Abstract
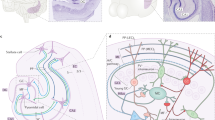
A distinct feature of the hippocampus of the brain is its unidirectional tri-synaptic pathway originating from the entorhinal cortex and projecting to the dentate gyrus (DG) then to area CA3 and subsequently, area CA1 of the Ammon’s horn. Each of these areas of the hippocampus has its own cellular structure and distinctive function. The principal neurons in these areas are granule cells in the DG and pyramidal cells in the Ammon’s horn’s CA1 and CA3 areas with a vast network of interneurons. This review discusses the fundamental differences between the CA1 and DG areas regarding cell morphology, synaptic plasticity, signaling molecules, ability for neurogenesis, vulnerability to various insults and pathologies, and response to pharmacological agents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA1:
-
Corno Amonis
- DG:
-
dentate gyrus
- I/O:
-
imput/output
- LTP:
-
long-term potentiation
- E-LTP:
-
early-phase LTP
- L-LTP:
-
late-phase LTP
- LTD:
-
long-term depression
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
nitric oxide synthase
- P-CaMKII:
-
phosphorylated calcium calmodulin kinase II
- GTPase:
-
guanidine triphosphotase
- UCH-L1:
-
ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase-L1
- fEPSP:
-
field excitatory postsynaptic potential
- GABA:
-
gamma aminobutyric acid
- TEA:
-
tetraethylammonium
- VDCC:
-
voltage-dependent calcium channel
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate
- AMPA:
-
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid
- BDNF:
-
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- IPSP:
-
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
- ERK1/2:
-
extracellular signal–regulated kinase
- SRLM:
-
stratum radiatum/stratum lacunosum-moleculare
- IPSC:
-
inhibitory postsynaptic current
- OZR:
-
obese Zucker rat
- A-beta:
-
Amyloid beta
- Egr:
-
early growth response protein-1
- BLA:
-
basolateral nucleus of the amygdala
References
Knowles WD (1992) Normal anatomy and neurophysiology of the hippocampal formation. J Clin Neurophysiol 9:252–263
Jackson TC, Foster TC (2009) Regional health and function in the hippocampus: Evolutionary compromises for a critical brain region. Bioscience Hypotheses 2:245–251
Jackson TC, Rani A, Kumar A, Foster TC (2009) Regional hippocampal differences in AKT survival signaling across the lifespan: Implications for CA1 vulnerability with aging. Cell Death Differ 16:439–448
McEwen BS (2001) Plasticity of the hippocampus: Adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci 933:265–277
Gerges NZ, Alkadhi KA (2004) Hypothyroidism impairs late LTP in CA1 region but not in dentate gyrus of the intact rat hippocampus: MAPK involvement. Hippocampus 14:40–45
Gerges NZ, Alzoubi KH, Alkadhi KA (2005) Role of phosphorylated CaMKII and calcineurin in the differential effect of hypothyroidism on LTP of CA1 and dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 15:480–490
Dao AT, Zagaar MA, Levine AT, Alkadhi KA (2016) Comparison of the effect of exercise on late-phase LTP of the dentate gyrus and CA1 of Alzheimer’s disease model. Mol Neurobiol 53:6859–6868
Stabel J, Ficker E, Heinemann U (1992) Young CA1 pyramidal cells of rats, but not dentate gyrus granule cells, express a delayed inward rectifying current with properties of IQ. Neurosci Lett 135:231–234
Ormerod BK, Palmer TD, Caldwell MA (2008) Neurodegeneration and cell replacement. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 363:153–170
Pawluski JL, Brummelte S, Barha CK, Crozier TM, Galea LA (2009) Effects of steroid hormones on neurogenesis in the hippocampus of the adult female rodent during the estrous cycle, pregnancy, lactation and aging. Front Neuroendocrinol 30:343–357
Sawada M, Sawamoto K (2013) Mechanisms of neurogenesis in the normal and injured adult brain. Keio J Med 62:13–28
Anacker C, Hen R (2017) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility linking memory and mood. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:335–346
Lee E, Son H (2009) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and related neurotrophic factors. BMB Rep 42:239–244
