Abstract
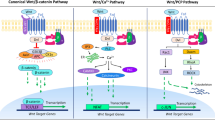
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a significant health concern, as it presently has no effective treatment in the clinical setting. Inflammation is a key player in the pathophysiological process of SCI, with a number of studies evidencing that the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway may impede the inflammatory response and improve SCI. OTULIN, as a de-ubiquitination enzyme, the most notable is its anti-inflammatory effect. OTULIN can inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway to suppress the inflammatory reaction via de-ubiquitination. In addition, OTULIN may promote vascular regeneration through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in the wake of SCI. In this review, we analyze the structure and physiological function of OTULIN, along with both NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Furthermore, we examine the significant role of OTULIN in SCI through its impairment of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which could open the possibility of it being a novel interventional target for the condition.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Zhou J, Li Z, Wu T, Zhao Q, Zhao Q, Cao Y (2020) LncGBP9/miR-34a axis drives macrophages toward a phenotype conducive for spinal cord injury repair via STAT1/STAT6 and SOCS3. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01805-5
Gedde MH, Lilleberg HS, Aßmus J, Gilhus NE, Rekand T (2019) Traumatic vs non-traumatic spinal cord injury: a comparison of primary rehabilitation outcomes and complications during hospitalization. J Spinal Cord Med 42(6):695–701. https://doi.org/10.1080/10790268.2019.1598698
Jaja BNR, Jiang F, Badhiwala JH, Schär R, Kurpad S, Grossman RG, Harrop JS, Guest JD, Toups EG, Shaffrey CI, Aarabi B, Boakye M, Fehlings MG, Wilson JR (2019) Association of pneumonia, wound infection, and sepsis with clinical outcomes after acute traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 36(21):3044–3050. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.6245
Li X, Zhan J, Hou Y, Hou Y, Chen S, Luo D, Luan J, Wang L et al (2019) Coenzyme Q10 regulation of apoptosis and oxidative stress in H2O2 induced BMSC death by modulating the Nrf-2/NQO-1 signaling pathway and its application in a model of spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:6493081. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6493081
Anjum A, Yazid MD, Fauzi Daud M, Idris J, Ng AMH, Selvi Naicker A, Ismail OHR, Athi Kumar RK et al (2020) Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci 21(20):7533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207533
Okada S, Hara M, Kobayakawa K, Matsumoto Y, Nakashima Y (2018) Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res 126:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2017.10.004
Yao C, Cao X, Yu B (2021) Revascularization after traumatic spinal cord injury. Front Physiol 12:631500. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.631500
Venkatesh K, Ghosh SK, Mullick M, Manivasagam G, Sen D (2019) Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, treatment strategies, associated challenges, and future implications. Cell Tissue Res 377(2):125–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03039-1
Doglio MG, Verboom L, RuilovaSosoranga E, Frising UC, Asaoka T, Gansemans Y, Van Nieuwerburgh F, van Loo G et al (2023) Myeloid OTULIN deficiency couples RIPK3-dependent cell death to Nlrp3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β secretion. Sci Immunol. 8(89):eadf4404. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.adf4404
Shi R, Shi X, Qin D, Tang S, Vermeulen M, Zhang X (2021) SNX27-driven membrane localisation of OTULIN antagonises linear ubiquitination and NF-κB signalling activation. Cell Biosci 11(1):146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00659-5
Yalcın T, Kaya S, Kuloğlu T (2024) Resveratrol may dose-dependently modulate nephrin and OTULIN levels in a doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity model. Toxicol Mech Methods 34(1):98–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2023.2268717
Liu S, Li Y, Choi HMC, Sarkar C, Koh EY, Wu J, Lipinski MM (2018) Lysosomal damage after spinal cord injury causes accumulation of RIPK1 and RIPK3 proteins and potentiation of necroptosis. Cell Death Dis 9(5):476. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0469-1
Kist M, Kőműves LG, Goncharov T, Dugger DL, Yu C, Roose-Girma M, Newton K, Webster JD et al (2021) Impaired RIPK1 ubiquitination sensitizes mice to TNF toxicity and inflammatory cell death. Cell Death Differ 28(3):985–1000. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00629-3
Douglas T, Saleh M (2019) Post-translational modification of OTULIN regulates ubiquitin dynamics and cell death. Cell Rep 29(11):3652-3663.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.014
Fu Y, Wang H, Dai H, Zhu Q, Cui CP, Sun X, Li Y, Deng Z et al (2021) OTULIN allies with LUBAC to govern angiogenesis by editing ALK1 linear polyubiquitin. Mol Cell 81(15):3187-3204.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.05.031
