Abstract
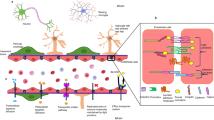
Immune stimulation might be involved in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder (MDD). This stimulation induces indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), an enzyme that reduces the tryptophan bioavailability to synthesize serotonin. IDO products, kynurenine metabolites, exert neurotoxic/neuroprotective actions through glutamate receptors. Thus, we study elements of these pathways linked to kynurenine metabolite activity examining whether antidepressants (ADs) can modulate them. Male Wistar rats were exposed to chronic mild stress (CMS), and some of them were treated with ADs. The expression of elements of the IDO pathway, including kynurenine metabolites, and their possible modulation by ADs was studied in the frontal cortex (FC). CMS increased IDO expression in FC compared to control group, and ADs restored the IDO expression levels to control values. CMS-induced IDO expression led to increased levels of the excitotoxic quinolinic acid (QUINA) compared to control, and ADs prevented the rise in such levels. Neither CMS nor ADs changed significantly the antiexcitotoxic kynurenic acid (KYNA) levels. The QUINA/KYNA ratio, calculated as excitotoxicity risk indicator, increased after CMS and ADs prevented this increase. CMS lowered excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)-1 and EAAT-4 expression, and some ADs restored their expression levels. Furthermore, CMS decreased N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR)-2A and 2B protein expression, and ADs mitigated this decrease. Our research examines the link between CMS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines and the kynurenine pathway; it shows that CMS alters the kynurenine pathway in rat FC. Importantly, it also reveals the ability of classic ADs to prevent potentially harmful situations related to the brain scenario caused by CMS.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcus M, Yasamy MT, van Ommeren M, Chisholm D (2012) Depression, a global public health concern. WHO Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse, pp 1–8
Global Burden of Disease Study C (2015) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 386(9995):743–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4
Disease GBD, Injury I, Prevalence C (2016) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388(10053):1545–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6
Berton O, Nestler EJ (2006) New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(2):137–151. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1846
Mrazek DA, Hornberger JC, Altar CA, Degtiar I (2014) A review of the clinical, economic, and societal burden of treatment-resistant depression: 1996–2013. Psychiatr Serv 65(8):977–987. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201300059
Miller AH, Raison CL (2016) The role of inflammation in depression: from evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat Rev Immunol 16(1):22–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2015.5
O'Connor JC, Andre C, Wang Y, Lawson MA, Szegedi SS, Lestage J, Castanon N, Kelley KW et al (2009) Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediate the upregulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and the induction of depressive-like behavior in mice in response to bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J Neurosci 29(13):4200–4209. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5032-08.2009
Raison CL, Dantzer R, Kelley KW, Lawson MA, Woolwine BJ, Vogt G, Spivey JR, Saito K et al (2010) CSF concentrations of brain tryptophan and kynurenines during immune stimulation with IFN-alpha: relationship to CNS immune responses and depression. Mol Psychiatry 15(4):393–403. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2009.116
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Lawson MA, Kelley KW (2011) Inflammation-associated depression: from serotonin to kynurenine. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36(3):426–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.09.012
Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47(4):351–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00230-9
Kutsuwada T, Kashiwabuchi N, Mori H, Sakimura K, Kushiya E, Araki K, Meguro H, Masaki H et al (1992) Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature 358(6381):36–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/358036a0
Monyer H, Sprengel R, Schoepfer R, Herb A, Higuchi M, Lomeli H, Burnashev N, Sakmann B et al (1992) Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes. Science 256(5060):1217–1221. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.256.5060.1217
Liu T, Zhong S, Liao X, Chen J, He T, Lai S, Jia Y (2015) A meta-analysis of oxidative stress markers in depression. PLoS One 10(10):e0138904. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138904
Martin-Hernandez D, Bris AG, MacDowell KS, Garcia-Bueno B, Madrigal JL, Leza JC, Caso JR (2016) Modulation of the antioxidant nuclear factor (erythroid 2-derived)-like 2 pathway by antidepressants in rats. Neuropharmacology 103:79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.11.029
O'Donovan SM, Sullivan CR, McCullumsmith RE (2017) The role of glutamate transporters in the pathophysiology of neuropsychiatric disorders. NPJ Schizophr 3(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-017-0037-1