Yamashima T, Tonchev AB, Vachkov IH, Popivanova BK, Seki T, Sawamoto K, Okano H (2004) Vascular adventitia generates neuronal progenitors in the monkey hippocampus after ischemia. Hippocampus 14:861–875
Parfitt KD, Doze VA, Madison DV, Browning MD (1992) Isoproterenol increases the phosphorylation of the synapsins and increases synaptic transmission in dentate gyrus but not in area CA1, of the hippocampus. Hippocampus 2:59–64
Davis S, Laroche S (1996) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors induce differential effects on synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus and CA1 of the hippocampus in the anaesthetized rat. Neuropharmacology 35:337–346
Hsu JC, Zhang Y, Takagi N, Gurd JW, Wallace MC, Zhang L, Eubanks JH (1998) Decreased expression and functionality of NMDA receptor complexes persist in the CA1, but not in the dentate gyrus after transient cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:768–775
Yao H, Huang YH, Liu ZW, Wan Q, Ding AS, Zhao B, Fan M, Wang FZ (1998) The different responses to anoxia in cultured CA1 and DG neurons from newborn rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao 50:61–66
Matthies H, Schroeder H, Becker A, Loh H, Höllt V, Krug M (2000) Lack of expression of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus but not in the CA1 region of the hippocampus of mu-opioid receptor-deficient mice. Neuropharmacology 39:952–960
Xiong ZQ, Stringer JL (2000) Extracellular pH responses in CA1 and the dentate gyrus during electrical stimulation, seizure discharges, and spreading depression. J Neurophysiol 83:3519–3524
Gilbert PE, Kesner RP, Lee I (2001) Dissociating hippocampal subregions: Double dissociation between dentate gyrus and CA1. Hippocampus 11:626–636
Song D, Xie X, Wang Z, Berger TW (2001) Differential effect of TEA on long-term synaptic modification in hippocampal CA1 and dentate gyrus in vitro. Neurobiol Learn Mem 76:375–387
Stuart G, Spruston N (1998) Determinants of voltage attenuation in neocortical pyramidal neuron dendrites. J Neurosci 18:3501–3510
Stuart GJ, Spruston N (2015) Dendritic integration: 60 years of progress. Nat Neurosci 18:1713–1721
Golding NL, Mickus TJ, Katz Y, Kath WL, Spruston N (2005) Factors mediating powerful voltage attenuation along CA1 pyramidal neuron dendrites. J Physiol 568(Pt 1):69–82
Schmidt-Hieber C, Jonas P, Bischofberger J (2007) Subthreshold dendritic signal processing and coincidence detection in dentate gyrus granule cells. J Neurosci 27:8430–8441
Haberly LB Parallel-distributed processing in olfactory cortex: new insights from morphological and physiological analysis of neuronal circuitry Chem Senses 2001; 26:551–576.
Wilson DA, Sullivan RM (2011) Cortical processing of odor objects. Neuron 72:506–519
Ishizuka N, Weber J, Amaral DG (1990) Organization of intrahippocampal projections originating from CA3 pyramidal cells in the rat. J Comp Neurol 295:580–623
Trieu BH, Kramár EA, Cox CD, Jia Y, Wang W, Gall CM, Lynch G (2015) Pronounced differences in signal processing and synaptic plasticity between piriform-hippocampal network stages: A prominent role for adenosine. J Physiol 593:2889–2907
Imdahl A, Hossmann K (1986) Morphometric evaluation of post-ischemic capillary perfusion in selectively vulnerable areas of gerbil brain. Acta Neuropathol 69:267–271
Suzuki R, Yamaguchi T, Kirino T, Orzi F, Klatzo I (1983) The effects of 5-minute ischemia in Mongolian gerbils: I. Blood-brain barrier, cerebral blood flow, and local cerebral glucose utilization changes. Acta Neuropathol 60:207–216
Melnikova T, Park D, Becker L, Lee D, Cho E, Sayyida N, Tian J, Bandeen-Roche K et al (2016 Dec) Sex-related dimorphism in dentate gyrus atrophy and behavioral phenotypes in an inducible tTa:APPsi transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 96:171–185
Kiryk A, Sowodniok K, Kreiner G, Rodriguez-Parkitna J, Sönmez A, Górkiewicz T, Bierhoff H, Wawrzyniak M et al (2013 Nov 11) Impaired rRNA synthesis triggers homeostatic responses in hippocampal neurons. Front Cell Neurosci 7:207
Penner MR, Parrish RR, Hoang LT, Roth TL, Lubin FD, Barnes CA (2016 Aug) Age-related changes in Egr1 transcription and DNA methylation within the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 26(8):1008–1020
