Abstract
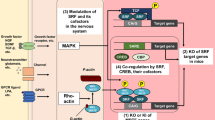
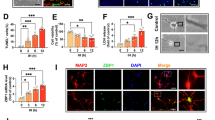
Prenatal hypoxia (PH) is one of the most common complications of obstetrics and is closely associated with many neurological disorders such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment. Our previous study found that Zfp462 heterozygous (Het) mice exhibit significant anxiety-like behavior. Interestingly, offspring mice with PH also have anxiety-like behaviors in adulthood, accompanied by reduced expression of Zfp462 and increased expression of miR-377-3p; however, the exact regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, western blotting, gene knockdown, immunofluorescence, dual-luciferase reporter assay, immunoprecipitation, cell transfection with miR-377-3p mimics or inhibitors, quantitative real-time PCR, and rescue assay were used to detect changes in the miR-377-3p-Zfp462-Pbx1 (pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox1) pathway in the brains of prenatal hypoxic offspring to explain the pathogenesis of anxiety-like behaviors. We found that Zfp462 deficiency promoted Pbx1 protein degradation through ubiquitination and that Zfp462 Het mice showed downregulation of the protein kinase B (PKB, also called Akt)-glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β)-cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) pathway and hippocampal neurogenesis with anxiety-like behavior. In addition, PH mice exhibited upregulation of miR-377-3p, downregulation of Zfp462/Pbx1-Akt-GSK3β-CREB pathway activity, reduced hippocampal neurogenesis, and an anxiety-like phenotype. Intriguingly, miR-377-3p directly targets the 3′UTR of Zfp462 mRNA to regulate Zfp462 expression. Importantly, microinjection of miR-377-3p antagomir into the hippocampal dentate gyrus of PH mice upregulated Zfp462/Pbx1-Akt-GSK3β-CREB pathway activity, increased hippocampal neurogenesis, and improved anxiety-like behaviors. Collectively, our findings demonstrated a crucial role for miR-377-3p in the regulation of hippocampal neurogenesis and anxiety-like behaviors via the Zfp462/Pbx1-Akt-GSK3β-CREB pathway. Therefore, miR-377-3p could be a potential therapeutic target for anxiety-like behavior in prenatal hypoxic offspring.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- PH:
-
Prenatal hypoxia
- Het:
-
Heterozygous
- KO:
-
Knockout
- FOAD:
-
Fetal origin adult diseases
- Pbx1:
-
Pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox1
- OFT:
-
Open field test
- IP:
-
Immunoprecipitation
- EPM:
-
Elevated plus maze
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- ACSF:
-
Artificial cerebrospinal fluid
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- Akt/PKB:
-
Protein kinase B
- GSK3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β
- CREB:
-
cAMP response element-binding protein
References
Barker DJ, Winter PD, Osmond C, Margetts B, Simmonds SJ (1989) Weight in infancy and death from ischaemic heart disease. Lancet 2(8663):577–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90710-1
Wang B, Zeng H, Liu J, Sun M (2021) Effects of prenatal hypoxia on nervous system development and related diseases. Front Neurosci 15:755554. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.755554
Giussani DA, Davidge ST (2013) Developmental programming of cardiovascular disease by prenatal hypoxia. J Dev Orig Health Dis 4(5):328–337. https://doi.org/10.1017/S204017441300010X
Sandau US, Handa RJ (2007) Glucocorticoids exacerbate hypoxia-induced expression of the pro-apoptotic gene Bnip3 in the developing cortex. Neuroscience 144(2):482–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.003
Gumusoglu SB, Chilukuri ASS, Santillan DA, Santillan MK, Stevens HE (2020) Neurodevelopmental outcomes of prenatal preeclampsia exposure. Trends Neurosci 43(4):253–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2020.02.003
Piesova M, Mach M (2020) Impact of perinatal hypoxia on the developing brain. Physiol Res 69(2):199–213. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.934198
Matrosova VY, Orlovskaya IA, Kozlova DV, Kozlov VA (2000) Effects of prenatal hypoxia on the formation of immune deficiency in newborn mice. Bull Exp Biol Med 129(6):564–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02434878
Doan VD, Gagnon S, Joseph V (2004) Prenatal blockade of estradiol synthesis impairs respiratory and metabolic responses to hypoxia in newborn and adult rats. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 287(3):R612–R618. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00627.2003
Nalivaeva NN, Turner AJ, Zhuravin IA (2018) Role of prenatal hypoxia in brain development, cognitive functions, and neurodegeneration. Front Neurosci 12:825. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00825