Murrough JW, Abdallah CG, Mathew SJ (2017) Targeting glutamate signalling in depression: progress and prospects. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(7):472–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2017.16
Hill MN, Hellemans KG, Verma P, Gorzalka BB, Weinberg J (2012) Neurobiology of chronic mild stress: parallels to major depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(9):2085–2117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.07.001
Patricio P, Mateus-Pinheiro A, Irmler M, Alves ND, Machado-Santos AR, Morais M, Correia JS, Korostynski M et al (2015) Differential and converging molecular mechanisms of antidepressants’ action in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neuropsychopharmacology 40(2):338–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.176
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1(2):94–99. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.72351
Willner P (2005) Chronic mild stress (CMS) revisited: consistency and behavioural-neurobiological concordance in the effects of CMS. Neuropsychobiology 52(2):90–110. https://doi.org/10.1159/000087097
Bravo L, Mico JA, Rey-Brea R, Perez-Nievas B, Leza JC, Berrocoso E (2012) Depressive-like states heighten the aversion to painful stimuli in a rat model of comorbid chronic pain and depression. Anesthesiology 117(3):613–625. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182657b3e
Martin-Hernandez D, Caso JR, Bris AG, Maus SR, Madrigal JL, Garcia-Bueno B, MacDowell KS, Alou L et al (2016) Bacterial translocation affects intracellular neuroinflammatory pathways in a depression-like model in rats. Neuropharmacology 103:122–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.12.003
Kusmider M, Solich J, Palach P, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M (2007) Effect of citalopram in the modified forced swim test in rats. Pharmacol Rep 59(6):785–788
Reneric JP, Lucki I (1998) Antidepressant behavioral effects by dual inhibition of monoamine reuptake in the rat forced swimming test. Psychopharmacology 136(2):190–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050555
Garate I, Garcia-Bueno B, Madrigal JL, Bravo L, Berrocoso E, Caso JR, Mico JA, Leza JC (2011) Origin and consequences of brain Toll-like receptor 4 pathway stimulation in an experimental model of depression. J Neuroinflammation 8:151. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-8-151
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40(15):e115. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks596
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Pringle TH, Zahler AM, Haussler D (2002) The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 12(6):996–1006. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.229102
Savitz J, Drevets WC, Wurfel BE, Ford BN, Bellgowan PS, Victor TA, Bodurka J, Teague TK et al (2015) Reduction of kynurenic acid to quinolinic acid ratio in both the depressed and remitted phases of major depressive disorder. Brain Behav Immun 46:55–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.02.007
Dang YH, Ma XC, Zhang JC, Ren Q, Wu J, Gao CG, Hashimoto K (2014) Targeting of NMDA receptors in the treatment of major depression. Curr Pharm Des 20(32):5151–5159. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612819666140110120435
Liu YN, Peng YL, Liu L, Wu TY, Zhang Y, Lian YJ, Yang YY, Kelley KW et al (2015) TNFalpha mediates stress-induced depression by upregulating indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in a mouse model of unpredictable chronic mild stress. Eur Cytokine Netw 26(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1684/ecn.2015.0362
Ruddick JP, Evans AK, Nutt DJ, Lightman SL, Rook GA, Lowry CA (2006) Tryptophan metabolism in the central nervous system: medical implications. Expert Rev Mol Med 8(20):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1462399406000068
Sekine A, Kuroki Y, Urata T, Mori N, Fukuwatari T (2016) Inhibition of large neutral amino acid transporters suppresses kynurenic acid production via inhibition of kynurenine uptake in rodent brain. Neurochem Res 41(9):2256–2266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1940-y
Babcock TA, Carlin JM (2000) Transcriptional activation of indoleamine dioxygenase by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in interferon-treated epithelial cells. Cytokine 12:588–594. https://doi.org/10.1006/cyto.1999.0661
Capuron L, Ravaud A, Neveu PJ, Miller AH, Maes M, Dantzer R (2002) Association between decreased serum tryptophan concentrations and depressive symptoms in cancer patients undergoing cytokine therapy. Mol Psychiatry 7:468–473. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000995
Garcia-Bueno B, Caso JR, Perez-Nievas BG, Lorenzo P, Leza JC (2007) Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists on brain glucose and glutamate transporters after stress in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(6):1251–1260. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301252
Madrigal JL, Caso JR, de Cristobal J, Cardenas A, Leza JC, Lizasoain I, Lorenzo P, Moro MA (2003) Effect of subacute and chronic immobilisation stress on the outcome of permanent focal cerebral ischaemia in rats. Brain Res 979(1–2):137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(03)02892-0