Lardenoije R, van den Hove DLA, Havermans M, van Casteren A, Le KX, Palmour R, Lemere CA, Rutten BPF (2018 Jan) Age-related epigenetic changes in hippocampal subregions of four animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 86:1–15
Becq H, Jorquera I, Ben-Ari Y, Weiss S, Represa A (2005 Feb 5) Differential properties of dentate gyrus and CA1 neural precursors. J Neurobiol 62(2):243–261
Sharvit A, Segal M, Kehat O, Stork O, Richter-Levin G (2015) Differential modulation of synaptic plasticity and local circuit activity in the dentate gyrus and CA1 regions of the rat hippocampus by corticosterone. Stress. 18(3):319–327
Arima-Yoshida F, Watabe AM, Manabe T (2011 May) The mechanisms of the strong inhibitory modulation of long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 33(9):1637–1646
Frahm C, Draguhn A (2001 Dec 14) GAD and GABA transporter (GAT-1) mRNA expression in the developing rat hippocampus. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 132(1):1–13
Coultrap S, Nixon K, Alvestad R, Valenzuela C, Browning M (2005) Differential expression of NMDA receptor subunits and splice variants among the CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Mol Brain Res 135:104–111
Lalonde CC, Mielke JG (2014) Selective vulnerability of hippocampal sub-fields to oxygen-glucose deprivation is a function of animal age. Brain Res 1543:271–279
Lamsa KP, Heeroma JH, Somogyi P, Rusakov DA, Kullmann DM (2007) Anti-Hebbian long-term potentiation in the hippocampal feedback inhibitory circuit. Science 315(5816):1262–1266
Wiltgen BJ, Royle GA, Gray EE, Abdipranoto A, Thangthaeng N, Jacobs N, Saab F, Tonegawa S et al (2010) A role for calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity and learning. PLoS One 29:5(9)
Weiss JH (2011) Ca permeable AMPA channels in diseases of the nervous system. Front Mol Neurosci 4:42
Kannangara TS, Eadie BD, Bostrom CA, Morch K, Brocardo PS, Christie BR (2015) GluN2A−/− mice lack bidirectional synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus and perform poorly on spatial pattern separation tasks. Cereb Cortex 25:2102–2113
Vicini S, Wang JF, Li JH, Zhu WJ, Wang YH, Luo JH, Wolfe BB, Grayson DR (1998) Functional and pharmacological differences between recombinant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Neurophysiol 79:555–566
Dingledine R, Borges BD, Traynelis SF (1999) The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 51:7–62
Cunha RA (2001) Regulation of the ecto-nucleotidase pathway in rat hippocampal nerve terminals. Neurochem Res 26:979–991
Lovatt D, Xu Q, Liu W, Takano T, Smith NA, Schnermann J, Tieu K, Nedergaard M (2012) Neuronal adenosine release, and not astrocytic ATP release, mediates feedback inhibition of excitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:6265–6270
Lee KS, Schubert P, Reddington M, Kreutzberg GW (1986) The distribution of adenosine A1 receptors and 5′-nucleotidase in the hippocampal formation of several mammalian species. J Comp Neurol 246:427–434
Schoen SW, Kreutzberg GW (1994) Synaptic 5′-nucleotidase activity reflects lesion-induced sprouting within the adult rat dentate gyrus. Exp Neurol 127:106–118
Dumont Y, Fournier A, St-Pierre S, Schwartz TW, Quirion R (1990) Differential distribution of neuropeptide Y, and Y, receptors in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 191:501–503
Dumont Y, Martel J-C, Fournier A, St-Pierre S, Quirion R (1992) Neuropeptide Y and neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes in brain and periuheral tissues. Prog Neurobiol 38:125–167
Dumont Y, Fournier-A S-PS, Quirion R (1993) Comparative characterization and autoradiographic distribution of neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes in the rat brain. J Neurosci 13:73–86
Aicher SA, Springton M, Berger SB, Reis DJ, Wahlestedt C (1991) Receptor-selective analogs demonstrate NPY/PYY receptor heterogeneity in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 130:32–36
Wahlestedt C, Reis DJ (1993) Neuropeptide Y-related peptides and their receptors-are the receptors potential therapeutic drug targets? Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 33:309–352
