Abstract
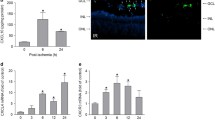
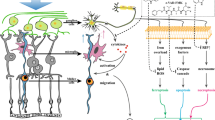
Retinal ischemia exists in various ischemic retinopathies including glaucoma, contributing to the death of retinal neurons. Calcium binding protein S100A4 is important in tumors, and our previous study found that S100A4 protects retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) against retinal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. This study was aimed to further discuss the neuroprotection and mechanisms of S100A4 in retinal I/R of mice. The rAAV-EF1α-s100a4-EGFP-WPRE or rAAV-EF1α-EGFP-WPRE-Pa was injected intravitreally 4 weeks before I/R. S100A4, molecules in TLR4 signaling pathway and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress branches, inflammatory molecules, and surviving RGCs and cholinergic amacrine (ChAT) cells were determined by quantitative PCR, western blot, or immunofluorescent staining. The apoptosis and necrosis of retinal neurons induced by I/R were inhibited by overexpressed S100A4. RGCs, ChAT cells, and the retinal function were preserved by S100A4 overexpressing 7 days after I/R. Mechanistically, the beneficial effects of S100A4 may be mediated by inhibiting the activation of TLR4 signaling pathway and alleviating ER stress, leading to the attenuation of inflammatory response of the retina after I/R. Our findings indicated that S100A4 has neuroprotective effect against retinal I/R injury, and promoting S100A4 expression may be an effective strategy to inhibit retinal neurons from degeneration in ischemic retinopathy.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Research data is available when required.
References
Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY (2014) Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 121:2081–2090
Maggio F (2015) Glaucomas. Top Companion Anim Med 30:86–96
Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G, Graham M, Melena J (2004) Retinal ischemia: mechanisms of damage and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res 23:91–147
Shosha E, Xu Z, Yokota H et al (2016) Arginase 2 promotes neurovascular degeneration during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis 7:e2483
Palmhof M, Frank V, Rappard P et al (2019) From ganglion cell to photoreceptor layer: timeline of deterioration in a rat ischemia/reperfusion model. Front Cell Neurosci 13:174
Hayreh SS, Zimmerman MB, Kimura A, Sanon A (2004) Central retinal artery occlusion. Retinal survival time. Exp Eye Res 78:723–736
Tarabykina S, Kriajevska M, Scott DJ et al (2000) Heterocomplex formation between metastasis-related protein S100A4 (Mts1) and S100A1 as revealed by the yeast two-hybrid system. FEBS Lett 475:187–191
Donato R (2003) Intracellular and extracellular roles of S100 proteins. Microsc Res Tech 60:540–551
Schneider M, Hansen JL, Sheikh SP (2008) S100A4: a common mediator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, fibrosis and regeneration in diseases? J Mol Med (Berl) 86:507–522
Ambartsumian N, Klingelhofer J, Grigorian M et al (2001) The metastasis-associated Mts1(S100A4) protein could act as an angiogenic factor. Oncogene 20:4685–4695
Gross SR, Sin CG, Barraclough R, Rudland PS (2014) Joining S100 proteins and migration: for better or for worse, in sickness and in health. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:1551–1579
Donato R, Cannon BR, Sorci G et al (2013) Functions of S100 proteins. Curr Mol Med 13:24–57
Dmytriyeva O, Pankratova S, Owczarek S et al (2012) The metastasis-promoting S100A4 protein confers neuroprotection in brain injury. Nat Commun 3:1197
Pedersen MV, Kohler LB, Grigorian M et al (2004) The Mts1/S100A4 protein is a neuroprotectant. J Neurosci Res 77:777–786
Abu El-Asrar AM, Nawaz MI, De Hertogh G et al (2014) S100A4 is upregulated in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and correlates with markers of angiogenesis and fibrogenesis. Mol Vis 20:1209–1224
Maddala R, Gao J, Mathias RT et al (2021) Absence of S100A4 in the mouse lens induces an aberrant retina-specific differentiation program and cataract. Sci Rep 11:2203
Cheng G, Tian K, Zhang L, Yang N, Xing Y, He T (2016) S100A4 gene silencing in oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy inhibits retinal neovascularization via down-regulation of CREB expression. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 254:97–108
Cheng G, He T, Xing Y (2016) Silencing of S100A4, a metastasis-associated protein, inhibits retinal neovascularization via the downregulation of BDNF in oxygen-induced ischaemic retinopathy. Eye (Lond) 30:877–887
Yang J, Yang N, Luo J et al (2020) Overexpression of S100A4 protects retinal ganglion cells against retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Exp Eye Res 201:108281
Sakamoto K, Yonoki Y, Kubota Y et al (2006) Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors abolished histological protection by late ischemic preconditioning in rat retina. Exp Eye Res 82:512–518
