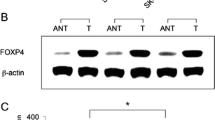
Abstract
CUGBP1, which is involved in posttranscriptional regulatory networks, may control cell growth, activation and differentiation. Meanwhile, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) acts as a basic leucine zipper transcription factor which controls differentiation-dependent gene expression and inhibits cell proliferation. To date, very little is known about the association between CUGBP 1 and C/EBPα in regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). CUGBP1 and C/EBPα mRNA expressions were analyzed in NSCLC tumor and adjacent normal tissues, and the relationship in clinicopathological parameters was evaluated. Knockdown of CUGBP1 and C/EBPα regulated by CUGBP1 in NSCLC cell line was identified by real-time PCR and Western blot. The effect of depletion of CUGBP1 was evaluated by MTT assay and Annexin/Propidium Iodide Apoptosis assay. CUGBP1 is highly expressed and expression of C/EBPα is low in NSCLC tissues. The correlation analysis revealed that there was negative correlation between the expression of CUGBP 1 and C/EBPα. Knockdown of CUGBP1 effectively silenced the expression of CUGBP1 and up-regulated C/EBPα. Also, suppression of CUGBP1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in A549 cells. These observations suggest that the first proof the overexpression of CUGBP1 in NSCLC contributes to tumorigenesis through down-regulation of C/EBPα. Knockdown of CUGBP1 or up-regulation C/EBPα might be a potential therapeutic approach for human non-small cell lung cancers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiu Y, Morii E, Tomita Y, Zhang B, Matsumura A, Kitaichi M, et al. Prognostic significance of pre B cell leukemia transcription factor 2 (PBX2) expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(7):1198–209. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01156.x.
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21208.
Zhang Z, Wang T, Zhang J, Cai X, Pan C, Long Y, et al. Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in resected non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(8):e106053. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106053.
Chen J, Wang R, Zhang K, Chen LB. Long non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18(12):2425–36. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12431.
Rattenbacher B, Beisang D, Wiesner DL, Jeschke JC, von Hohenberg M, St Louis-Vlasova IA, et al. Analysis of CUGBP1 targets identifies GU-repeat sequences that mediate rapid mRNA decay. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(16):3970–80. doi:10.1128/MCB.00624-10.
Timchenko LT, Miller JW, Timchenko NA, DeVore DR, Datar KV, Lin L, et al. Identification of a (CUG)n triplet repeat RNA-binding protein and its expression in myotonic dystrophy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996;24(22):4407–14.
Iakova P, Wang GL, Timchenko L, Michalak M, Pereira-Smith OM, Smith JR, et al. Competition of CUGBP1 and calreticulin for the regulation of p21 translation determines cell fate. The EMBO journal. 2004;23(2):406–17. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600052.
Gareau C, Fournier MJ, Filion C, Coudert L, Martel D, Labelle Y, et al. p21(WAF1/CIP1) upregulation through the stress granule-associated protein CUGBP1 confers resistance to bortezomib-mediated apoptosis. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(5):e20254. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020254.
Moraes KC, Wilusz CJ, Wilusz J. CUG-BP binds to RNA substrates and recruits PARN deadenylase. RNA. 2006;12(6):1084–91. doi:10.1261/rna.59606.
Salisbury E, Sakai K, Schoser B, Huichalaf C, Schneider-Gold C, Nguyen H, et al. Ectopic expression of cyclin D3 corrects differentiation of DM1 myoblasts through activation of RNA CUG-binding protein, CUGBP1. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(11–12):2266–78. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.04.018.
Zheng Y, Miskimins WK. CUG-binding protein represses translation of p27Kip1 mRNA through its internal ribosomal entry site. RNA Biol. 2011;8(3):365–71.
Kress C, Gautier-Courteille C, Osborne HB, Babinet C, Paillard L. Inactivation of CUG-BP1/CELF1 causes growth, viability, and spermatogenesis defects in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(3):1146–57. doi:10.1128/MCB.01009-06.
Jiao W, Zhao J, Wang M, Wang Y, Luo Y, Zhao Y, et al. CUG-binding protein 1 (CUGBP1) expression and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol Off Publ Fed Spanish Oncol Soc Natl Cancer Inst Mexico. 2013;15(10):789–95. doi:10.1007/s12094-013-1005-5.
Gao C, Yu Z, Liu S, Xin H, Li X. Overexpression of CUGBP1 is associated with the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3103-1.
Schuster MB, Porse BT. C/EBPalpha: a tumour suppressor in multiple tissues? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1766(1):88–103. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.02.003.
Flodby P, Barlow C, Kylefjord H, Ahrlund-Richter L, Xanthopoulos KG. Increased hepatic cell proliferation and lung abnormalities in mice deficient in CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(40):24753–60.
Tomizawa M, Watanabe K, Saisho H, Nakagawara A, Tagawa M. Down-regulated expression of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha and beta genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a possible prognostic marker. Anticancer Res. 2003;23(1A):351–4.
Porse BT, Pedersen TA, Xu X, Lindberg B, Wewer UM, Friis-Hansen L, et al. E2F repression by C/EBPalpha is required for adipogenesis and granulopoiesis in vivo. Cell. 2001;107(2):247–58.
Iakova P, Awad SS, Timchenko NA. Aging reduces proliferative capacities of liver by switching pathways of C/EBPalpha growth arrest. Cell. 2003;113(4):495–506.