McQuiston AR, Petrozzino JJ, Connor JA, Colmers WF (1996) Neuropeptide Y1 receptors inhibit N-type calcium currents and reduce transient calcium increases in rat dentate granule cells. J Neurosci 16:1422–1429
Silva AP, Carvalho AP, Carvalho CM, Malva JO (2001) Modulation of intracellular calcium changes and glutamate release by neuropeptide Y1 and Y2 receptors in the rat hippocampus: Differential effects in CA1, CA3 and dentate gyrus. J Neurochem 79:286–296
Westerink RH, Beekwilder JP, Wadman WJ (2012) Differential alterations of synaptic plasticity in dentate gyrus and CA1 hippocampal area of Calbindin-D28K knockout mice. Brain Res 23(1450):1–10
Abrahám H, Veszprémi B, Kravják A, Kovács K, Gömöri E, Seress L (2009) Ontogeny of calbindin immunoreactivity in the human hippocampal formation with a special emphasis on granule cells of the dentate gyrus. Int J Dev Neurosci 27:115–127
Sloviter RS (1989) Calcium-binding protein (calbindin-D28k) and parvalbumin immunocytochemistry: Localization in the rat hippocampus with specific reference to the selective vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to seizure activity. J Comp Neurol 280:183–196
Frantz GD, Tobin AJ (1994) Cellular distribution of calbindin D28K mRNAs in the adult mouse brain. J Neurosci Res 37:287–302
Müller A, Kukley M, Stausberg P, Beck H, Müller W, Dietrich D (2005) Endogenous Ca2+ buffer concentration and Ca2+ microdomains in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 25:558–565
Schwaller B (2010) Cytosolic Ca2+ buffers. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2(11):a004051. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a004051 Epub 2010 Oct 13
Scharfman HE, Schwartzkroin PA (1989) Protection of dentate hilar cells from prolonged stimulation by intracellular calcium chelation. Science 246(4927):257–260
Maglóczky Z, Halász P, Vajda J, Czirják S, Freund TF (1997) Loss of Calbindin-D28K immunoreactivity from dentate granule cells in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 76:377–385
Stefanits H, Wesseling C, Kovacs GG (2014) Loss of Calbindin immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus distinguishes Alzheimer’s disease from other neurodegenerative dementias. Neurosci Lett 566:137–141
Baba A, Yamada MK, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N, Ikegaya Y (2002) Different Ca2+ dynamics between isolated hippocampal pyramidal cells and dentate granule cells. J Neurocytol 31:41–48
AbrahamWC M-PSE, Logan B (1996) Low-frequency stimulation does not readily cause long-term depression or depotentiation in the dentate gyrus of awake rats. Brain Res 722:217–221
Kramar EA, Babayan AH, Gavin CF, Cox CD, Jafari M, Gall CM, Rumbaugh G, Lynch G (2012) Synaptic evidence for the efficacy of spaced learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:5121–5126
Izaki Y, Arita J (1996) Long-term potentiation in the rat hippocampal CA1 region is inhibited selectively at the acquisition stage of discriminatory avoidance learning. Brain Res 723:162–168
Velísek L, Stanton PK, Moshé SL, Vathy I (2000) Prenatal morphine exposure enhances seizure susceptibility but suppresses long-term potentiation in the limbic systemof adult male rats. Brain Res 869:186–193
Pöschel B, Stanton PK (2007) Comparison of cellular mechanisms of long-term depression of synaptic strength at perforant path-granule cell and Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses. Prog Brain Res 163:473–500
Vouimba RM, Richter-Levin G (2005) Physiological dissociation in hippocampal sub-regions in response to amygdala stimulation. Cereb Cortex 15:1815–1821
Vouimba R, Yaniv D, Richter-Levin G (2007) Glucocorticoid receptors and beta-adrenoceptors in BLA modulate synaptic plasticity in hippocampal DG but not in CA1. Neuropharmacology 52:244–252
Akirav I, Richter-Levin G (1999) Biphasic modulation of hippocampal plasticity by behavioral stress and basolateral amygdala stimulation in the rat. J Neurosci 19:10530–10535
Vouimba RM, Richter-Levin G (2013) Different patterns of amygdala priming differentially affect dentate gyrus plasticity and corticosterone, but not CA1 plasticity. Front Neural Circuits 7:80
Tran TT, Srivareerat M, Alhaider IA, Alkadhi KA (2011) Chronic psychosocial stress enhances long-term depression in a subthreshold amyloid-beta rat model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 119:408–416