Xu T, Fan X, Zhao M, Wu M, Li H, Ji B, Zhu X, Li L et al (2021) DNA methylation-reprogrammed Ang II (angiotensin II) type 1 receptor-early growth response gene 1-protein kinase C epsilon axis underlies vascular hypercontractility in antenatal hypoxic offspring. Hypertension 77(2):491–506. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16247
Torres-Cuevas I, Corral-Debrinski M, Gressens P (2019) Brain oxidative damage in murine models of neonatal hypoxia/ischemia and reoxygenation. Free Radic Biol Med 142:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.06.011
Oechmichen M, Meissner C (2006) Cerebral hypoxia and ischemia: the forensic point of view: a review. J Forensic Sci 51(4):880–887. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2006.00174.x
Fan JM, Chen XQ, Jin H, Du JZ (2009) Gestational hypoxia alone or combined with restraint sensitizes the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and induces anxiety-like behavior in adult male rat offspring. Neuroscience 159(4):1363–1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.02.009
Zeng H, Wei B, Liu J, Lu L, Li L, Wang B, Sun M (2022) Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates ten-eleven translocated methylcytosine dioxygenase 1-c-Myc binding involved in depression-like behavior in prenatal hypoxia offspring. Neuroscience 502:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.08.014
Wei B, Li L, He A, Zhang Y, Sun M, Xu Z (2016) Hippocampal NMDAR-Wnt-Catenin signaling disrupted with cognitive deficits in adolescent offspring exposed to prenatal hypoxia. Brain Res 1631:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.11.041
Chang YS, Stoykova A, Chowdhury K, Gruss P (2007) Graded expression of Zfp462 in the embryonic mouse cerebral cortex. Gene Expr Patterns 7(4):405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.modgep.2006.11.009
Yelagandula R, Stecher K, Novatchkova M, Michetti L, Michlits G, Wang J, Hofbauer P, Vainorius G et al (2023) ZFP462 safeguards neural lineage specification by targeting G9A/GLP-mediated heterochromatin to silence enhancers. Nat Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-022-01051-2
Laurent A, Masse J, Omilli F, Deschamps S, Richard-Parpaillon L, Chartrain I, Pellerin I (2009) ZFPIP/Zfp462 is maternally required for proper early Xenopus laevis development. Dev Biol 327(1):169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.12.005
Wang B, Zheng Y, Shi H, Du X, Zhang Y, Wei B, Luo M, Wang H et al (2017) Zfp462 deficiency causes anxiety-like behaviors with excessive self-grooming in mice. Genes Brain Behav 16(2):296–307. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbb.12339
Laurent A, Masse J, Deschamps S, Burel A, Omilli F, Richard-Parpaillon L, Pellerin I (2009) Interaction of ZFPIP with PBX1 is crucial for proper expression of neural genetic markers during Xenopus development. Develop Growth Differ 51(8):699–706. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-169X.2009.01129.x
Laurent A, Bihan R, Deschamps S, Guerrier D, Dupe V, Omilli F, Burel A, Pellerin I (2007) Identification of a new type of PBX1 partner that contains zinc finger motifs and inhibits the binding of HOXA9-PBX1 to DNA. Mech Dev 124(5):364–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mod.2007.01.008
Liu Y, Xu X, Lin P, He Y, Zhang Y, Cao B, Zhang Z, Sethi G et al (2019) Inhibition of the deubiquitinase USP9x induces pre-B cell homeobox 1 (PBX1) degradation and thereby stimulates prostate cancer cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem 294(12):4572–4582. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.006057
Grebbin BM, Hau AC, Gross A, Anders-Maurer M, Schramm J, Koss M, Wille C, Mittelbronn M et al (2016) Pbx1 is required for adult subventricular zone neurogenesis. Development 143(13):2281–2291. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.128033
Jiang Y, Liu F, Zou F, Zhang Y, Wang B, Zhang Y, Lian A, Han X et al (2019) PBX homeobox 1 enhances hair follicle mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and reprogramming through activation of the AKT/glycogen synthase kinase signaling pathway and suppression of apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther 10(1):268. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1382-y
Wei X, Yu L, Li Y (2018) PBX1 promotes the cell proliferation via JAK2/STAT3 signaling in clear cell renal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 500(3):650–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.127
Remesal L, Roger-Baynat I, Chirivella L, Maicas M, Brocal-Ruiz R, Perez-Villalba A, Cucarella C, Casado M et al (2020) PBX1 acts as terminal selector for olfactory bulb dopaminergic neurons. Development 147(8). https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.186841