Gong B, Radulovic M, Figueiredo-Pereira ME, Cardozo C (2016) The ubiquitin-proteasome system: potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease and spinal cord injury. Front Mol Neurosci 9:4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2016.00004
Ohtake F, Saeki Y, Ishido S, Kanno J, Tanaka K (2016) The K48–K63 branched ubiquitin chain regulates NF-κB signaling. Mol Cell 64(2):251–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.014
Xu P, Duong DM, Seyfried NT, Cheng D, Xie Y, Robert J, Rush J, Hochstrasser M et al (2009) Quantitative proteomics reveals the function of unconventional ubiquitin chains in proteasomal degradation. Cell 137(1):133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.041
Li Y, Reverter D (2021) Molecular mechanisms of DUBs regulation in signaling and disease. Int J Mol Sci 22(3):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22030986
Makarova KS, Aravind L, Koonin EV (2000) A novel superfamily of predicted cysteine proteases from eukaryotes, viruses and Chlamydia pneumoniae. Trends Biochem Sci 25(2):50–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01530-3
Verboom L, Hoste E, van Loo G (2021) OTULIN in NF-kB signaling, cell death, and disease. Trends Immunol 42(7):590–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2021.05.003
Schünke H, Göbel U, Dikic I, Pasparakis M (2021) OTULIN inhibits RIPK1-mediated keratinocyte necroptosis to prevent skin inflammation in mice. Nat Commun 12(1):5912. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25945-1
Liu C, Chen S, Zhang H, Chen Y, Gao Q, Chen Z, Liu Z, Wang J (2021) Bioinformatic analysis for potential biological processes and key targets of heart failure-related stroke. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 22(9):718–732. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000544
Bian Y, Qin C, Xin Y, Yu Y, Chen H, Wang G, Xie K, Yu Y (2018) Itraq-based quantitative proteomic analysis of lungs in murine polymicrobial sepsis with hydrogen gas treatment. Shock 49(2):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000927
Wang W, Li M, Ponnusamy S, Chi Y, Xue J, Fahmy B, Fan M, Miranda-Carboni GA et al (2020) ABL1-dependent OTULIN phosphorylation promotes genotoxic Wnt/β-catenin activation to enhance drug resistance in breast cancers. Nat Commun 11(1):3965. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17770-9
Damgaard RB, Jolin HE, Allison MED, Davies SE, Titheradge HL, McKenzie ANJ, Komander D (2020) OTULIN protects the liver against cell death, inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer. Cell Death Differ 27(5):1457–1474. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0532-1
Hoste E, Lecomte K, Annusver K, Vandamme N, Roels J, Maschalidi S, Verboom L, Vikkula HK et al (2021) OTULIN maintains skin homeostasis by controlling keratinocyte death and stem cell identity. Nat Commun 12(1):5913. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25944-2
Damgaard RB, Walker JA, Marco-Casanova P, Morgan NV, Titheradge HL, Elliott PR, McHale D, Maher ER et al (2016) The Deubiquitinase OTULIN Is an essential negative regulator of inflammation and autoimmunity. Cell 166(5):1215-1230.e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.019
van Wijk SJL, Fricke F, Herhaus L, Gupta J, Hötte K, Pampaloni F, Grumati P, Kaulich M et al (2017) Linear ubiquitination of cytosolic Salmonella typhimurium activates NF-κB and restricts bacterial proliferation. Nat Microbiol 2:17066. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.66
Keusekotten K, Elliott PR, Glockner L, Fiil BK, Damgaard RB, Kulathu Y, Wauer T, Hospenthal MK et al (2013) OTULIN antagonizes LUBAC signaling by specifically hydrolyzing Met1-linked polyubiquitin. Cell 153(6):1312–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.014
van Well EM, Bader V, Patra M, Sánchez-Vicente A, Meschede J, Furthmann N, Schnack C, Blusch A et al (2019) A protein quality control pathway regulated by linear ubiquitination. EMBO J 38(9):e100730. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018100730
Zhou L, Ge Y, Fu Y, Wu B, Zhang Y, Li L, Cui CP, Wang S et al (2021) Global screening of LUBAC and OTULIN interacting proteins by human proteome microarray. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:686395. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.686395
Elliott PR, Nielsen SV, Marco-Casanova P, Fiil BK, Keusekotten K, Mailand N, Freund SM, Gyrd-Hansen M et al (2014) Molecular basis and regulation of OTULIN-LUBAC interaction. Mol Cell 54(3):335–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.018
Li M, Li L, Asemota S, Kakhniashvili D, Narayanan R, Wang X, Liao FF (2022) Reciprocal interplay between OTULIN-LUBAC determines genotoxic and inflammatory NF-κB signal responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119(33):e2123097119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2123097119
Schaeffer V, Akutsu M, Olma MH, Gomes LC, Kawasaki M, Dikic I (2014) Binding of OTULIN to the PUB domain of HOIP controls NF-κB signaling. Mol Cell 54(3):349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.016