Alkadhi KA, Tran TT (2014) Chronic psychosocial stress impairs early LTP but not late LTP in the dentate gyrus of at-risk rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1588:150–158
Gerges NZ, Stringer JL, Alkadhi KA (2001) Combination of hypothyroidism and stress abolishes early LTP in the CA1 but not dentate gyrus of hippocampus of adult rats. Brain Res 922:250–260
Alzoubi KH, Aleisa AM, Alkadhi KA (2005) Impairment of long-term potentiation in the CA1, but not dentate gyrus, of the hippocampus in obese Zucker rats: Role of calcineurin and phosphorylated CaMKII. J Mol Neurosci 27:337–346
Pavlides C, Ogawa S, Kimura A, McEwen BS (1996) Role of adrenal steroid mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in long-term potentiation in the CA1 field of hippocampal slices. Brain Res 738:229–235
Xu L, Holscher C, Anwyl R, Rowan MJ (1998) Glucocorticoid receptor and protein/RNA synthesis-dependent mechanisms underlie the control of synaptic plasticity by stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3204–3208
Vouimba RM, Muñoz C, Diamond DM (2006) Differential effects of predator stress and the antidepressant tianeptine on physiological plasticity in the hippocampus and basolateral amygdala. Stress 9:29–40
Bramham CR, Southard T, Ahlers ST, Sarvey JM (1998) Acute cold stress leading to elevated corticosterone neither enhances synaptic efficacy nor impairs LTP in the dentate gyrus of freely moving rats. Brain Res 789:245–255
Yamada K, McEwen BS, Pavlides C (2003) Site and time dependent effects of acute stress on hippocampal long-term potentiation in freely behaving rats. Exp Brain Res 152:52–59
Aleisa AM, Alzoubi KH, Gerges NZ, Alkadhi KA (2006) Nicotine blocks stress-induced impairment of spatial memory and LTP of the hippocampal CA1 region. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9:417–426
Dringenberg HC, Oliveira D, Habib D (2008) Predator (cat hair)-induced enhancement of hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats: Involvement of acetylcholine. Learn Mem 15:112–116
Diamond DM, Bennett MC, Fleshner M, Rose GM (1992) Inverted-U relationship between the level of peripheral corticosterone and the magnitude of hippocampal primed burst potentiation. Hippocampus 2:421–430
Pavlides C, Watanabe Y, McEwen BS (1993) Effects of glucocorticoids on hippocampal long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 3:183–192
Sui L, Ge SY, Ruan DY, Chen JT, Xu YZ, Wang M (2000a) Age-related impairment of long-term depression in area CA1 and dentate gyrus of rat hippocampus following developmental lead exposure in vitro. Neurotoxicol Teratol 22:381–387
Sui L, Ruan DY, Ge SY, Meng XM (2000b) Two components of long-term depression are impaired by chronic lead exposure in area CA1 and dentate gyrus of rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurotoxicol Teratol 22:741–749
Dietz B, Manahan-Vaughan D (2017) Hippocampal long-term depression is facilitated by the acquisition and updating of memory of spatial auditory content and requires mGlu5 activation. Neuropharmacology 115:30–41
Gerges NZ, Aleisa AM, Schwarz LA, Alkadhi KA (2003) Chronic psychosocial stress decreases calcineurin in the dentate gyrus: A possible mechanism for preservation of early LTP. Neuroscience 117:869–874
Alzoubi KH, Aleisa AM, Alkadhi KA (2007) Nicotine prevents disruption of the late phase LTP-related molecular cascade in adult-onset hypothyroidism. Hippocampus 17:654–664
Figueroa-Mendez R, Rivas-Arancibia S (2015) Vitamin C in health and disease: Its role in the metabolism of cells and redox state in the brain. Front Physiol 6:397
Ferreira NR, Lourenco CF, Barbosa RM, Laranjinha J (2015) Coupling of ascorbate and nitric oxide dynamics in vivo in the rat hippocampus upon glutamatergic neuronal stimulation: A novel functional interplay. Brain Res Bull 114:13–19
Suárez I, Bodega G, Fernández B (2002) Glutamine synthetase in brain: Effect of ammonia. Neurochem Int 41:123–142
Nakajima K, Kanamatsu T, Takezawa Y, Kohsaka S (2015) Up-regulation of glutamine synthesis in microglia activated with endotoxin. Neurosci Lett 591:99–104
