S 2008 Expression of a harpin-encoding gene in rice confers durable nonspecific resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Biotechnol. J. 6 73–81
Sloan J, Backhaus A, Malinowski R, McQueen-Mason S and Fleming AJ 2009 Phased control of expansin activity during leaf development identifies a sensitivity window for expansin-mediated induction of leaf growth. Plant Physiol. 151 1844–1854
Sun F, Liu P, Xu J and Dong H 2010 Mutation in RAP2.6L, a transactivator of the ERF transcription factor family, enhances Arabidopsis resistance to Pseudomonas syringae. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 74 295–302
Taiz L and Zeiger E 2010 Plant physiology (Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates)
Torres MA 2010 ROS in biotic interactions. Plant Physiol. 138 414–429
Uehlein N, Sperling H, Heckwolf M and Kaldenhoff R 2012 The Arabidopsis aquaporin PIP1;2 rules cellular CO2 uptake. Plant Cell Environ. 35 1077–1083
Wang G, Gao Y, Wang J, Yang L, Song R, Li X and Shi J 2011 Overexpression of two cambium-abundant Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) α-expansin genes ClEXPA1 and ClEXPA2 affect growth and development in transgenic tobacco and increase the amount of cellulose in stem cell walls. Plant Biotechnol. J. 9 486–502
Wang XY, Song CF, Miao WG, Ji ZL, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhang JH, Hu JS, Borth W and Wang JS 2008 Mutations in the N-terminal coding region of the harpin protein Hpa1 from Xanthomonas oryzae cause loss of hypersensitive reaction induction in tobacco. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 81 359–369
Wei ZM, Laby RJ, Zumoff CH, Bauer DW, He SY, Collmer A and Beer SV 1992 Harpin, elicitor of the hypersensitive response produced by the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Science 257 85–88
Wu X, Wu T, Long J, Yin Q, Zhang Y, Chen L, Liang Y, Liu R, Gao T and Dong H 2007 Productivity and biochemical properties of green tea in response to a bacterial type-III effector protein and its variants. J. Biosci. 32 1119–1132
Zabaleta E, Martin MV and Braun HP 2012 A basal carbon concentrating mechanism in plants. Plant Sci. 187 97–104
Zawoznik MS, Ameneiros M, Benavides MP, Vázquez S and Groppa MD 2011 Response to saline stress and aquaporin expression in Azospirillum-inoculated barley seedlings. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 90 1389–1397
Zhang C, Bao Z, Liang Y, Yang X, Wu X, Hong X and Dong H 2007 Abscisic acid mediates Arabidopsis drought tolerance induced by HrpNEa in the absence of ethylene signaling. Plant Mol. Biol. Rept. 25 94–114
Zhang L, Xiao SS, Li WQ, Feng W, Li J, Wu ZD, Gao XW, Liu FQ and Shao M 2011 Overexpression of a Harpin-encoding gene hrf1 in rice enhances drought tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 62 4129–4138
Zhu WG, Magbanua MM and White FF 2000 Identification of two novel hpaG-associated genes in the hpaG gene cluster of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. J. Bacteriol. 182 1844–1853
Acknowledgements
We thank our university colleague Professor Shiwei Guo for assistance with Li-6400XT and chlorophyll fluorescence analyser. This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation (31272072) and Novel Transgenic Organisms Breeding Project (2013ZX08002001-007) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: R GEETA
[Li X, Han L, Zhao Y, You Z, Dong H and Zhang C 2013 Hpa1 harpin needs nitroxyl terminus to promote vegetative growth and leaf photosynthesis in Arabidopsis. J. Biosci. 39 1–11] DOI 10.1007/s12038-013-9408-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Han, L., Zhao, Y. et al. Hpa1 harpin needs nitroxyl terminus to promote vegetative growth and leaf photosynthesis in Arabidopsis. J Biosci 39, 127–137 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9408-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9408-6