Jones K, Timchenko L, Timchenko NA. The role of CUGBP1 in age-dependent changes of liver functions. Ageing Res Rev. 2012;11(4):442–9. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2012.02.007.
Halmos B, Huettner CS, Kocher O, Ferenczi K, Karp DD, Tenen DG. Down-regulation and antiproliferative role of C/EBPalpha in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62(2):528–34.
Zahir ST, Mirtalebi M. Survival of patients with lung cancer, Yazd, Iran. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(9):4387–91.
Biesalski HK, Bueno de Mesquita B, Chesson A, Chytil F, Grimble R, Hermus RJ et al. European consensus statement on lung cancer: risk factors and prevention. Lung cancer panel. CA Cancer J Clin. 1998;48(3):167–76 (discussion 4–6).
Chawla R, Sathian B, Mehra A, Kiyawat V, Garg A, Sharma K. Awareness and assessment of risk factors for lung cancer in residents of Pokhara Valley, Nepal. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 2010;11(6):1789–93.
Zhai R, Yu X, Wei Y, Su L, Christiani DC. Smoking and smoking cessation in relation to the development of co-existing non-small cell lung cancer with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2014;134(4):961–70. doi:10.1002/ijc.28414.
Fong KM, Sekido Y, Gazdar AF, Minna JD. Lung cancer. 9: molecular biology of lung cancer: clinical implications. Thorax. 2003;58(10):892–900.
Li W, Deng J, Tang JX. Combined effects methylation of FHIT, RASSF1A and RARbeta genes on non-small cell lung cancer in the Chinese population. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(13):5233–7.
Wang GS, Cooper TA. Splicing in disease: disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8(10):749–61. doi:10.1038/nrg2164.
Le Tonqueze O, Gschloessl B, Namanda-Vanderbeken A, Legagneux V, Paillard L, Audic Y. Chromosome wide analysis of CUGBP1 binding sites identifies the tetraspanin CD9 mRNA as a target for CUGBP1-mediated down-regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(4):884–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.020.
Chung HK, Rao JN, Zou T, Liu L, Xiao L, Gu H, et al. Jnk2 deletion disrupts intestinal mucosal homeostasis and maturation by differentially modulating RNA-binding proteins HuR and CUGBP1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;306(12):C1167–75. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00093.2014.
Guerzoni C, Bardini M, Mariani SA, Ferrari-Amorotti G, Neviani P, Panno ML, et al. Inducible activation of CEBPB, a gene negatively regulated by BCR/ABL, inhibits proliferation and promotes differentiation of BCR/ABL-expressing cells. Blood. 2006;107(10):4080–9. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-08-3181.
Kuyumcu-Martinez NM, Wang GS, Cooper TA. Increased steady-state levels of CUGBP1 in myotonic dystrophy 1 are due to PKC-mediated hyperphosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2007;28(1):68–78. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.027.
Talwar S, Balasubramanian S, Sundaramurthy S, House R, Wilusz CJ, Kuppuswamy D, et al. Overexpression of RNA-binding protein CELF1 prevents apoptosis and destabilizes pro-apoptotic mRNAs in oral cancer cells. RNA Biol. 2013;10(2):277–86. doi:10.4161/rna.23315.
Wu LN, Xue YJ, Zhang LJ, Ma XM, Chen JF. Si-RNA mediated knockdown of CELF1 gene suppressed the proliferation of human lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13(1):115. doi:10.1186/1475-2867-13-115.
Zhang DE, Zhang P, Wang ND, Hetherington CJ, Darlington GJ, Tenen DG. Absence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor signaling and neutrophil development in CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(2):569–74.
Timchenko NA, Wilde M, Nakanishi M, Smith JR, Darlington GJ. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha) inhibits cell proliferation through the p21 (WAF-1/CIP-1/SDI-1) protein. Genes Dev. 1996;10(7):804–15.
Slomiany BA, D’Arigo KL, Kelly MM, Kurtz DT. C/EBPalpha inhibits cell growth via direct repression of E2F-DP-mediated transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(16):5986–97.
Johansen LM, Iwama A, Lodie TA, Sasaki K, Felsher DW, Golub TR, et al. c-Myc is a critical target for c/EBPalpha in granulopoiesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(11):3789–806. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.11.3789-3806.2001.
Wu L, Timmers C, Maiti B, Saavedra HI, Sang L, Chong GT, et al. The E2F1-3 transcription factors are essential for cellular proliferation. Nature. 2001;414(6862):457–62. doi:10.1038/35106593.
Wang QF, Cleaves R, Kummalue T, Nerlov C, Friedman AD. Cell cycle inhibition mediated by the outer surface of the C/EBPalpha basic region is required but not sufficient for granulopoiesis. Oncogene. 2003;22(17):2548–57. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206360.
Wang GL, Salisbury E, Shi X, Timchenko L, Medrano EE, Timchenko NA. HDAC1 cooperates with C/EBPalpha in the inhibition of liver proliferation in old mice. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(38):26169–78. doi:10.1074/jbc.M803544200.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the department of Science & Technology of Shandong province (Contract No. 2012YD18042 and 2010GWZ20260). This work was supported, in part, by the Wu jieping medical Foundation of China (Contract No. 320.6753.1219 and 320.6750.13210).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of Qingdao University Medical College and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Haijiao Lu and Zhuang Yu have contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Yu, Z., Liu, S. et al. CUGBP1 promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis via down-regulating C/EBPα in human non-small cell lung cancers. Med Oncol 32, 82 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0544-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0544-8