Zhao M, Song K, Hao W, Wang L, Patil G, Li Q, Xu L, Hua F et al (2020) Non-proteolytic ubiquitination of OTULIN regulates NF-κB signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Biol 12(3):163–175. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjz081
Damgaard RB, Elliott PR, Swatek KN, Maher ER, Stepensky P, Elpeleg O, Komander D, Berkun Y (2019) OTULIN deficiency in ORAS causes cell type-specific LUBAC degradation, dysregulated TNF signalling and cell death. EMBO Mol Med 11(3):e9324. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201809324
Tao P, Wang S, Ozen S, Lee PY, Zhang J, Wang J, Han H, Yang Z et al (2021) Deubiquitination of proteasome subunits by OTULIN regulates type I IFN production. Sci Adv 7(47):eabi6794. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abi6794
Napetschnig J, Wu H (2013) Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys 42:443–468. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130338
Hinz M, Scheidereit C (2014) The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep 15(1):46–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/embr.201337983
Feoktistova M, Makarov R, Yazdi AS, Panayotova-Dimitrova D (2021) RIPK1 and TRADD regulate TNF-induced signaling and ripoptosome formation. Int J Mol Sci 22(22):12459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212459
Lei CQ, Wu X, Zhong X, Jiang L, Zhong B, Shu HB (2019) USP19 Inhibits TNF-α- and IL-1β-triggered NF-κB activation by deubiquitinating TAK1. J Immunol 203(1):259–268. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1900083
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H (2020) Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00312-6
Chen ZJ (2012) Ubiquitination in signaling to and activation of IKK. Immunol Rev 246(1):95–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01108.x
Iwai K (2012) Diverse ubiquitin signaling in NF-κB activation. Trends Cell Biol 22(7):355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2012.04.001
Shibata Y, Komander D (2022) LUBAC. Curr Biol 32(11):R506–R508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2022.04.041
Fuseya Y, Fujita H, Kim M, Ohtake F, Nishide A, Sasaki K, Saeki Y, Tanaka K et al (2020) The HOIL-1L ligase modulates immune signalling and cell death via monoubiquitination of LUBAC. Nat Cell Biol 22(6):663–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-020-0517-9
Ikeda F, Deribe YL, Skånland SS, Stieglitz B, Grabbe C, Franz-Wachtel M, van Wijk SJ, Goswami P et al (2011) SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis. Nature 471(7340):637–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09814
Lork M, Verhelst K, Beyaert R (2017) CYLD, A20 and OTULIN deubiquitinases in NF-κB signaling and cell death: so similar, yet so different. Cell Death Differ 24(7):1172–1183. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.46
Wertz IE, O’Rourke KM, Zhou H, Eby M, Aravind L, Seshagiri S, Wu P, Wiesmann C et al (2004) De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature 430(7000):694–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02794
Workman LM, Habelhah H (2013) TNFR1 signaling kinetics: spatiotemporal control of three phases of IKK activation by posttranslational modification. Cell Signal 25(8):1654–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.005
Pflug KM, Sitcheran R (2020) Targeting NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) in immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21(22):8470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228470
Yin L, Wu L, Wesche H, Arthur CD, White JM, Goeddel DV, Schreiber RD (2001) Defective lymphotoxin-beta receptor-induced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in NIK-deficient mice. Science 291(5511):2162–2165. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1058453
Chen B, Li C, Yao J, Shi L, Liu W, Wang F, Huo S, Zhang Y et al (2020) Zebrafish NIK mediates IFN induction by regulating activation of IRF3 and NF-κB. J Immunol 204(7):1881–1891. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1900561
Wang RP, Zhang M, Li Y, Diao FC, Chen D, Zhai Z, Shu HB (2008) Differential regulation of IKK alpha-mediated activation of IRF3/7 by NIK. Mol Immunol 45(7):1926–1934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.10.034
Awasthee N, Rai V, Chava S, Nallasamy P, Kunnumakkara AB, Bishayee A, Chauhan SC, Challagundla KB et al (2019) Targeting IκappaB kinases for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 56:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.02.007
Bainter W, Lougaris V, Wallace JG, Badran Y, Hoyos-Bachiloglu R, Peters Z, Wilkie H, Das M et al (2021) Combined immunodeficiency with autoimmunity caused by a homozygous missense mutation in inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase alpha (IKKα). Sci Immunol 6(63):eabf6723. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abf6723
Sun SC (2017) The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 17(9):545–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.52
