Abstract
Oral administration of low doses (1.25, 2.5, or 5 mg/kg) of cypermethrin to pregnant Wistar rats from gestation days 5 to 21 led to dose-dependent differences in the induction of cytochrome P450 2D1 (CYP2D1) and 3A1 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein in brain regions isolated from the offsprings postnatally at 3 weeks that persisted up to adulthood (12 weeks). Similar alterations were observed in the expression of GABAergic, muscarinic, dopaminergic, and serotonergic neurotransmitter receptors in brain regions of rat offsprings. Rechallenge of the prenatally exposed offsprings at adulthood (12 weeks old) with cypermethrin (p.o., 10 mg/kg for 6 days) led to a greater magnitude of alterations in the expression of CYPs, neurotransmitter receptors, and neurotransmitter receptor binding in the brain regions when compared to the control offsprings treated at adulthood with cypermethrin or prenatally exposed offsprings. A greater magnitude of decrease was also observed in the spontaneous locomotor activity (SLA) in prenatally exposed offsprings rechallenged with cypermethrin. The present data indicating similarities in the alterations in the expression of CYPs (2D1 and 3A1) and neurotransmitter receptors in brain has led us to suggest that endogenous function regulating CYPs is possibly associated with neurotransmission processes. A greater magnitude of alterations in CYP2D1, 3A1, neurotransmitter receptors, and SLA in rechallenged animals has further provided evidence that alterations in CYPs are possibly linked with neurotransmission processes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 October 2014
An erratum to this article has been published.
02 September 2019
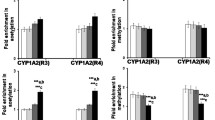
The original version of this article unfortunately contained errors in Fig.��4a. Representative image of b-actin of brain region were copied incorrectly during the preparation of the figures.
02 September 2019
The original version of this article unfortunately contained errors in Fig.��4a. Representative image of b-actin of brain region were copied incorrectly during the preparation of the figures.
References
Shafer TJ, Meyer DA, Crofton KM (2005) Developmental neurotoxicity of pyrethroid insecticides: critical review and future research needs. Environ Health Perspect 113(2):123
Bjorling-Poulsen M, Andersen HR, Grandjean P (2008) Potential developmental neurotoxicity of pesticides used in Europe. Environ Heal 7(1):50
Eriksson P (1996) Developmental neurotoxicity of environmental agents in the neonate. Neurotoxicology 18(3):719–726
London L, Beseler C, Bouchard MF, Bellinger DC, Colosio C, Grandjean P, Harari R, Kootbodien T, Kromhout H, Little F (2012) Neurobehavioral and neurodevelopmental effects of pesticide exposures. Neurotoxicology 33(4):887–896
Ray DE, Fry JR (2006) A reassessment of the neurotoxicity of pyrethroid insecticides. Pharmacol Ther 111(1):174–193
Crofton KM, Reiter LW (1987) Pyrethroid insecticides and the gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor complex: motor activity and the acoustic startle response in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243(3):946–954
Ray DE, Ray D, Forshaw PJ (2000) Pyrethroid insecticides: poisoning syndromes, synergies, and therapy. Clin Toxicol 38(2):95–101
Aziz MH, Agrawal AK, Adhami VM, Shukla Y, Seth PK (2001) Neurodevelopmental consequences of gestational exposure (GD14-GD20) to low dose deltamethrin in rats. Neurosci Lett 300(3):161–165
Ansari RW, Shukla RK, Yadav RS, Seth K, Pant AB, Singh D, Agrawal AK, Islam F, Khanna VK (2012) Cholinergic dysfunctions and enhanced oxidative stress in the neurobehavioral toxicity of lambda-cyhalothrin in developing rats. Neurotoxicol Res 22(4):292–309
Ansari RW, Shukla RK, Yadav RS, Seth K, Pant AB, Singh D, Agrawal AK, Islam F, Khanna VK (2012) Involvement of dopaminergic and serotonergic systems in the neurobehavioral toxicity of lambda-cyhalothrin in developing rats. Toxicol Lett 211(1):1–9
Malaviya M, Husain R, Seth PK (1993) Perinatal effects of two pyrethroid insecticides on brain neurotransmitter function in the neonatal rat. Vet Hum Toxicol 35(2):119–122
Dayal M, Parmar D, Dhawan A, Dwivedi UN, Doehmer J, Seth PK (1999) Induction of rat brain and liver cytochrome P450 1A1/1A2 and 2B1/2B2 isoenzymes by deltamethrin. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 7(3):169–178
Dayal M, Parmar D, Dhawan A, Ali M, Dwivedi UN, Seth PK (2003) Effect of pretreatment of cytochrome P450 (P450) modifiers on neurobehavioral toxicity induced by deltamethrin. Food Chem Toxicol 41(3):431–437