White BC, Sullivan JM, DeGracia DJ, O’Neil BJ, Neumar RW, Grossman LI, Rafols JA, Krause GS (2000) Brain ischemia and reperfusion: Molecular mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurol Sci 179:1–33
Szatkowski M, Barbour B, Attwell D (1990) Nonvesicular release of glutamate from glial cells by reversed electrogenic glutamate uptake. Nature 348:443–446
Zhang M, Li WB, Liu YX, Liang CJ, Liu LZ, Cui X, Gong JX, Gong SJ et al (2011) High expression of GLT-1 in hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus subfields contributes to their inherent resistance to ischemia in rats. Neurochem Int 59:1019–1028
Setsuie R, Wada K (2007) Functions of UCH-L1 and its relation to neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem Int 51:105–111
Jara JH, Frank DD, Özdinler PH (2013) Could dysregulation of UPS be a common underlying mechanism for cancer and neurodegeneration? Lessons from UCHL. Cell Biochem Biophys 67:45–53
Ferguson SM, De Camilli P (2012) Dynamin, a membrane-remodelling GTPase. Nat Rev Mo Cell Biol 13:75–88
Gubellini P, Bisso GM, Ciofi-Luzzatto A, Fortuna S, Lorenzini P, Michalek H, Scarsella G (1997) Ubiquitin-mediated stress response in a rat model of brain transient ischemia/hypoxia. Neurochem Res 22:93–100
Lee CH, Won MH (2014) Increased dynamin-1 and -2 protein expression in the aged gerbil hippocampus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34:791–796
Lynch MA, Bliss TV (1986) Noradrenaline modulates the release of [14C] glutamate from dentate but not from CA1/CA3 slices of rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 25:493–498
Frey U, Matthies H, Reymann KG, Matthies H (1991) The effect of dopaminergic D1 receptor blockade during tetanization on the expression of long-term potentiation in the rat CA1 region in vitro. Neurosci Lett 129:111–114
Frey U, Schroeder H, Matthies H (1990) Dopaminergic antagonists prevent long-term maintenance of posttetanic LTP in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res 522:69–75
Otmakhova NA, Lisman JE (1996) D1/D5 dopamine receptor activation increases the magnitude of early long-term potentiation at CA1 hippocampal synapses. J Neurosci 16:7478–7486
Otmakhova NA, Lisman JE (1998) D1/D5 dopamine receptors inhibit depotentiation at CA1 synapses via cAMP-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci 18:1270–1279
Kulla A, Manahan-Vaughan D (2000) Depotentiation in the dentate gyrus of freely moving rats is modulated by D1/D5 dopamine receptors. Cereb Cortex 10:614–620
Knox LT, Jing Y, Fleete MS, Collie ND, Zhang H, Liu P (2011) Scopolamine impairs behavioural function and arginine metabolism in the rat dentate gyrus. Neuropharmacology 61:1452–1462
Caine SB, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (1992) Hippocampal modulation of acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:1201–1208
Sato Y, Aoki M (1997) Regional differences in the depressant effects of midazolam on excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 223:181–184
Sato Y, Fujito Y, Aoki M (1997) Differential effects of a benzodiazepine on synaptic transmissions in rat hippocampal neurons in vitro. Brain Res 773:98–107
Kobayashi S, Fujito Y, Matsuyama K, Aoki M (2004) Differential effects of midazolam on inhibitory postsynaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal cells and dentate gyrus granule cells of rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res 1003:176–182
Miller MW (1995) Generation of neurons in the rat dentate gyrus and hippocampus: Effects of prenatal and postnatal treatment with ethanol, alcohol. Clin Exp Res 19:1500–1509
Tran TD, Kelly SJ (2003) Critical periods for ethanol-induced cell loss in the hippocampal formation. Neurotoxicol Teratol 25:519–528
Zhao WF, Ruan DY, Xu YZ, Chen JT, Wang M, Ge SY (1999) The effects of chronic lead exposure on long-term depression in area CA1 and dentate gyrus of rat hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res 818:153–159
Musumeci G, Castrogiovanni P, Castorina S, Imbesi R, Szychlinska MA, Scuderi S, Loreto C, Giunta S. Changes in serotonin (5-HT) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDFN) expression in frontal cortex and hippocampus of aged rat treated with high tryptophan diet. Brain Res Bull 2015; 119(Pt A):12–18.