Zusso M, Lunardi V, Franceschini D, Pagetta A, Lo R, Stifani S, Frigo AC, Giusti P et al (2019) Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1538-9
Tang J, Xu L, Zeng Y, Gong F (2021) Effect of gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 91:107272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107272
Yuan Y, Men W, Shan X, Zhai H, Qiao X, Geng L, Li C (2020) Baicalein exerts neuroprotective effect against ischaemic/reperfusion injury via alteration of NF-kB and LOX and AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Inflammopharmacology 28(5):1327–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00714-6
Khan M, Shah SA, Kim MO (2018) 17β-estradiol via SIRT1/acetyl-p53/NF-kB signaling pathway rescued postnatal rat brain against acute ethanol intoxication. Mol Neurobiol 55(4):3067–3078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0520-8
Seo EJ, Fischer N, Efferth T (2018) Phytochemicals as inhibitors of NF-κB for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Res 129:262–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.030
Li Y, Führer M, Bahrami E, Socha P, Klaudel-Dreszler M, Bouzidi A, Liu Y, Lehle AS et al (2019) Human RIPK1 deficiency causes combined immunodeficiency and inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(3):970–975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1813582116
Tang TT, Wang B, Li ZL, Wen Y, Feng ST, Wu M, Liu D, Cao JY et al (2021) Kim-1 targeted extracellular vesicles: a new therapeutic platform for RNAi to treat AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 32(10):2467–2483. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2020111561
Sehnert B, Burkhardt H, Dübel S, Voll RE (2020) Cell-type targeted NF-kappaB inhibition for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Cells 9(7):1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071627
Fei M, Li Z, Cao Y, Jiang C, Lin H, Chen Z (2021) MicroRNA-182 improves spinal cord injury in mice by modulating apoptosis and the inflammatory response via IKKβ/NF-κB. Lab Invest 101(9):1238–1253. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-021-00606-5
Liu Z, Yao X, Sun B, Jiang W, Liao C, Dai X, Chen Y, Chen J et al (2021) Pretreatment with kaempferol attenuates microglia-mediate neuroinflammation by inhibiting MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. Free Radic Biol Med 168:142–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.037
Jin X, Liu MY, Zhang DF, Zhong X, Du K, Qian P, Yao WF, Gao H et al (2019) Baicalin mitigates cognitive impairment and protects neurons from microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasomes and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 25(5):575–590. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13086
Xu H, Wang Y, Luo Y (2021) OTULIN is a new target of EA treatment in the alleviation of brain injury and glial cell activation via suppression of the NF-κB signalling pathway in acute ischaemic stroke rats. Mol Med 27(1):37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00297-0
Peltzer N, Darding M, Montinaro A, Draber P, Draberova H, Kupka S, Rieser E, Fisher A et al (2018) LUBAC is essential for embryogenesis by preventing cell death and enabling haematopoiesis. Nature 557(7703):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0064-8
Shimizu Y, Peltzer N, Sevko A, Lafont E, Sarr A, Draberova H, Walczak H (2017) The Linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex acts as a liver tumor suppressor and inhibits hepatocyte apoptosis and hepatitis. Hepatology 65(6):1963–1978. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29074
Verboom L, Anderson CJ, Jans M, Petta I, Blancke G, Martens A, Sze M, Hochepied T et al (2023) OTULIN protects the intestinal epithelium from apoptosis during inflammation and infection. Cell Death Dis 14(8):534. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-06058-7
Kaya S, Yalcın T (2023) In an experimental myocardial infarction model, L-arginine pre-intervention may exert cardioprotective effects by regulating OTULIN levels and mitochondrial dynamics. Cell Stress Chaperones 28(6):811–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-023-01373-6
Nusse R, Varmus HE (1982) Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell 31(1):99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3
Reyes M, Flores T, Betancur D, Peña-Oyarzún D, Torres VA (2020) Wnt/β-catenin signaling in oral carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 21(13):4682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134682
Janda CY, Waghray D, Levin AM, Thomas C, Garcia KC (2012) Structural basis of Wnt recognition by Frizzled. Science 337(6090):59–64. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222879
Majidinia M, Aghazadeh J, Jahanban-Esfahlani R, Yousefi B (2018) The roles of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in tissue development and regenerative medicine. J Cell Physiol 233(8):5598–5612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26265
