Abstract
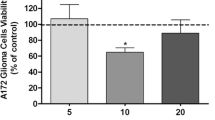
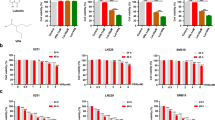
Glioblastoma multiform (GBM) is a primary malignant brain tumor with a few therapeutic targets available for it. The interaction between the immune system and glioma is an important factor that could lead to novel therapeutic approaches to fight glioma. In this study, we investigated in vitro anti-inflammatory and apoptotic activity of atorvastatin in different concentrations 1, 5, and 10 μM on glioma spheroid cells cultured in a three-dimensional model in fibrin gel that indicate the complex in vivo microenvironment better than a simple two-dimensional cell culture. A mechanistic insight into the role of IL-17RA, TRAF3IP2, and apoptotic genes in progression of glioma could provide an important way for therapy of malignant tumors with manipulation of this inflammatory axis. To reach for these aims, after 24 and 48 h exposure with different concentrations of atorvastatin, caspase-8, caspase-3, Bcl-2, TRAF3IP2, and IL-17RA gene expression were assayed. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay and cell cycle assay were used for evaluating the cell apoptosis and proliferation. The results showed that atorvastatin has anti-inflammatory and apoptotic effects against glioma spheroids. Atorvastatin induced the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-8 and downregulated the expression of Bcl-2, TRAF3IP2, and IL-17RA especially at 10 μM concentration. These effects are dose dependent. The most likely mechanisms are the inhibition of inflammation by IL-17RA interaction with TRAF3IP2 and NF-κB signaling pathway. Finally, these results suggest that atorvastatin could be used as an anti-cancer agent for glioblastoma treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
06 May 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Galvão RP, Zong H (2013) Inflammation and gliomagenesis: bi-directional communication at early and late stages of tumor progression. Curr Pathobiology Reports 1(1):19–28
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL et al (2007) Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21(21):2683–2710
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A (2009) Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 30(7):1073–1081
Sciume G, Santoni A and Bernardini G (2010) Chemokines and glioma: invasion and more. J Neuroimmunol 224(1–2):8–12
Yeung YT, McDonald KL, Grewal T, Munoz L (2013) Interleukins in glioblastoma pathophysiology: implications for therapy. Br J Pharmacol 168(3):591–606
Bhat KP, Balasubramaniyan V, Vaillant B, Ezhilarasan R, Hummelink K, Hollingsworth F, Wani K, Heathcock L et al (2013) Mesenchymal differentiation mediated by NF-kappaB promotes radiation resistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 24(3):331–346
Guo J, Shinriki S, Su Y, Nakamura T, Hayashi M, Tsuda Y, Murakami Y, Tasaki M et al (2014) Hypoxia suppresses cylindromatosis (CYLD) expression to promote inflammation in glioblastoma: possible link to acquired resistance to anti-VEGF therapy. Oncotarget 5(15):6353–6364
Barcellos-Hoff MH, Newcomb EW, Zagzag D, Narayana A (2009) Therapeutic targets in malignant glioblastoma microenvironment. Semin Radiat Oncol 19(3):163–170
Anderson JC, McFarland BC, Gladson CL (2008) New molecular targets in angiogenic vessels of glioblastoma tumours. Expert Rev Mol Med 10:e23
Daugherty SE, Moore SC, Pfeiffer RM, Inskip PD, Park Y, Hollenbeck A, Rajaraman P (2011) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glioma in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Cancer Prev Res 4(12):2027–2034
Riad A, Du J, Stiehl S, Westermann D, Mohr Z, Sobirey M, Doehner W, Adams V et al (2007) Low-dose treatment with atorvastatin leads to anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharmacol 569(3):204–211
Jain MK, Ridker PM (2005) Anti-inflammatory effects of statins: clinical evidence and basic mechanisms. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(12):977–987