Hirota K, Roth SH (1997) The effects of sevoflurane on population spikes in CA1 and dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus in vitro. Anesth Analg 85:426–230
Hasegawa Y, Ogiue-Ikeda M, Tanabe N, Kimoto T, Hojo Y, Yamazaki T, Kawato S (2013) Bisphenol A significantly modulates long-term depression in the hippocampus as observed by multi-electrode system. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 34:129–134
Aleisa AM, Helal G, Alhaider IA, Alzoubi KH, Srivareerat M, Tran TT, Al-Rejaie SS, Alkadhi KA (2011a) Acute nicotine treatment prevents REM sleep deprivation-induced learning and memory impairment in rat. Hippocampus 21:899–909
Aleisa AM, Alzoubi KH, Alkadhi KA (2011b) Post-learning REM sleep deprivation impairs long-term memory: Reversal by acute nicotine treatment. Neurosci Lett 499:28–31
Alhaider IA, Aleisa AM, Tran TT, Alzoubi KH, Alkadhi KA (2010) Chronic caffeine treatment prevents sleep deprivation-induced impairment of cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. Sleep 33:437–444
Zagaar M, Alhaider I, Dao A, Levine A, Alkarawi A, Alzubaidy M, Alkadhi K (2012) The beneficial effects of regular exercise on cognition in REM sleep deprivation: Behavioral, electrophysiological and molecular evidence. Neurobiol Dis 45:1153–1162
Zagaar M, Dao A, Alhaider I, Alkadhi K (2013) Regular treadmill exercise prevents sleep deprivation-induced disruption of synaptic plasticity and associated signaling cascade in the dentate gyrus. Mol Cell Neurosci 56:375–383
Raven F, Meerlo P, Van der Zee EA, Abel T, Havekes R. (2018) A brief period of sleep deprivation causes spine loss in the dentate gyrus of mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 (Epub ahead of press)
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239:57–69
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB, Plum F (1982) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol 111:491–498
Smith M, Auer R, Siesjo B (1986) The density and distribution of ischemic brain injury in the rat following 2–10 min forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 64:319–332
Schmidt-Kastner R, Hossmann KA (1988) Distribution of ischemic neuronal damage in the dorsal hippocampus of rat. Acta Neuropathol 76:411–421
Kadar T, Dachir S, Shukitt-Hale B, Levy A (1998) Sub-regional hippocampal vulnerability in various animal models leading to cognitive dysfunction. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 105:987–1004
Ouyang YB, Voloboueva LA, Xu LJ, Giffard RG (2007) Selective dysfunction of hippocampal CA1 astrocytes contributes to delayed neuronal damage after transient forebrain ischemia. J Neurosci 27:4253–4260
Ouyang YB, Xu L, Liu S, Giffard RG (2014) Role of astrocytes in delayed neuronal death: GLT-1 and its novel regulation by microRNAs. Adv Neurobiol 11:171–188
Stary CM (2016) Exploring and exploiting unique properties of the hippocampal dentate gyrus for post-stroke therapy: Astrocytes link ischemic resistance with neurogenic potential. Neural Regen Res 11:1756–1757
Aitken EG, Schiff SJ (1986) Selective neuronal vulnerability to hypoxia in vitro. Neurosci Lett 67:92–96
Kass IS, Lipton P (1986) Calcium and long-term transmission damage following anoxia in dentate gyrus and CAI regions of the rat hippocampal slice. J Physiol Lond 378:313–334
Choi DW (1990) Cerebral hypoxia: Some new approaches and unanswered questions. J Neurosci 10:2493–2501
Mitani A, Yanase H, Sakai K, Wake Y, Kataoka K (1993) Origin of intracellular Ca2+ elevation induced by in vitro ischemia-like condition in hippocampal slices. Brain Res 601:103–110
Shimizu H, Mizuguchi A, Aoki M (1996) Differential responses between CA1 pyramidal cells and granule cells to ischemic insult in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett 203:195–198
Li Y, Zhu X, Ju S, Yan J, Wang D, Zhu Y, Zang F (2017) Detection of volume alterations in hippocampal subfields of rats under chronic unpredictable mild stress using 7T MRI: A follow-up study. J Magn Reson Imaging 46:1456–1463
Gerges NZ, Alzoubi KH, Park CR, Diamond MD, Alkadhi KA (2004) Adverse effect of the combination of hypothyroidism and chronic psychosocial stress on hippocampus-dependent memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 155(1):77–84
Alzoubi KH, Aleisa AM, Gerges NZ, Alkadhi KA (2006) Nicotine reverses adult-onset hypothyroidism-induced impairment of learning and memory: Behavioral and electrophysiological studies. J Neurosci Res 84:944–453
Alzoubi KH, Gerges NZ, Aleisa AM, Alkadhi KA (2009) Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism-induced impairment of hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: Behavioral, electrophysiological, and molecular studies. Hippocampus 19:66–78