Choudary PV, Molnar M, Evans SJ, Tomita H, Li JZ, Vawter MP, Myers RM, Bunney WE Jr et al (2005) Altered cortical glutamatergic and GABAergic signal transmission with glial involvement in depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15653–15658. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507901102
Zink M, Vollmayr B, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Henn FA (2010) Reduced expression of glutamate transporters vGluT1, EAAT2 and EAAT4 in learned helpless rats, an animal model of depression. Neuropharmacology 58(2):465–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.09.005
Zhang XH, Jia N, Zhao XY, Tang GK, Guan LX, Wang D, Sun HL, Li H et al (2013) Involvement of pGluR1, EAAT2 and EAAT3 in offspring depression induced by prenatal stress. Neuroscience 250:333–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.04.031
Golembiowska K, Dziubina A (2000) Effect of acute and chronic administration of citalopram on glutamate and aspartate release in the rat prefrontal cortex. Pol J Pharmacol 52(6):441–448
Lin TY, Yang TT, Lu CW, Wang SJ (2011) Inhibition of glutamate release by bupropion in rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(2):598–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.12.029
Musazzi L, Milanese M, Farisello P, Zappettini S, Tardito D, Barbiero VS, Bonifacino T, Mallei A et al (2010) Acute stress increases depolarization-evoked glutamate release in the rat prefrontal/frontal cortex: the dampening action of antidepressants. PLoS One 5(1):e8566. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008566
Sanacora G, Treccani G, Popoli M (2012) Towards a glutamate hypothesis of depression: an emerging frontier of neuropsychopharmacology for mood disorders. Neuropharmacology 62(1):63–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.036
Hashimoto K, Sawa A, Iyo M (2007) Increased levels of glutamate in brains from patients with mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 62(11):1310–1316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.03.017
Lou JS, Li CY, Yang XC, Fang J, Yang YX, Guo JY (2010) Protective effect of gan mai da zao decoction in unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced behavioral and biochemical alterations. Pharm Biol 48(12):1328–1336. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880201003789440
Feyissa AM, Chandran A, Stockmeier CA, Karolewicz B (2009) Reduced levels of NR2A and NR2B subunits of NMDA receptor and PSD-95 in the prefrontal cortex in major depression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33(1):70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.10.005
Ampuero E, Rubio FJ, Falcon R, Sandoval M, Diaz-Veliz G, Gonzalez RE, Earle N, Dagnino-Subiabre A et al (2010) Chronic fluoxetine treatment induces structural plasticity and selective changes in glutamate receptor subunits in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 169(1):98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.04.035
Erburu M, Munoz-Cobo I, Diaz-Perdigon T, Mellini P, Suzuki T, Puerta E, Tordera RM (2017) SIRT2 inhibition modulate glutamate and serotonin systems in the prefrontal cortex and induces antidepressant-like action. Neuropharmacology 117:195–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.033
Burgdorf J, Zhang XL, Nicholson KL, Balster RL, Leander JD, Stanton PK, Gross AL, Kroes RA et al (2013) GLYX-13, a NMDA receptor glycine-site functional partial agonist, induces antidepressant-like effects without ketamine-like side effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(5):729–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.246
Zanos P, Moaddel R, Morris PJ, Georgiou P, Fischell J, Elmer GI, Alkondon M, Yuan P et al (2016) NMDAR inhibition-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolites. Nature 533(7604):481–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17998
Toth E, Gersner R, Wilf-Yarkoni A, Raizel H, Dar DE, Richter-Levin G, Levit O, Zangen A (2008) Age-dependent effects of chronic stress on brain plasticity and depressive behavior. J Neurochem 107(2):522–532. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05642.x
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI13/01102) and Fondos Europeos de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) and the Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad (MINECO; SAF2016-75500-R), and CIBERSAM to JCL, including an Intramural Translational Project awarded to JRC from the CIBERSAM (SAM15PINT1514). BGB and JRC are postdoctoral Ramón y Cajal fellows (MINECO). HTB was funded by the CONACYT (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología, Mexico).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors provide full disclosure of any and all biomedical financial interests.
The authors declare that there are not conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Dr. Javier R. Caso is the first corresponding author and Dr. Juan C.Leza is the co-corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martín-Hernández, D., Tendilla-Beltrán, H., Madrigal, J.L.M. et al. Chronic Mild Stress Alters Kynurenine Pathways Changing the Glutamate Neurotransmission in Frontal Cortex of Rats. Mol Neurobiol 56, 490–501 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1096-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1096-7