Blanco-Colio LM, Tuñón J, Martín-Ventura JL, Egido J (2003) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of statins. Kidney Int 63(1):12–23
Gómez-Gerique JA, Ros E, Oliván J, Mostaza JM, Vilardell M, Pintó X, Civeira F, Hernández A et al (2002) Effect of atorvastatin and bezafibrate on plasma levels of C-reactive protein in combined (mixed) hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis 162(2):245–251
Ferro D, Parrotto S, Basili S, Alessandri C, Violi F (2000) Simvastatin inhibits the monocyte expression of proinflammatory cytokines in patients with hypercholesterolemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 36(2):427–431
Stanislaus R, Gilg AG, Singh AK, Singh I (2002) Immunomodulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rats by Lovastatin. Neurosci Lett 333(3):167–170
Antonopoulos AS, Margaritis M, Lee R, Channon K, Antoniades C (2012) Statins as anti-inflammatory agents in atherogenesis: molecular mechanisms and lessons from the recent clinical trials. Curr Pharm Des 18(11):1519–1530
Onishi RM, Gaffen SL (2010) Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease. Immunology 129(3):311–321
Miossec P (2009) IL-17 and Th17 cells in human inflammatory diseases. Microbes Infect 11(5):625–630
Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE (2007) IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol 25:821–852
Hwang SY, Kim JY, Kim KW, Park MK, Moon Y, Kim WU, Kim HY (2004) IL-17 induces production of IL-6 and IL-8 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via NF-κB-and PI3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathways. Arthritis Res Ther 6(2):1
Gu C, Wu L, Li X (2013) IL-17 family: cytokines, receptors and signaling. Cytokine 64(2):477–485
Li X, Commane M, Nie H, Hua X, Chatterjee-Kishore M, Wald D, Haag M, Stark GR (2000) Act1, an NF-κB-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(19):10489–10493
Ellinghaus E, Ellinghaus D, Stuart PE, Nair RP, Debrus S, Raelson JV, Belouchi M, Fournier H et al (2010) Genome-wide association study identifies a psoriasis susceptibility locus at TRAF3IP2. Nat Genet 42(11):991–995
Jiang P, Mukthavaram R, Chao Y, Nomura N, Bharati IS, Fogal V, Pastorino S, Teng D et al (2014) In vitro and in vivo anticancer effects of mevalonate pathway modulation on human cancer cells. Br J Cancer 111(8):1562–1571
Altwairgi AK (2015) Statins are potential anticancerous agents (review). Oncol Rep 33(3):1019–1039
Wu XD, Zeng K, Xue FQ, Chen JH, Chen YQ (2013) Statins are associated with reduced risk of gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69(10):1855–1860
Tapia-Pérez JH, Kirches E, Mawrin C, Firsching R, Schneider T (2011) Cytotoxic effect of different statins and thiazolidinediones on malignant glioma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67(5):1193–1201
Nielsen SF, Nordestgaard BG, Bojesen SE (2012) Statin use and reduced cancer-related mortality. N Engl J Med 367(19):1792–1802
Zhang Z, Li C, Shang L, Zhang Y, Zou R, Zhan Y, Bi B (2016) Sulforaphane induces apoptosis and inhibits invasion in U251MG glioblastoma cells. Springerplus 5(235):016–1910
Xu X, Farach-Carson MC, Jia X (2014) Three-dimensional in vitro tumor models for cancer research and drug evaluation. Biotechnol Adv 32(7):1256–1268
Kula M, Tanriverdi G, Oksuz E, Bilir A, Shahzadi A, Yazici Z (2014) Simvastatin and dexamethasone potentiate antitumor activity of fotemustine. Int J Pharmacol 10(5):267–274
Obara S, Nakata M, Takeshima H, Kuratsu JI, Maruyama I, Kitajima I (2002) Inhibition of migration of human glioblastoma cells by cerivastatin in association with focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Cancer Lett 185(2):153–161
Takahashi HK, Nishibori M (2007) The antitumour activities of statins. Curr Oncol 14(6):246
Hindler K, Cleeland CS, Rivera E, Collard CD (2006) The role of statins in cancer therapy. Oncologist 11(3):306–315
