Abstract
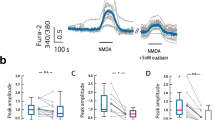
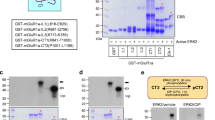
NMDA receptors play a crucial role in regulating synaptic plasticity and memory. Activation of NMDA receptors changes intracellular concentrations of Na+ and K+, which are subsequently restored by Na/K-ATPase. We used immunochemical and biochemical methods to elucidate the potential mechanisms of interaction between these two proteins. We observed that NMDA receptor and Na/K-ATPase interact with each other and this interaction was shown for both isoforms of α subunit (α1 and α3) of Na/K-ATPase expressed in neurons. Using Western blotting, we showed that long-term exposure of the primary culture of cerebellar neurons to nanomolar concentrations of ouabain (a cardiotonic steroid, a specific ligand of Na/K-ATPase) leads to a decrease in the levels of NMDA receptors which is likely mediated by the α3 subunit of Na/K-ATPase. We also observed a decrease in enzymatic activity of the α1 subunit of Na/K-ATPase caused by NMDA receptor activation. This effect is mediated by an increase in intracellular Ca2+. Thus, Na/K-ATPase and NMDA receptor can interact functionally by forming a macromolecular complex which can be important for restoring ionic balance after neuronal excitation. Furthermore, this interaction suggests that NMDA receptor function can be regulated by endogenous cardiotonic steroids which recently have been found in cerebrospinal fluid or by pharmacological drugs affecting Na/K-ATPase function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skou JC, Esmann M (1992) The Na, K-ATPase. J Bioenerg Biomembr 24(3):249–261
Erecinska M, Silver IA (1994) Ions and energy in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol 43(1):37–71
Dobretsov M, Stimers JR (2005) Neuronal function and alpha3 isoform of the Na/K-ATPase. Front Biosci: J Virtual Libr 10:2373–2396
Lingrel JB, Williams MT, Vorhees CV, Moseley AE (2007) Na, K-ATPase and the role of alpha isoforms in behavior. J Bioenerg Biomembr 39(5–6):385–389. doi:10.1007/s10863-007-9107-9
de Carvalho AP, Sweadner KJ, Penniston JT, Zaremba J, Liu L, Caton M, Linazasoro G, Borg M, Tijssen MA, Bressman SB, Dobyns WB, Brashear A, Ozelius LJ (2004) Mutations in the Na+/K + −ATPase alpha3 gene ATP1A3 are associated with rapid-onset dystonia parkinsonism. Neuron 43(2):169–175. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.06.028
Rosewich H, Thiele H, Ohlenbusch A, Maschke U, Altmuller J, Frommolt P, Zirn B, Ebinger F, Siemes H, Nurnberg P, Brockmann K, Gartner J (2012) Heterozygous de-novo mutations in ATP1A3 in patients with alternating hemiplegia of childhood: a whole-exome sequencing gene-identification study. Lancet Neurol 11(9):764–773. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70182-5
Kometiani P, Li J, Gnudi L, Kahn BB, Askari A, Xie Z (1998) Multiple signal transduction pathways link Na+/K + −ATPase to growth-related genes in cardiac myocytes. The roles of Ras and mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem 273(24):15249–15256
Antolovic R, Bauer N, Mohadjerani M, Kost H, Neu H, Kirch U, Grunbaum EG, Schoner W (2000) Endogenous ouabain and its binding globulin: effects of physical exercise and study on the globulin’s tissue distribution. Hypertens Res: Off J Japan Soc Hypertens 23(Suppl):S93–S98
Schoner W (2002) Endogenous cardiac glycosides, a new class of steroid hormones. Eur J Biochem / FEBS 269(10):2440–2448
Xie Z, Kometiani P, Liu J, Li J, Shapiro JI, Askari A (1999) Intracellular reactive oxygen species mediate the linkage of Na+/K + −ATPase to hypertrophy and its marker genes in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 274(27):19323–19328
Aizman O, Uhlen P, Lal M, Brismar H, Aperia A (2001) Ouabain, a steroid hormone that signals with slow calcium oscillations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(23):13420–13424. doi:10.1073/pnas.221315298
Yuan Z, Cai T, Tian J, Ivanov AV, Giovannucci DR, Xie Z (2005) Na/K-ATPase tethers phospholipase C and IP3 receptor into a calcium-regulatory complex. Mol Biol Cell 16(9):4034–4045. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-04-0295
Xie Z, Cai T (2003) Na + −K + −−ATPase-mediated signal transduction: from protein interaction to cellular function. Mol Interv 3(3):157–168. doi:10.1124/mi.3.3.157
Bulygina ER, Lyapina LY, Boldyrev AA (2002) Activation of glutamate receptors inhibits Na/K-ATPase of cerebellum granule cells. Biochem Biokhim 67(9):1001–1005
Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF (1999) The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 51(1):7–61
VanDongen AM (2009) Biology of the NMDA receptor. Frontiers in neuroscience. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Stelmashook EV, Weih M, Zorov D, Victorov I, Dirnagl U, Isaev N (1999) Short-term block of Na+/K + −ATPase in neuro-glial cell cultures of cerebellum induces glutamate dependent damage of granule cells. FEBS Lett 456(1):41–44