Harvey BH, Oosthuizen F, Brand L, Wegener G, Stein DJ (2004) Stress-restress evokes sustained iNOS activity and altered GABA levels and NMDA receptors in rat hippocampus. Psychopharmacology 175(4):494–502
Kroetz DL, Zeldin DC (2002) Cytochrome P450 pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 13(3):273–283
Puga A, Tomlinson CR, Xia Y (2005) Ah receptor signals cross-talk with multiple developmental pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 69(2):199–207
Schumacher M, Weill-Engerer S, Liere P, Robert F, Franklin RJM, Garcia-Segura LM, Lambert JJ, Mayo W, Melcangi RC, Parducz A (2003) Steroid hormones and neurosteroids in normal and pathological aging of the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 71(1):3–29
Miksys SL, Tyndale RF (2002) Drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450s in the brain. J Psychiatry Neurosci 27(6):406
Scollon EJ, Starr JM, Godin SJ, DeVito MJ, Hughes MF (2009) In vitro metabolism of pyrethroid pesticides by rat and human hepatic microsomes and cytochrome P450 isoforms. Drug Metab Dispos 37(1):221–228
Monostory K, Dvorak Z (2011) Steroid regulation of drug-metabolizing cytochromes P450. Curr Drug Metab 12(2):154–172
Dutheil F, Beaune P, Loriot M-A (2008) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in the central nervous system: contribution of cytochrome P450 enzymes in normal and pathological human brain. Biochimie 90(3):426–436
Ferguson CS, Tyndale RF (2011) Cytochrome P450 enzymes in the brain: emerging evidence of biological significance. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(12):708–714
Gervasini G, Martinez C, Benitez J, Agandez JAG (2007) Effect of neurotransmitters on NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase in vitro activity. Drug Metab Lett 1(3):172–175
Bromek E, Haduch A, Władysława AD (2010) The ability of cytochrome P450 2D isoforms to synthesize dopamine in the brain: an in vitro study. Eur J Pharmacol 626(2):171–178
Haduch A, Bromek E, Władysława AD (2013) Role of brain cytochrome P450 (CYP2D) in the metabolism of monoaminergic neurotransmitters. Pharmacol Rep 65(6):1519–1528
Haduch A, Bromek E, Sadakierska-Chudy A, Wajcikowski J, Władysława AD (2013) The catalytic competence of cytochrome P450 in the synthesis of serotonin from 5-methoxytryptamine in the brain: an in vitro study. Pharmacol Res 67(1):53–59
Nissbrandt H, Bergquist F, Jonason J, Engberg G (2001) Inhibition of cytochrome P450 2E1 induces an increase in extracellular dopamine in rat substantia nigra: a new metabolic pathway? Synapse 40(4):294–301
Shahabi HN, Andersson DR, Nissbrandt H (2008) Cytochrome P450 2E1 in the substantia nigra: relevance for dopaminergic neurotransmission and free radical production. Synapse 62(5):379–388
Vaglini F, Pardini C, Viaggi C, Corsini GU (2001) Cytochrome p450 and parkinsonism: protective role of CYP2E1. Funct Neurol 16(4; SUPP):107–112
Roberge C, M-Je B, Anderson A (2004) GABAA central benzodiazepine receptor and peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands as inducers of phenobarbital-inducible CYP2B and CYP3A. Biochem Pharmacol 68(7):1383–1389
Singh A, Yadav S, Srivastava V, Kumar R, Singh D, Sethumadhavan R, Parmar D (2013) Imprinting of cerebral and hepatic cytochrome P450s in rat offsprings exposed prenatally to low doses of cypermethrin. Mol Neurobiol 48(1):128–140
Iversen LL, Glowinski J (1966) Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain-II. J Neurochem 13(8):671–682
Parmar D, Dhawan A, Seth PK (1998) Evidence for O-dealkylation of 7-pentoxyresorufin by cytochrome P450 2B1/2B2 isoenzymes in brain. Mol Cell Biochem 189(1–2):201–205
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Yamaguchi M, Yamauchi A, Nishimura M, Ueda N, Naito S (2005) Soybean oil fat emulsion prevents cytochrome P450 mRNA down-regulation induced by fat-free overdose total parenteral nutrition in infant rats. Biol Pharm Bull 28(1):143–147
Andoh H, Yoshikawa M, Kawaguchi M, Matsumoto H, Yamazaki K, Oka T (2006) The selective action of D2 dopamine receptor antisense oligodeoxynucleotide on the expression of the dopamine receptor subtype mRNA in rat striatum. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 31(2):73–77
Borges MO, Abreu ML, Porto CS, Avellar MC (2001) Characterization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 142(11):4701–4710
Li H, Kraus A, Wu J, Huguenard JR, Fisher RS (2006) Selective changes in thalamic and cortical GABAA receptor subunits in a model of acquired absence epilepsy in the rat. Neuropharmacology 51(1):121–128
Ruddell RG, Oakley F, Hussain Z, Yeung I, Bryan-Lluka LJ, Ramm GA, Mann DA (2006) A role for serotonin (5-HT) in hepatic stellate cell function and liver fibrosis. Am J Pathol 169(3):861–876