Wang G, Dinkins M, He Q, Zhu G, Poirier C, Campbell A, Mayer-Proschel M, Bieberich E (2012) Astrocytes secrete exosomes enriched with proapoptotic ceramide and prostate apoptosis response 4 (PAR-4) potential mechanism of apoptosis induction in Alzheimer disease (AD). J Biol Chem 287(25):21384–21395
Fromigué O, Hamidouche Z, Marie PJ (2008) Blockade of the RhoA-JNK-c-Jun-MMP2 cascade by atorvastatin reduces osteosarcoma cell invasion. J Biol Chem 283(45):30549–30556
Gray GK, McFarland BC, Nozell SE, Benveniste EN (2014) NF-kappaB and STAT3 in glioblastoma: therapeutic targets coming of age. Expert Rev Neurother 14(11):1293–1306
McFarland BC, Gray GK, Nozell SE, Hong SW, Benveniste EN (2013) Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by the STAT3 inhibitor JSI-124 in human glioblastoma cells. Mol Cancer Res 11(5):494–505
Wood WG, Igbavboa U, Muller WE, Eckert GP (2013) Statins, Bcl-2, and apoptosis: cell death or cell protection? Mol Neurobiol 48(2):308–314
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS, Liang J (2005) Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 37(11):719–727
Sarma JD, Ciric B, Marek R, Sadhukhan S, Caruso ML et al (2009) Functional interleukin-17 receptor A is expressed in central nervous system glia and upregulated in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation 6:14
Parajuli P, Mittal S (2013) Role of IL-17 in glioma progression. J Spine Neurosurg 1:1–4
Parajuli P, Anand R, Mandalaparty C, Suryadevara R, Sriranga PU et al (2016) Preferential expression of functional IL-17R in glioma stem cells: potential role in self-renewal. Oncotarget 7(5):6121
Yang B, Kang H, Fung A, Zhao H, Wang T, Ma D (2014) The role of interleukin 17 in tumour proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Mediat Inflamm 1:1–12
Tabarkiewicz J, Pogoda K, Karczmarczyk A, Pozarowski P, Giannopoulos K (2015) The role of IL-17 and Th17 lymphocytes in autoimmune diseases. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 63(6):435–449
Wang K, Kim MK, Di Caro G, Wong J, Shalapour S, Wan J, Zhang W, Zhong Z et al (2014) Interleukin-17 receptor a signaling in transformed enterocytes promotes early colorectal tumorigenesis. Immunity 41(6):1052–1063
Hunter CA (2007) Act1-ivating IL-17 inflammation. Nat Immunol 8(3):232–234
Valente AJ, Sakamuri SS, Siddesha JM, Yoshida T, Gardner JD, Prabhu R, Siebenlist U, Chandrasekar B (2013) TRAF3IP2 mediates interleukin-18-induced cardiac fibroblast migration and differentiation. Cell Signal 25(11):2176–2184
Venkatesan B, Valente AJ, Das NA, Carpenter AJ, Yoshida T, Delafontaine JL, Siebenlist U, Chandrasekar B (2013) CIKS (Act1 or TRAF3IP2) mediates high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction. Cell Signal 25(1):359–371
Valente AJ, Irimpen AM, Siebenlist U, Chandrasekar B (2014) OxLDL induces endothelial dysfunction and death via TRAF3IP2: inhibition by HDL3 and AMPK activators. Free Radic Biol Med 70:117–128
Gaffen SL (2009) Structure and signaling in the IL-17 receptor superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol 9(8):556–567
Acknowledgments
We thank the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) for the financial support (grant number 93051217) and Tehran University of Medical Sciences for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Dr. Jafar Ai is the first corresponding author.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0577-4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayat, N., Ebrahimi-Barough, S., Norouzi-Javidan, A. et al. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Atorvastatin by Suppressing TRAF3IP2 and IL-17RA in Human Glioblastoma Spheroids Cultured in a Three-dimensional Model: Possible Relevance to Glioblastoma Treatment. Mol Neurobiol 55, 2102–2110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0445-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0445-2