Reines A, Pena C, de Rodriguez LAG (2001) [3H]dizocilpine binding to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor is modulated by an endogenous Na+, K + −ATPase inhibitor. Comparison with ouabain. Neurochem Int 39(4):301–310
Bersier MG, Miksztowicz V, Pena C, de Lores RAG (2005) Modulation of aspartate release by ascorbic acid and endobain E, an endogenous Na+, K + −ATPase inhibitor. Neurochem Res 30(4):479–486
Bersier MG, Pena C, de Lores RAG (2008) The expression of NMDA receptor subunits in cerebral cortex and hippocampus is differentially increased by administration of endobain E, a Na+, K + −ATPase inhibitor. Neurochem Res 33(1):66–72. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9412-z
Moseley AE, Williams MT, Schaefer TL, Bohanan CS, Neumann JC, Behbehani MM, Vorhees CV, Lingrel JB (2007) Deficiency in Na, K-ATPase alpha isoform genes alters spatial learning, motor activity, and anxiety in mice. J Neurosci 27(3):616–626. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI. 4464-06.2007
Husi H, Ward MA, Choudhary JS, Blackstock WP, Grant SG (2000) Proteomic analysis of NMDA receptor-adhesion protein signaling complexes. Nat Neurosci 3(7):661–669. doi:10.1038/76615
Blom H, Ronnlund D, Scott L, Spicarova Z, Widengren J, Bondar A, Aperia A, Brismar H (2011) Spatial distribution of Na + −K + −ATPase in dendritic spines dissected by nanoscale superresolution STED microscopy. BMC Neurosci 12:16. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-12-16
Yudowski GA, Efendiev R, Pedemonte CH, Katz AI, Berggren PO, Bertorello AM (2000) Phosphoinositide-3 kinase binds to a proline-rich motif in the Na+, K + −ATPase alpha subunit and regulates its trafficking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(12):6556–6561. doi:10.1073/pnas.100128297
Liu L, Zhao X, Pierre SV, Askari A (2007) Association of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway with digitalis-induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293(5):C1489–C1497. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00158.2007
Zampar GG, Chesta ME, Carbajal A, Chanaday NL, Diaz NM, Casale CH, Arce CA (2009) Acetylated tubulin associates with the fifth cytoplasmic domain of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase: possible anchorage site of microtubules to the plasma membrane. Biochem J 422(1):129–137. doi:10.1042/BJ20082410
Khodorov BI, Storozhevykh TP, Surin AM, Iuriavichus AI, Sorokina EG, Borodin AV, Vinskaia NP, Khaspekov LG, Pinelis VG (2001) The leading role of mitochondrial depolarization in the mechanism of glutamate-induced disorder in Ca (2+)-homeostasis. Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zh Imeni IM Sechenova / Rossiiskaia Akademiia nauk 87(4):459–467
Petrushanko I, Bogdanov N, Bulygina E, Grenacher B, Leinsoo T, Boldyrev A, Gassmann M, Bogdanova A (2006) Na-K-ATPase in rat cerebellar granule cells is redox sensitive. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290(4):R916–R925. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00038.2005
Zhang Q, Xu X, Li T, Lu Y, Ruan Q, Lu Y, Wang Q, Dong F, Yang Y, Zhang G (2014) Exposure to bisphenol-A affects fear memory and histone acetylation of the hippocampus in adult mice. Horm Behav 65(2):106–113. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2013.12.004
Yatime L, Laursen M, Morth JP, Esmann M, Nissen P, Fedosova NU (2011) Structural insights into the high affinity binding of cardiotonic steroids to the Na+, K + −ATPase. J Struct Biol 174(2):296–306. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2010.12.004
Boldyrev A, Bulygina E, Gerassimova O, Lyapina L, Schoner W (2004) Functional relationship between Na/K-ATPase and NMDA-receptors in rat cerebellum granule cells. Biochem Biokhim 69(4):429–434
Sweadner KJ (1985) Enzymatic properties of separated isozymes of the Na, K-ATPase. Substrate affinities, kinetic cooperativity, and ion transport stoichiometry. J Biol Chem 260(21):11508–11513
Zhang L, Guo F, Su S, Guo H, Xiong C, Yin J, Li W, Wang Y (2012) Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase inhibition upregulates NMDA-evoked currents in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 26(4):503–512. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2011.00947.×
Inoue N, Soga T, Kato T (1999) Glutamate receptors mediate regulation of Na pump isoform activities in neurons. Neuroreport 10(16):3289–3293
Rambo LM, Ribeiro LR, Schramm VG, Berch AM, Stamm DN, Della-Pace ID, Silva LF, Furian AF, Oliveira MS, Fighera MR, Royes LF (2012) Creatine increases hippocampal Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity via NMDA-calcineurin pathway. Brain Res Bull 88(6):553–559. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.06.007
