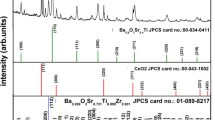
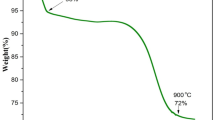
Abstract
A new approach of using AC conductivity as function of frequency and temperature has been proposed for analysing ferroelectric ceramic materials, especially those having Debye-type dielectric dispersion. A theoretical model for the AC conductivity has been validated with the measurements performed on 0.64PMN–0.36PT ceramic material. It has been found that the slope of the conductivity vs. frequency curve of the material having Debye-type dielectric dispersion shows a significant change at a certain frequency, called knee frequency, which shifts towards the high-frequency side when the temperature is increased. The signature parameters of the electrical conductivity curve have been identified that can be used for a quick estimate of the dielectric dispersion behaviour of the material. The difference in the slope of the two regions, separated by the knee frequency, is found to have a strong correlation with the relaxation time distribution factor.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu P, Ji Y, Neumann N, Lee S, Luo H and Es-Souni M 2012 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 59 1983
Kazys R J, Sliteris R and Sestoke J 2015 Proc. IEEE Int. Ultrason. Symp. p 5
Zhang Z, Li F, Chen R, Zhang T, Cao X, Zhang S et al 2018 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 65 223
Fei C, Yang Y, Guo F, Lin P, Chen Q, Zhou Q et al 2018 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 65 2087
Wattananukulchai P and Isarakorn D 2019 Proc. ECTI-CON 2018-15th Int. Conf. Electr. Eng. Comput. Telecommun. Inf. Technol. p 188
HussainA, Sinha N, Bhandari S, Yadav H and Kumar B 2016 J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 4 337
Singh A K and Pandey D 2003 Phys. Rev. B 67 064102
Singh A K and Pandey D 2006 Phys. Rev. B 74 024101
Singh A K, Pandey D and Zaharko O 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 99 076105
Singh A K and Pandey D 2011 Ferroelectrics 326 91
Fang Z, Tian X, Zheng F, Jiang X, Ye W, Qin Y et al 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 7550
Roed E S, Andersen K K, Bring M, Tichy F, Asjord E M and Hoff L 2019 Proc. IEEE Int. Ultrason. Symp. p 1781
Zhang Z 2020 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 67 2085
Zhang Q, Su M, Li F, Liu R, Cai R, Li G et al 2020 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 67 2354
Ren M, Xia W, Xing J, Yang J and Liang Y 2021 Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Appl. Ferroelectrics p 1
Chen H, Mirg S, Osman M, Agarwal S, Cai J, Biskowitz R et al 2021 IEEE Sensors Lett. 5 5
Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang H, Gu Z and Zou H 2021 Ceram. Int. 12 3
Li J, Zhou G, Hong Y, He W, Wang S, Chen Y et al 2022 Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 337 113415
Jiang Z, Hou C, Fei C, Li Z and Ye Z G 2022 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 69 795
Jia H, Mi J, Li Z and Wang L 2021 Ceram. Int. 11 1
Saxena A, Hussain A, Saxena A, Joseph A J and Saxena R S 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 26258
Fu H and Cohen R H 2000 Nature 403 281
Cole K S and Cole R H 1941 J. Chem. Phys. 9 341
Acknowledgement
We thank Dr Abid Hussain, Assistant Professor, ARSD College, University of Delhi, for providing the measurement data. We are also grateful to the Principal of Hindu College, Principal of Hansraj College, University of Delhi, and Director SSPL, Delhi, for their support and encouragement to carry out this work and publish it.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, A., Saxena, A. & Saxena, R.S. Analysing dielectric dispersion of 0.64PMN–0.36PT ceramics using electrical conductivity. Bull Mater Sci 46, 124 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-023-02965-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-023-02965-9