Kempermann G, Kronenberg G (2003) Depressed new neurons--adult hippocampal neurogenesis and a cellular plasticity hypothesis of major depression. Biol Psychiatry 54(5):499–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00319-6
Snyder JS, Soumier A, Brewer M, Pickel J, Cameron HA (2011) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis buffers stress responses and depressive behaviour. Nature 476(7361):458–461. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10287
Mishra A, Singh S, Tiwari V, Parul, Shukla S (2019) Dopamine D1 receptor activation improves adult hippocampal neurogenesis and exerts anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effect via activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathways in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 122:170–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2018.11.020
Evans J, Sun Y, McGregor A, Connor B (2012) Allopregnanolone regulates neurogenesis and depressive/anxiety-like behaviour in a social isolation rodent model of chronic stress. Neuropharmacology 63(8):1315–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.08.012
Qiao X, Gai H, Su R, Deji C, Cui J, Lai J, Zhu Y (2018) PI3K-AKT-GSK3beta-CREB signaling pathway regulates anxiety-like behavior in rats following alcohol withdrawal. J Affect Disord 235:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.04.039
Moriguchi S, Shinoda Y, Yamamoto Y, Sasaki Y, Miyajima K, Tagashira H, Fukunaga K (2013) Stimulation of the sigma-1 receptor by DHEA enhances synaptic efficacy and neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of olfactory bulbectomized mice. PLoS One 8(4):e60863. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060863
Gao Q, Jeon SJ, Jung HA, Lee HE, Park SJ, Lee Y, Lee Y, Ko SY et al (2015) Nodakenin enhances cognitive function and adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Neurochem Res 40(7):1438–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1612-3
Miyata S, Kumagaya R, Kakizaki T, Fujihara K, Wakamatsu K, Yanagawa Y (2019) Loss of glutamate decarboxylase 67 in somatostatin-expressing neurons leads to anxiety-like behavior and alteration in the Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathway. Front Behav Neurosci 13:131. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00131
Bali A, Jaggi AS (2016) Investigations on GSK-3beta/NF-kB signaling in stress and stress adaptive behavior in electric foot shock subjected mice. Behav Brain Res 302:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.014
Wu Q, Li Y, Xiao B (2013) DISC1-related signaling pathways in adult neurogenesis of the hippocampus. Gene 518(2):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.01.015
Qiao J, Rong L, Wang Z, Zhang M (2017) Involvement of Akt/GSK3beta/CREB signaling pathway on chronic omethoate induced depressive-like behavior and improvement effects of combined lithium chloride and astaxanthin treatment. Neurosci Lett 649:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.03.048
Zhao F, Tao W, Shang Z, Zhang W, Ruan J, Zhang C, Zhou L, Aiello H et al (2020) Facilitating granule cell survival and maturation in dentate gyrus with baicalin for antidepressant therapeutics. Front Pharmacol 11:556845. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.556845
Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka D, Sobolewski C, Foti M (2019) Deciphering miRNAs’ action through miRNA editing. Int J Mol Sci 20:24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246249
Jin J, Kim SN, Liu X, Zhang H, Zhang C, Seo JS, Kim Y, Sun T (2016) miR-17-92 cluster regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis, anxiety, and depression. Cell Rep 16(6):1653–1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.06.101
Hommers L, Raab A, Bohl A, Weber H, Scholz CJ, Erhardt A, Binder E, Arolt V et al (2015) MicroRNA hsa-miR-4717-5p regulates RGS2 and may be a risk factor for anxiety-related traits. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 168B(4):296–306. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32312
Zhou M, Wang M, Wang X, Liu K, Wan Y, Li M, Liu L, Zhang C (2018) Abnormal expression of microRNAs induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in rat hippocampal tissues. Mol Neurobiol 55(2):917–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0365-6
Gururajan A, Naughton ME, Scott KA, O'Connor RM, Moloney G, Clarke G, Dowling J, Walsh A et al (2016) MicroRNAs as biomarkers for major depression: a role for let-7b and let-7c. Transl Psychiatry 6(8):e862. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.131
