Abstract
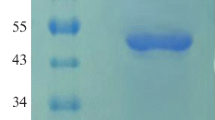
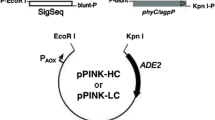
The overexpression of the native gene encoding the thermostable Bacillus subtilis US417 phytase using Pichia pastoris system is described. The phytase gene, in which the sequence encoding the signal peptide was replaced by that of the α-factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, was placed under the control of the methanol-inducible promoter of the alcohol oxidase 1 gene and expressed in Pichia pastoris. Small-scale expression experiments and activity assays were used to screen positive colonies. A recombinant strain was selected and produces 43 and 227 U/mL of phytase activity in shake flasks and in high-cell-density fermentation, respectively. The purified phytase was glycosylated protein and varied in size (50–65 kDa). It has a molecular mass of 43 kDa when it was deglycosylated. The purified r-PHY maintains 100 % of its activity after 10 min incubation at 75 °C and pH 7.5. This thermostable phytase, which is also active over broad pH ranges, may be useful as feed additives, since it can resist the temperature used in the feed-pelleting process.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy, N. R., Sathe, S. K., & Salunkhe, D. K. (1982). Phytates in legumes and cereals. Advances in Food Research, 28, 1–92.
Nayani, N. R., & Markakis, P. (1983). Effects of inositol phosphates on mineral utilization. Federal Reserve, 45, 819–826.
Abulkalam, M. S. (2008). Demonizing phytate. Nature Biotechnology, 26, 496–497.
Simons, P. C., Versteegh, H. A. J., Jongbloed, A. W., Kemme, P. A., Slump, P., Bos, K. D., et al. (1990). Improvement of phosphorus availability by microbial phytase in broilers and pigs. British Journal of Nutrition, 64, 525–540.
Pen, J., Verwoerd, T. C., Van Paridon, P. A., & Beudeker, R. F. (1993). Phytase-containing transgenic seeds as a novel feed additive for improved phosphorus utilization. Bioresource Technology, 11, 811–814.
Lei, X. G., Porres, J. M., Mullaney, E. J., & Brinch-Pedersen, H. (2007). Phytase: source, structure and application. In J. Polaina & A. P. MacCabe (Eds.), Industrial enzymes: Structure, function and applications (pp. 505–529). Dordrecht: Springer.
Mullaney, E. J., & Ullah, A. H. (2007). Phytases: Attributes, catalytic mechanisms and applications. In L. Turner, A. E. Richardson, & E. J. Mullaney (Eds.), Inositol phosphates: Linking agriculture and the environment (pp. 97–110). Oxford: CAB International.
Oh, B. H. (2000). Crystal structures of a novel thermostable phytase in partially and fully calcium-loaded states. Natural Structural Biology, 7, 147–153.
Kerovuo, J., Lauraeus, M., Nurminen, P., Kalkkinen, N., & Apajalahti, J. (1998). Isolation, characterization, molecular gene cloning, and sequencing of a novel phytase from Bacillus subtilis. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 64, 2079–2085.
Kim, Y. O., Kim, H. K., Bae, K. S., Yu, J. H., & Oh, T. K. (1998). Purification and properties of a thermostable phytase from Bacillus sp. DS11. Enyzme and Microbial Technology, 22, 2–7.
Kim, D. H., Oh, B. C., Choi, W. C., Lee, J. K., & Oh, T. K. (1999). Enzymatic evaluation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens phytase as a feed additive. Biotechnology Letters, 20, 925–927.
Oh, B. C., Choi, W. C., Park, S., Kim, Y. O., & Oh, T. K. (2004). Biochemical properties and substrate specificities of alkaline and histidine acid phytases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 63, 362–372.
Choi, Y. M., Suh, H. J., & Kim, J. M. (2001). Purification and properties of extracellular phytase from Bacillus sp. KHU-10. Journal of Protein Chemistry, 20, 287–292.
Tye, A. J., Siu, F. K. Y., Leung, T. Y. C., & Lim, B. L. (2002). Molecular cloning and the biochemical characterization of two novel phytases from B. subtilis 168 and B. licheniformis. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 59, 190–197.
Lee, J., Choi, Y., Lee, P. C., Kang, S., Bok, J., & Cho, J. (2007). Recombinant production of Penicillium oxalicum PJ3 phytase in Pichia Pastoris. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 23, 443–446.
Soni, S. K., & Khire, J. M. (2007). Production and partial characterization of two types of phytase from Aspergillus niger NCIM 563 under submerged fermentation conditions. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 23, 1585–1593.
Fu, D. W., Huang, H. Q., Luo, H. Y., Wang, Y. R., Yang, P. L., Meng, K., et al. (2008). A highly pH-stable phytase from Yersinia kristeensenii: cloning, expression, and characterization. Enyzme and Microbial Technology, 42, 499–505.
Guerrero-Olazaran, M., Rodriguez-Blanco, L., Carreon-Trevino, J. G., Gallegos-Lopez, J. A., & Viader-Salvado, J. M. (2010). Expression of a Bacillus phytase C gene in Pichia pastoris and properties of the recombinant enzyme. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 76, 5601–5608.
Viader-Salvado, J. M., Gallegos-Lopez, J. A., Carreon-Trevin, J. G., Castillo-Galva, M., Rojo-Domínguez, A., & Guerrero-Olazara, M. (2010). Design of thermostable beta-Propeller phytases with activity over a broad range of pHs and their overproduction by Pichia pastoris Appl. Environmental Microbiology, 76, 6423–6430.