MacDonald BT, He X (2012) Frizzled and LRP5/6 receptors for Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(12):a007880. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a007880
Feng Y, Ren J, Gui Y, Wei W, Shu B, Lu Q, Xue X, Sun X et al (2018) Wnt/β-catenin-promoted macrophage alternative activation contributes to kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 29(1):182–193. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2017040391
Huang W, Wang P, Shen T, Hu C, Han Y, Song M, Bian Y, Li Y et al (2017) Aluminum trichloride inhibited osteoblastic proliferation and downregulated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 177(2):323–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0880-3
Bertozzi A, Wu CC, Hans S, Brand M, Weidinger G (2022) Wnt/β-catenin signaling acts cell-autonomously to promote cardiomyocyte regeneration in the zebrafish heart. Dev Biol 481:226–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.11.001
Rivkin E, Almeida SM, Ceccarelli DF, Juang YC, MacLean TA, Srikumar T, Huang H, Dunham WH et al (2013) The linear ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinase gumby regulates angiogenesis. Nature 498(7454):318–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12296
Wang Q, Huang X, Su Y, Yin G, Wang S, Yu B, Li H, Qi J et al (2022) Activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway mitigates blood-brain barrier dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 236. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac236
Sun X, Peng X, Cao Y, Zhou Y, Sun Y (2020) ADNP promotes neural differentiation by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Nat Commun 11(1):2984. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16799-0
Xiang Z, Zhang S, Yao X, Xu L, Hu J, Yin C, Chen J, Xu H (2021) Resveratrol promotes axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury through activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 13(20):23603–23619. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203628
Zajac E, Schweighofer B, Kupriyanova TA, Juncker-Jensen A, Minder P, Quigley JP, Deryugina EI (2013) Angiogenic capacity of M1- and M2-polarized macrophages is determined by the levels of TIMP-1 complexed with their secreted proMMP-9. Blood 122(25):4054–4067. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-05-501494
Gao ZS, Zhang CJ, Xia N, Tian H, Li DY, Lin JQ, Mei XF, Wu C (2021) Berberine-loaded M2 macrophage-derived exosomes for spinal cord injury therapy. Acta Biomater 126:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.03.018
Hamzah RN, Alghazali KM, Biris AS, Griffin RJ (2021) Exosome traceability and cell source dependence on composition and cell-cell cross talk. Int J Mol Sci 22(10):5346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105346
Kore RA, Henson JC, Hamzah RN, Griffin RJ, Tackett AJ, Ding Z, Mehta JL (2019) Molecular events in MSC exosome mediated cytoprotection in cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep 9(1):19276. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55694-7
Tian Y, Li S, Song J, Ji T, Zhu M, Anderson GJ, Wei J, Nie G (2014) A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 35(7):2383–2390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.11.083
Luo Z, Peng W, Xu Y, Xie Y, Liu Y, Lu H, Cao Y, Hu J (2021) Exosomal OTULIN from M2 macrophages promotes the recovery of spinal cord injuries via stimulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway-mediated vascular regeneration. Acta Biomater 136:519–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.09.026
Weber A, Elliott PR, Pinto-Fernandez A, Bonham S, Kessler BM, Komander D, El Oualid F, Krappmann D (2017) A linear diubiquitin-based probe for efficient and selective detection of the deubiquitinating enzyme OTULIN. Cell Chem Biol 24(10):1299-1313.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.08.006
Stangl A, Elliott PR, Pinto-Fernandez A, Bonham S, Harrison L, Schaub A, Kutzner K, Keusekotten K et al (2019) Regulation of the endosomal SNX27-retromer by OTULIN. Nat Commun 10(1):4320. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12309-z
Krönke J, Udeshi ND, Narla A, Grauman P, Hurst SN, McConkey M, Svinkina T, Heckl D et al (2014) Lenalidomide causes selective degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in multiple myeloma cells. Science 343(6168):301–305. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1244851
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (no. LY19H170001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL designed the study. QW, LW, MH, YZ, BOAB, and XL prepared the first draft of the manuscript. QW, LW, MH, YZ, BOAB, and XL revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors agreed to publish this article.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, L., Botchway, B.O.A. et al. OTULIN Can Improve Spinal Cord Injury by the NF-κB and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways. Mol Neurobiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-024-04134-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-024-04134-3