Maffioletti E, Cattaneo A, Rosso G, Maina G, Maj C, Gennarelli M, Tardito D, Bocchio-Chiavetto L (2016) Peripheral whole blood microRNA alterations in major depression and bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 200:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.04.021
Wang H, Qi C, Wan D (2021) MicroRNA-377-3p targeting MMP-16 inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth, invasion, and interstitial transition. Ann Transl Med 9(2):124. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-8027
Jiang L, Cao H, Deng T, Yang M, Meng T, Yang H, Luo X (2021) Serum exosomal miR-377-3p inhibits retinal pigment epithelium proliferation and offers a biomarker for diabetic macular edema. J Int Med Res 49(4):3000605211002975. https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605211002975
Wang H, Wei Z, Li H, Guan Y, Han Z, Wang H, Liu B (2020) MiR-377-3p inhibits atherosclerosis-associated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via targeting neuropilin2. Biosci Rep 40:6. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20193425
Ding S, Wu X, Li G, Han M, Zhuang Y, Xu T (2005) Efficient transposition of the piggyBac (PB) transposon in mammalian cells and mice. Cell 122(3):473–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.013
Ding S, Xu T, Wu X (2014) Generation of genetically engineered mice by the piggyBac transposon system. Methods Mol Biol 1194:171–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1215-5_9
Shmelkov SV, Hormigo A, Jing D, Proenca CC, Bath KG, Milde T, Shmelkov E, Kushner JS et al (2010) Slitrk5 deficiency impairs corticostriatal circuitry and leads to obsessive-compulsive-like behaviors in mice. Nat Med 16(5):598–602. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2125
Xu X, Yang H, Lin YF, Li X, Cape A, Ressler KJ, Li S, Li XJ (2010) Neuronal Abelson helper integration site-1 (Ahi1) deficiency in mice alters TrkB signaling with a depressive phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(44):19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1013032107
Wang B, Xia L, Zhu D, Zeng H, Wei B, Lu L, Li W, Shi Y et al (2022) Paternal high-fat diet altered sperm 5′'tsRNA-Gly-GCC is associated with enhanced gluconeogenesis in the offspring. Front Mol Biosci 9:857875. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.857875
Wang B, Xin N, Qian X, Zhai L, Miao Z, Yang Y, Li S, Sun M et al (2021) Ahi1 regulates the nuclear translocation of glucocorticoid receptor to modulate stress response. Transl. Psychiatry 11(1):188. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01305-x
Revest JM, Dupret D, Koehl M, Funk-Reiter C, Grosjean N, Piazza PV, Abrous DN (2009) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is involved in anxiety-related behaviors. Mol Psychiatry 14(10):959–967. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2009.15
Wang X, Meng FS, Liu ZY, Fan JM, Hao K, Chen XQ, Du JZ (2013) Gestational hypoxia induces sex-differential methylation of Crhr1 linked to anxiety-like behavior. Mol Neurobiol 48(3):544–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8444-4
Wu X, Liang Y, Jing X, Lin D, Chen Y, Zhou T, Peng S, Zheng D et al (2018) Rifampicin prevents SH-SY5Y cells from rotenone-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta/CREB signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 43(4):886–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2494-y
Xu XF, Wang YC, Zong L, Chen ZY, Li Y (2018) Elevating integrin-linked kinase expression has rescued hippocampal neurogenesis and memory deficits in an AD animal model. Brain Res 1695:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.05.024
Ducsay CA, Goyal R, Pearce WJ, Wilson S, Hu XQ, Zhang L (2018) Gestational hypoxia and developmental plasticity. Physiol Rev 98(3):1241–1334. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00043.2017
Xue Q, Zhang L (2009) Prenatal hypoxia causes a sex-dependent increase in heart susceptibility to ischemia and reperfusion injury in adult male offspring: role of protein kinase C epsilon. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330(2):624–632. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.109.153239
Ostadal B, Ostadalova I, Szarszoi O, Netuka I, Olejnickova V, Hlavackova M (2021) Sex-dependent effect of perinatal hypoxia on cardiac tolerance to oxygen deprivation in adults. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 99(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2020-0310
Yan HL, Sun XW, Wang ZM, Liu PP, Mi TW, Liu C, Wang YY, He XC et al (2019) MiR-137 deficiency causes anxiety-like behaviors in mice. Front Mol Neurosci 12:260. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2019.00260
