Abstract
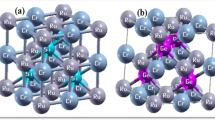
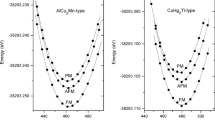
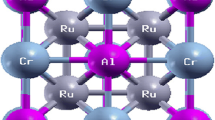
In this study, we have predicted the ground-state properties of the half-Heusler RuCrSb compound using the plane-wave pseudopotential method. The structural optimization signifies that the material is energetically favoured in the ferrimagnetic state in α-phase with optimized lattice parameter 6.025 Å. The positive cohesive energy as well as elastic constants indicate that the compound is thermodynamically and mechanically stable. The absence of a negative phonon dispersion curve also confirms that the sample material is dynamically durable. In order to explore the nature of bonding forces and determine the mechanical strength of the system, the elastic properties have been computed. Moreover, using the quasi-harmonic Debye model, it has been possible to determine the thermodynamical properties with regard to temperature for various pressures. For the strongly correlated d-transition electrons of the studied compound, we incorporated on-site Coulomb repulsion term (U) on GGA scheme during electronic and magnetic calculations. The studied compound reveals half-metallic performance, i.e., it conveys 100% spin polarization at the Fermi energy level (\({E}_{{\text{F}}}\)) under both GGA and GGA + U approximations. The total magnetic moments (\({M}_{{\text{t}}}\)) of the sample material is 1 \({\mu }_{B}\), which is in good agreement with the 18 Slater-Pauling rule; i.e., \({M}_{{\text{t}}}\) = \({Z}_{{\text{t}}}\) – 18. The magnetism source is predominantly from the Cr atom in the studied compound. Moreover, the electronic properties are also supported by the fermi surface, charge density distribution and the Bader charge method. As the Curie temperature (\({T}_{{\text{C}}}\)) of the studied material is observed to be higher than room temperature; the material is suitable for spintronic applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galanakis I, Dederichs P H and Papanikolaou N 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 134428
Gruhn T 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 125210
Kalita D, Ram M, Limbu N and Saxena A 2022 Int. J. Quantum Chem. 122 e26951
De Groot R A, Mueller F M, Engen P G V and Buschow K H J 1983 Phys. Rev. Lett. 50 2024
Ma J, Hegde V I, Munira K, Xie Y, Keshavarz S, Mildebrath D T et al 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 024411
Afaq A, Maaz H, Bakar A and Jamil M I 2019 J. Electron. Mater. 48 5323
Shi F, Si M S, Xie J, Mi K, Xiao C and Luo Q 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 215701
Nenuwe N O and Omugbe E 2023 Curr. Appl. Phys. 49 70
Rai D P and Thapa R K 2013 J. Korean Phys. Soc. 62 1652
Kalita D, Limbu N, Ram M, Kalita R and Saxena A 2021 Mater. Today Commun. 29 102799
Kalita D, Ram M, Limbu N and Saxena A 2021 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 34 85501
Giannozzi P, Baroni S, Bonini N, Calandra M, Car R, Cavazzoni C et al 2009 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21 395502
Perdew J P, Burke K and Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
Marzari N, Vanderbilt D, De Vita A and Payne M C 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 3296
Monkhorst H J and Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
Gunnarsson O, Andersen O K, Jepsen O and Zaanen J 1989 Phys. Rev. B 39 1708
Van Den Brink J, Meinders M B J and Sawatzky G A 1995 Phys. B 206 682
Dal Corso A 2016 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 28 075401
Francisco E, Recio J M, Blanco M A, Pendás A M and Costales A 1998 J. Phys. Chem. 102 1595
Kalita D, Ram M, Limbu N, Kalita R and Saxena A 2022 J. Solid State Chem. 310 122999
Murnaghan F D 1944 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 50 697
Enamullah, Sharma S K and Ahmed S S 2020 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 32 405501
Ahmad R and Mehmood N 2018 J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31 2637
Born M and Huang K 1965 Dynamical theory of crystal lattices (Oxford: Clarendon) 72 p 420
Galanakis I, Mavropoulos P and Dederichs P H 2006 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39 765
Lifshitz M I 1960 Sov. Phys. JETP 11 1130
Van Hove L 1953 Phys. Rev. 89 1189
Acknowledgements
D Kalita acknowledges the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India for providing financial assistance through INSPIRE fellowship with award number IF190898.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalita, D., Saxena, A. Estimation of some physical properties of new RuCrSb half-Heusler compound using first-principles formalism. Bull Mater Sci 47, 97 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-024-03158-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-024-03158-8