Miksys S, Rao Y, Sellers EM, Kwan M, Mendis D, Tyndale RF (2000) Regional and cellular distribution of CYP2D subfamily members in rat brain. Xenobiotica 30(6):547–564
Yadav S, Dhawan A, Seth PK, Singh RL, Parmar D (2006) Cytochrome P4503A: evidence for mRNA expression and catalytic activity in rat brain. Mol Cell Biochem 287(1–2):91–99
Khanna VK, Husain R, Seth PK (1994) Effect of protein malnutrition on the neurobehavioural toxicity of styrene in young rats. J Appl Toxicol 14(5):351–356
Anadon A, Martinez-Larranaga MR, Fernandez-Cruz ML, Diaz MJ, Fernandez MC, Martinez MA (1996) Toxicokinetics of deltamethrin and its 4′-OH-metabolite in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 141(1):8–16
Yadav S, Johri A, Dhawan A, Seth PK, Parmar D (2006) Regional specificity in deltamethrin induced cytochrome P450 expression in rat brain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 217(1):15–24
Schoedel KA, Sellers EM, Tyndale RF (2001) Induction of CYP2B1/2 and nicotine metabolism by ethanol in rat liver but not rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 62(8):1025–1036
Mäenpää J, Pelkonen O, Cresteil T, Rane A (1993) The role of cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) isoform(s) in oxidative metabolism of testosterone and benzphetamine in human adult and fetal liver. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 44(1):61–67
Nebert DW, Russell DW (2002) Clinical importance of the cytochromes P450. Lancet 360(9340):1155–1162
Hossain MM, Suzuki T, Sato I, Takewaki T, Suzuki K, Kobayashi H (2004) The modulatory effect of pyrethroids on acetylcholine release in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. Neurotoxicology 25(5):825–833
Hossain MM, Suzuki T, Unno T, Komori S, Kobayashi H (2008) Differential presynaptic actions of pyrethroid insecticides on glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the hippocampus. Toxicology 243(1):155–163
Daniels WMU, Pietersen CY, Carstens ME, Stein DJ (2004) Maternal separation in rats leads to anxiety-like behavior and a blunted ACTH response and altered neurotransmitter levels in response to a subsequent stressor. Metab Brain Dis 19(1–2):3–14
Martinez-Larranaga MR, Anadon A, Martinez MA, Martinez M, Castellano VJ, Diaz MJ (2003) 5-HT loss in rat brain by type II pyrethroid insecticides. Toxicol Ind Health 19:147–155
Cahir M, Ardis T, Reynolds GP, Cooper SJ (2007) Acute and chronic tryptophan depletion differentially regulate central 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptor binding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 190(4):497–506
Heal DJ, Philpot J, Molyneux SG, Metz A (1985) Intracerebroventricular administration of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine to mice increases both head-twitch response and the number of cortical 5-HT2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 24(12):1201–1205
Jorrgensen CV, Jacobsen JP, Caron MG, Klein AB, Knudsen GM, Mikkelsen JD (2013) Cerebral 5-HT2A receptor binding, but not mGluR2, is increased in tryptophan hydroxylase 2 decrease-of-function mice. Neurosci Lett 555:118–122
Niznik HB, Tyndale RF, Sallee FR, Gonzalez FJ, Hardwick JP, Inaba T, Kalow W (1990) The dopamine transporter and cytochrome P450IID1 (debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase) in brain: resolution and identification of two distinct [3H]GBR-12935 binding proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys 276(2):424–432
Riedl AG, Watts PM, Edwards RJ, Schulz-Utermoehl T, Boobis AR, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1999) Expression and localisation of CYP2D enzymes in rat basal ganglia. Brain Res 822(1):175–191
Martinez C, Gervasini G, Agundez JAG, Carrillo JA, Ramos SI, Garcia-Gamito FJ, Gallardo L, Benitez J (2000) Modulation of midazolam 1-hydroxylation activity in vitro by neurotransmitters and precursors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56(2):145–151
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Director, CSIR—Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, Lucknow, for his keen interest and support in carrying out the study. AS is thankful to CSIR, N. Delhi for providing Senior Research Fellowship. The financial assistance of the Department of Biotechnology, N. Delhi is also gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8960-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Mudawal, A., Shukla, R.K. et al. Effect of Gestational Exposure of Cypermethrin on Postnatal Development of Brain Cytochrome P450 2D1 and 3A1 and Neurotransmitter Receptors. Mol Neurobiol 52, 741–756 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8903-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8903-6