Strawn JR, Geracioti L, Rajdev N, Clemenza K, Levine A (2018) Pharmacotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder in adult and pediatric patients: an evidence-based treatment review. Expert Opin Pharmacother 19(10):1057–1070. https://doi.org/10.1080/14656566.2018.1491966
Choi IY, Cho ML, Cho KO (2022) Interleukin-17A mediates hippocampal damage and aberrant neurogenesis contributing to epilepsy-associated anxiety. Front Mol Neurosci 15:917598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2022.917598
Zhu J, Chen Z, Tian J, Meng Z, Ju M, Wu G, Tian Z (2017) miR-34b attenuates trauma-induced anxiety-like behavior by targeting CRHR1. Int J Mol Med 40(1):90–100. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.2981
Mannironi C, Biundo A, Rajendran S, De Vito F, Saba L, Caioli S, Zona C, Ciotti T et al (2018) miR-135a regulates synaptic transmission and anxiety-like behavior in amygdala. Mol Neurobiol 55(4):3301–3315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0564-9
Scott KA, Hoban AE, Clarke G, Moloney GM, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2015) Thinking small: towards microRNA-based therapeutics for anxiety disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 24(4):529–542. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.2014.997873
Im HI, Kenny PJ (2012) MicroRNAs in neuronal function and dysfunction. Trends Neurosci 35(5):325–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2012.01.004
Cheng LC, Pastrana E, Tavazoie M, Doetsch F (2009) miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat Neurosci 12(4):399–408. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2294
Issler O, Haramati S, Paul ED, Maeno H, Navon I, Zwang R, Gil S, Mayberg HS et al (2014) MicroRNA 135 is essential for chronic stress resiliency, antidepressant efficacy, and intact serotonergic activity. Neuron 83(2):344–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.042
Wei ZX, Xie GJ, Mao X, Zou XP, Liao YJ, Liu QS, Wang H, Cheng Y (2020) Exosomes from patients with major depression cause depressive-like behaviors in mice with involvement of miR-139-5p-regulated neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 45(6):1050–1058. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-0622-2
Zhang P, Wang W, Li M (2021) Circ_0010283/miR-377-3p/Cyclin D1 axis is associated with proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and inflammation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 78(3):437–447. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0000000000001076
Liu L, Wang H, Chen X, Zhang Y, Li W, Rao X, Liu Y, Zhao L et al (2021) Integrative analysis of long non-coding RNAs, messenger RNAs, and microRNAs indicates the neurodevelopmental dysfunction in the hippocampus of gut microbiota-dysbiosis mice. Front Mol Neurosci 14:745437. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2021.745437
Baudry A, Mouillet-Richard S, Schneider B, Launay JM, Kellermann O (2010) miR-16 targets the serotonin transporter: a new facet for adaptive responses to antidepressants. Science 329(5998):1537–1541. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1193692
Lv Q, Li Q, Zhang P, Jiang Y, Wang X, Wei Q, Cao S, Liao Z et al (2015, 2015) Disorders of microRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells: as novel biomarkers of ankylosing spondylitis and provocative therapeutic targets. Biomed Res Int:504208. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/504208
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82101793, 81974244), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20210092), Suzhou Natural Science Foundation (SKJY2021061), and Suzhou city “Gu Su Wei Sheng Ren Cai” Research Project (GSWS2022010). We appreciate the support of the Jiangsu Innovative and Entrepreneurial Talent Programme (JSSCBS20211567) and the support of Suzhou city “Gu Su Wei Sheng Ren Cai” program (2021057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the Laboratory Animal Management Regulations with approval of the Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (No. 2020179).
Consent for Publication
All authors have approved for publication.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Bin Wang and Yichen Zhu are co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1:
Figure S1–S5 and Table S1 (DOCX 1397 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhu, Y., Wei, B. et al. miR-377-3p Regulates Hippocampal Neurogenesis via the Zfp462-Pbx1 Pathway and Mediates Anxiety-Like Behaviors in Prenatal Hypoxic Offspring. Mol Neurobiol 61, 1920–1935 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03683-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03683-3