Sánchez-Huerta K, Pacheco-Rosado J, Gilbert ME (2015) Adult onset-hypothyroidism: Alterations in hippocampal field potentials in the dentate gyrus are largely associated with anaesthesia-induced hypothermia. J Neuroendocrinol 27:8–19
Fernandez-Lamo I, Montero-Pedrazuela A, Delgado-Garcia JM, Guadano-Ferraz A, Gruart A (2009) Effects of thyroid hormone replacement on associative learning and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in adult hypothyroid rats. Eur J Neurosci 30:679–692
Artis AS, Bitiktas S, Taskin E, Dolu N, Liman N, Suer C (2012) Experimental hypothyroidism delays field excitatory post-synaptic potentials and disrupts hippocampal long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation and Y-maze performance in adult rats. J Neuroendocrinol 24:422–433
Kerchner GA, Deutsch GK, Zeineh M, Dougherty RF, Saranathan M, Rutt BK (2012) Hippocampal CA1 apical neuropil atrophy and memory performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 63:194–202
Dao AT, Zagaar MA, Levine AT, Salim S, Eriksen JL, Alkadhi KA (2013) Treadmill exercise prevents learning and memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology. Curr Alzheimer Res 10:507–515
Hwang LL, Wang CH, Li TL, Chang SD, Lin LC, Chen CP, Chen CT, Liang KC et al (2010) Sex differences in high-fat diet-induced obesity, metabolic alterations and learning, and synaptic plasticity deficits in mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18:463–469
Porter D, Faivre E, Flatt PR, Hölscher C, Gault VA (2012) Actions of incretin metabolites on locomotor activity, cognitive function and in vivo hippocampal synaptic plasticity in high fat fed mice. Peptides 35:1–8
Lennox R, Porter DW, Flatt PR, Holscher C, Irwin N, Gault VA (2014) Comparison of the independent and combined effects of sub-chronic therapy with metformin and a stable GLP-1 receptor agonist on cognitive function, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and metabolic control in high-fat fed mice. Neuropharmacology 86:22–30
Pathak NM, Pathak V, Lynch AM, Irwin N, Gault VA, Flatt PR (2015) Stable oxyntomodulin analogues exert positive effects on hippocampal neurogenesis and gene expression as well as improving glucose homeostasis in high fat fed mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 412:95–103
Hao S, Dey A, Yu X, Stranahan AM (2016) Dietary obesity reversibly induces synaptic stripping by microglia and impairs hippocampal plasticity. Brain Behav Immun 51:230–239
Asadbegi M, Komaki A, Salehi I, Yaghmaei P, Ebrahim-Habibi A, Shahidi S, Sarihi A, Soleimani Asl S et al (2018) Effects of thymol on amyloid-β-induced impairments in hippocampal synaptic plasticity in rats fed a high-fat diet. Brain Res Bull 137:338–350
Foster TC (2002) Regulation of synaptic plasticity in memory and memory decline with aging. Prog Brain Res 138:283–303
Patrylo PR, Williamson A (2007) The effects of aging on dentate circuitry and function. Prog Brain Res 163:679–696
Rosenzweig ES, Barnes CA (2003) Impact of aging on hippocampal function: Plasticity, network dynamics, and cognition. Prog Neurobiol 69:143–179
Mattson MP, Wan R (2005) Beneficial effects of intermittent fasting and caloric restriction on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems. J Nutr Biochem 16:129–137
Greene JG, Borges K, Dingledine R (2009) Quantitative transcriptional neuroanatomy of the rat hippocampus: Evidence for wide-ranging, pathway-specific heterogeneity among three principal cell layers. Hippocampus 19:253–264
Zeier Z, Madorsky I, Xu Y, Ogle WO, Notterpek L, Foster TC (2011) Gene expression in the hippocampus: Regionally specific effects of aging and caloric restriction. Mech Ageing Dev 132:8–19
Funding
This work is supported by the Department of Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy as well as various internal grants (SGPs) from the University of Houston.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial Disclosure
The author declares no direct or indirect financial or personal relationships, interests, and affiliations relevant to the subject matter of the manuscript have occurred over the last 2 years, and none expected in the foreseeable future.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkadhi, K.A. Cellular and Molecular Differences Between Area CA1 and the Dentate Gyrus of the Hippocampus. Mol Neurobiol 56, 6566–6580 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1541-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1541-2