Stankowska DL, Minton AZ, Rutledge MA et al (2015) Neuroprotective effects of transcription factor Brn3b in an ocular hypertension rat model of glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56:893–907
Chiu K, Chang RC, So KF (2007) Intravitreous injection for establishing ocular diseases model. J Vis Exp:313
Liu W, Xia F, Ha Y et al (2019) Neuroprotective effects of HSF1 in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 60:965–977
Do YJ, Sul JW, Jang KH et al (2017) A novel RIPK1 inhibitor that prevents retinal degeneration in a rat glaucoma model. Exp Cell Res 359:30–38
Ha Y, Liu H, Xu Z et al (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-regulated CXCR3 pathway mediates inflammation and neuronal injury in acute glaucoma. Cell Death Dis 6:e1900
Minhas G, Sharma J, Khan N (2016) Cellular stress response and immune signaling in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Immunol 7:444
Jeon CJ, Strettoi E, Masland RH (1998) The major cell populations of the mouse retina. J Neurosci 18:8936–8946
Zhang C, Yu WQ, Hoshino A et al (2019) Development of ON and OFF cholinergic amacrine cells in the human fetal retina. J Comp Neurol 527:174–186
Chen GY, Nunez G (2010) Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol 10:826–837
Belvin MP, Anderson KV (1996) A conserved signaling pathway: the Drosophila toll-dorsal pathway. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:393–416
Schlueter C, Weber H, Meyer B et al (2005) Angiogenetic signaling through hypoxia: HMGB1: an angiogenetic switch molecule. Am J Pathol 166:1259–1263
Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Iwabe T, Takeuchi O, Akira S (2002) Differential involvement of IFN-beta in Toll-like receptor-stimulated dendritic cell activation. Int Immunol 14:1225–1231
Schneider A, Martin-Villalba A, Weih F, Vogel J, Wirth T, Schwaninger M (1999) NF-kappaB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 5:554–559
Qi Y, Zhao M, Bai Y et al (2014) Retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury is mediated by Toll-like receptor 4 activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55:5466–5475
Cerezo LA, Remakova M, Tomcik M et al (2014) The metastasis-associated protein S100A4 promotes the inflammatory response of mononuclear cells via the TLR4 signalling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:1520–1526
Kuramochi M, Izawa T, Pervin M, Bondoc A, Kuwamura M, Yamate J (2016) The kinetics of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and toll-like receptors during thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 68:471–477
Ha Y, Liu W, Liu H et al (2018) AAV2-mediated GRP78 transfer alleviates retinal neuronal injury by downregulating ER stress and Tau oligomer formation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 59:4670–4682
Nashine S, Liu Y, Kim BJ, Clark AF, Pang IH (2014) Role of C/EBP homologous protein in retinal ganglion cell death after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56:221–231
Li C, Wang L, Huang K, Zheng L (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in retinal vascular degeneration: protective role of resveratrol. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:3241–3249
Li H, Zhu X, Fang F, Jiang D, Tang L (2014) Down-regulation of GRP78 enhances apoptosis via CHOP pathway in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurosci Lett 575:68–73
Jiang M, Wang H, Liu Z et al (2020) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent activation of iNOS/NO-NF-kappaB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to endothelial inflammation and apoptosis associated with microgravity. FASEB J 34:10835–10849
Ambartsumian N, Klingelhofer J, Grigorian M (2019) The multifaceted S100A4 protein in cancer and inflammation. Methods Mol Biol:339–365
Hou S, Jiao Y, Yuan Q et al (2018) S100A4 protects mice from high-fat diet-induced obesity and inflammation. Lab Invest 98:1025–1038
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank Dr. Xinlan Lei, Dr. Qinqin Deng, and Dr. Chen Zhao for their expert and constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiayi Yang and Xiao Zhang: Study design, data collection and analysis, figures and original draft writing. Ying Li: Data collection and figures. Jiayi Yang and Xiao Zhang: Data interpretation. Ning Yang and Jinyuan Luo: Editing the manuscript. Tao He and Yiqiao Xing: Supervision, Study design, and reviewing and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was performed in line with the principles of the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent for Publication
All authors have given their consent to publish this article.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Zhang, X., Li, Y. et al. Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB pathway and endoplasmic reticulum stress by overexpressed S100A4 ameliorates retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury of mice. Mol Neurobiol 61, 2228–2240 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03709-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03709-w