Popp RL, Reneau JC, Brotherton BJ (2008) Activation of protein kinase C enhances NMDA-induced currents in primary cultured cerebellar granule cells: effect of temperature and NMDA NR2 subunit composition. Eur J Pharmacol 599(1–3):1–10. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.08.007
Miyakawa-Naito A, Uhlen P, Lal M, Aizman O, Mikoshiba K, Brismar H, Zelenin S, Aperia A (2003) Cell signaling microdomain with Na, K-ATPase and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor generates calcium oscillations. J Biol Chem 278(50):50355–50361. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305378200
Liu X, Spicarova Z, Rydholm S, Li J, Brismar H, Aperia A (2008) Ankyrin B modulates the function of Na, K-ATPase/inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor signaling microdomain. J Biol Chem 283(17):11461–11468. doi:10.1074/jbc.M706942200
Illarionova NB, Gunnarson E, Li Y, Brismar H, Bondar A, Zelenin S, Aperia A (2010) Functional and molecular interactions between aquaporins and Na, K-ATPase. Neuroscience 168(4):915–925. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.11.062
Zhang D, Hou Q, Wang M, Lin A, Jarzylo L, Navis A, Raissi A, Liu F, Man HY (2009) Na, K-ATPase activity regulates AMPA receptor turnover through proteasome-mediated proteolysis. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosc 29(14):4498–4511. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI. 6094-08.2009
Rose EM, Koo JC, Antflick JE, Ahmed SM, Angers S, Hampson DR (2009) Glutamate transporter coupling to Na, K-ATPase. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosc 29(25):8143–8155. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI. 1081-09.2009
Dvela M, Rosen H, Ben-Ami HC, Lichtstein D (2012) Endogenous ouabain regulates cell viability. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302(2):C442–C452. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00336.2011
Bagrov AY, Shapiro JI, Fedorova OV (2009) Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Rev 61(1):9–38. doi:10.1124/pr.108.000711
Farber NB (2003) The NMDA receptor hypofunction model of psychosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:119–130
Young KW, Garro MA, Challiss RA, Nahorski SR (2004) NMDA-receptor regulation of muscarinic-receptor stimulated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate production and protein kinase C activation in single cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurochem 89(6):1537–1546. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02458.×
Cheng SX, Aizman O, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Aperia A (1999) [Ca2+] i determines the effects of protein kinases A and C on activity of rat renal Na+, K + −ATPase. J Physiol 518(Pt 1):37–46
Lopina OD (2001) Interaction of Na, K-ATPase catalytic subunit with cellular proteins and other endogenous regulators. Biochem Biokhim 66(10):1122–1131
Horisberger JD, Kharoubi-Hess S (2002) Functional differences between alpha subunit isoforms of the rat Na, K-ATPase expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 539(Pt 3):669–680
Azarias G, Kruusmagi M, Connor S, Akkuratov EE, Liu XL, Lyons D, Brismar H, Broberger C, Aperia A (2013) A specific and essential role for Na, K-ATPase alpha3 in neurons co-expressing alpha1 and alpha3. J Biol Chem 288(4):2734–2743. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.425785
Karpova L, Eva A, Kirch U, Boldyrev A, Scheiner-Bobis G (2010) Sodium pump alpha1 and alpha3 subunit isoforms mediate distinct responses to ouabain and are both essential for survival of human neuroblastoma. FEBS J 277(8):1853–1860. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07602.×
Acknowledgments
We dedicate this article to the memory of Professor Alexander Boldyrev, who passed away in 2012. Professor Boldyrev worked for more than 40 years in this field and created the Moscow school of Na/K-ATPase research at Moscow State University. We thank Professor Amir Askari for the opportunity to perform a part of this work in his Laboratory. We also thank Professor Anita Aperia for the opportunity to do a part of this work in her Laboratory and for her comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by RFBR grants 12-04-31468 and 14-04-32123, the Russian President Grant for 2010/2011, and NIH HL036573. We also received financial support from internal postdoctoral grant from St. Petersburg State University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akkuratov, E.E., Lopacheva, O.M., Kruusmägi, M. et al. Functional Interaction Between Na/K-ATPase and NMDA Receptor in Cerebellar Neurons. Mol Neurobiol 52, 1726–1734 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8975-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8975-3