Zou, L. K., Wang, H. N., Pan, X., Tian, G. B., Xie, Z. W., Wu, Q., et al. (2008). Expression, purification and characterization of a phyAm-phyCs fusion phytase. Journal of Zheijang University Science B, 9, 536–545.
Wang, Q., Fu, S. J., Jian-Yi Sun, J. Y., & Weng, X. Y. (2011). Characterization of a thermostable alkaline phytase from Bacillus licheniformis ZJ-6 in Pichia pastoris. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 27, 1247–1253.
Farhat, A., Chouayekh, H., Farhat, M., Bouchaala, K., & Bejar, S. (2008). Gene cloning and characterization of a thermostable phytase from Bacillus subtilis US417 and assessment of its potential as a feed additive in comparison with a commercial enzyme. Molecular Biotechnology, 40, 127–135.
Gulati, H. K., Chadha, B. S., & Saini, H. S. (2007). Production and characterization of thermostable alkaline phytase from Bacillus laevolacticus isolated from rhizosphere soil. Journal of Industrial Microbiology, 34, 91–98.
Fu, S. J., Sun, J. Y., Qian, L. C., & Li, Z. Y. (2008). Bacillus phytases: present scenario and future perspectives. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 151, 1–8.
Cereghino, J. L., & Cregg, J. M. (2000). Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 24, 45–66.
Han, Y. M., & Lei, X. G. (1999). Role of glycosylation in the functional expression of an Aspergillus niger phytase (phyA) in Pichia pastoris. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 364, 83–90.
Wyss, M., Brugger, R., Kronenberger, A., Remy, R., Fimbel, R., Oesterhelt, G., et al. (1999). Biochemical characterization of fungal phytases (myo-inositol hexakisphosphatephosphohydrolases): catalytic properties. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 65, 367–373.
Rodriguez, E., Mullaney, E. J., & Lei, X. G. (2000). Expression of Aspergillus fumigates phytase gene in Pichia pastoris and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 268, 373–378.
Rodriguez, E., Wood, Z. A., Karplus, P. A., & Lei, X. G. (2000). Site directed mutagenesis improves catalytic efficiency and thermostability of Escherichia coli acid phosphatase/phytase expressed in Pichia pastoris. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 382, 105–112.
Tschopp, J. F., Sverlow, G., Kosson, R., Craig, W., & Grinna, L. (1987). High level secretion of glycosylated invertase in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology, 5, 1305–1308.
Laborde, C., Chemardin, P., Bigey, F., Combarnous, Y., Moulin, G., & Boze, H. (2004). Overexpression of ovine leptin in Pichia pastoris: physiological yeast response to leptin production and characterization of the recombinant hormone. Yeast, 21, 249–263.
Cregg, J. M., & Russell, K. A. (1998). Transformation. Methods in Molecular Biology, 103, 27–39.
Shrestha, B., Blondeau, K., Stevensa, W. F., & Hegarat, F. L. (2004). Expression of chitin deacetylase from Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in Pichia pastoris: purification and characterization. Protein Expression and Purification, 38, 196–204.
Engelen, A. J., van der Heeft, F. C., Randsdorp, P. H., & Smit, E. L. (1994). Simple and rapid determination of phytase activity. Journal of AOAC International, 77, 760–764.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Romanos, M., Scorer, C., Sreekrishna, K., & Clare, J. (1998). The generation of multicopy recombinant strains. Methods in Molecular Biology, 103, 55–72.
Clare, J. J., Romanos, M. A., Rayment, F. R., Rowendder, J. E., Smith, M. A., Payne, M. M., et al. (1991). Production of mouse epidermal growth factor in yeast: high-level secretion using Pichia pastoris strains containing multiple gene copies. Gene, 105, 205–212.
Farhat-Khemakhem, A., Ben Farhat, M., Boukhris, I., Bejar, W., Bouchaala, K., Kammoun, R., et al. (2012). Heterologous expression and optimization using experimental designs allowed highly efficient production of the PHY US417 phytase in Bacillus subtilis 168. AMB Express, 2, 10.
Kim, Y. O., Lee, J. K., Oh, B. C., & Oh, T. K. (1999). High level expression of a recombinant thermostable phytase in Bacillus subtilis. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 63(12), 2205–2207.
Vuolanto, A., von Weymarn, N., Kerovuo, J., Ojamo, H., & Leisola, M. (2001). Phytase production by high cell density culture of recombinant Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnology Letters, 23(10), 761–766.
Wang, H. N., Wu, Q., Zhao, H. X., Zou, L. K., & Liu, S. G. (2005). Secretory expression of Bacillus subtilis phytase phyC in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 31(5), 621–627.
Viader-Salvado, J. M., Castillo-Galvan, M., Fuentes-Garibay, J. A., Iracheta-Cardenas, M. M., & Guerrero-Olazaran, M. (2013). Optimization of five environmental factors to increase beta-propeller phytase production in Pichia pastoris and impact on the physiological response of the host. Biotechnology Progress, 29(6), 1377–1385.
Shimizu, M. (1992). Purification and characterization of phytase from Bacillus subtilis (natto) N-77. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 56, 1266–1269.
Powar, V. K., & Jagannathan, V. (1982). Purification and properties of phytate-specific phosphatase from Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Bacteriology, 151, 1102–1108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hmida-Sayari, A., Elgharbi, F., Farhat, A. et al. Overexpression and Biochemical Characterization of a Thermostable Phytase from Bacillus subtilis US417 in Pichia pastoris . Mol Biotechnol 56, 839–848 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-014-9764-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-014-9764-y